This document provides an overview of digital image processing, including:
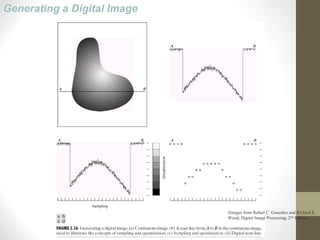
- It defines what a digital image is and how images are digitized through sampling and quantization.
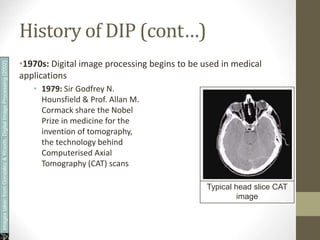
- It discusses the history of digital image processing from the 1920s to today, highlighting early applications and key advances like CAT scans.
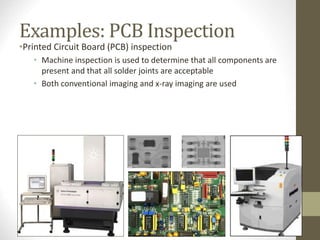
- It gives examples of current uses like image enhancement, medical imaging, industrial inspection, and computer vision tasks like face and object recognition.
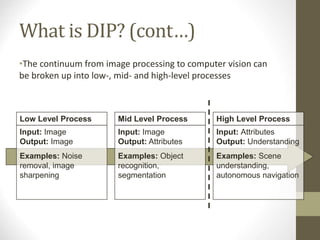
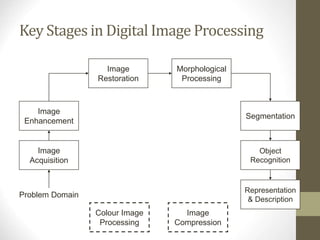
- It outlines the main stages of digital image processing pipelines including image acquisition, enhancement, restoration, segmentation, and compression.
- It provides context on the related field of computer vision and its goals of interpreting and understanding images.