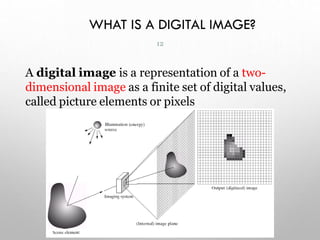
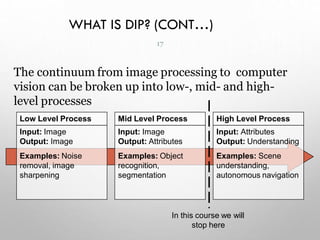
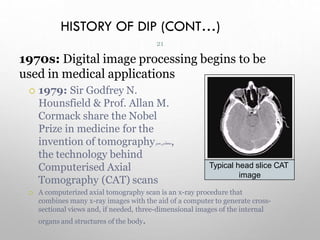
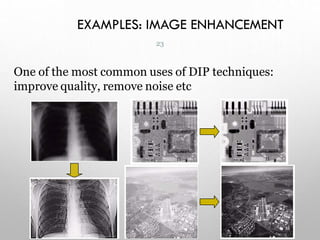
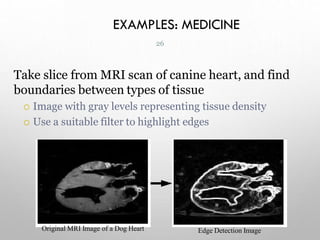
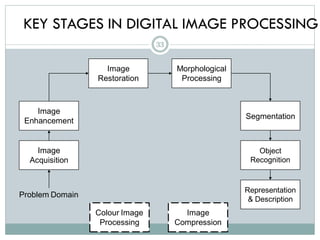
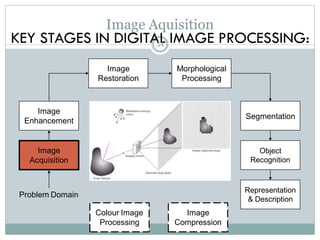
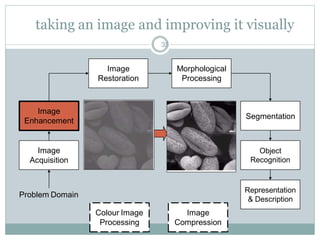
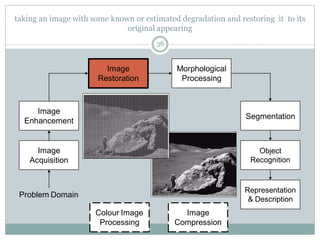
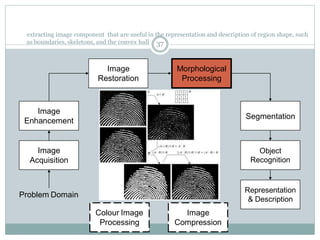
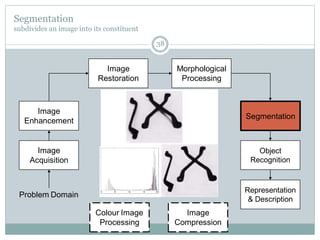
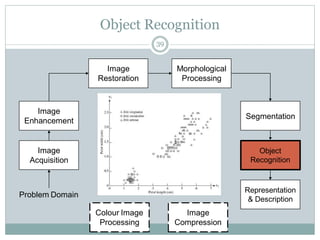
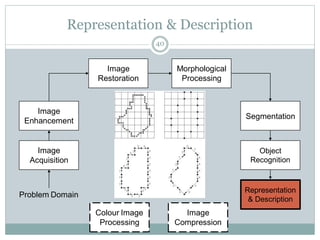
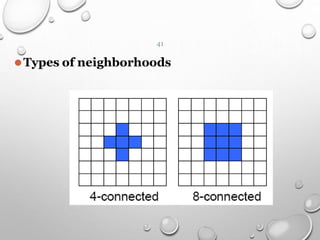
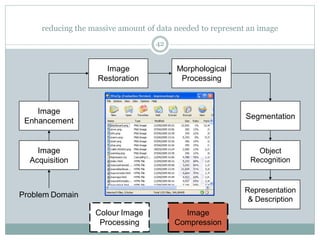
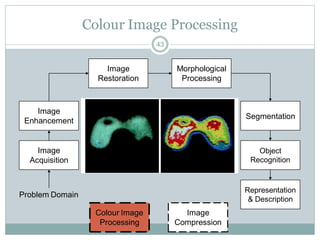
This document provides an introduction to digital image processing, covering its definition, history, and practical applications across various fields such as medicine, law enforcement, and industrial inspection. It outlines key processes in digital image processing, including image acquisition, restoration, segmentation, and object recognition. The document emphasizes the significance of image processing for both human interpretation and machine perception.