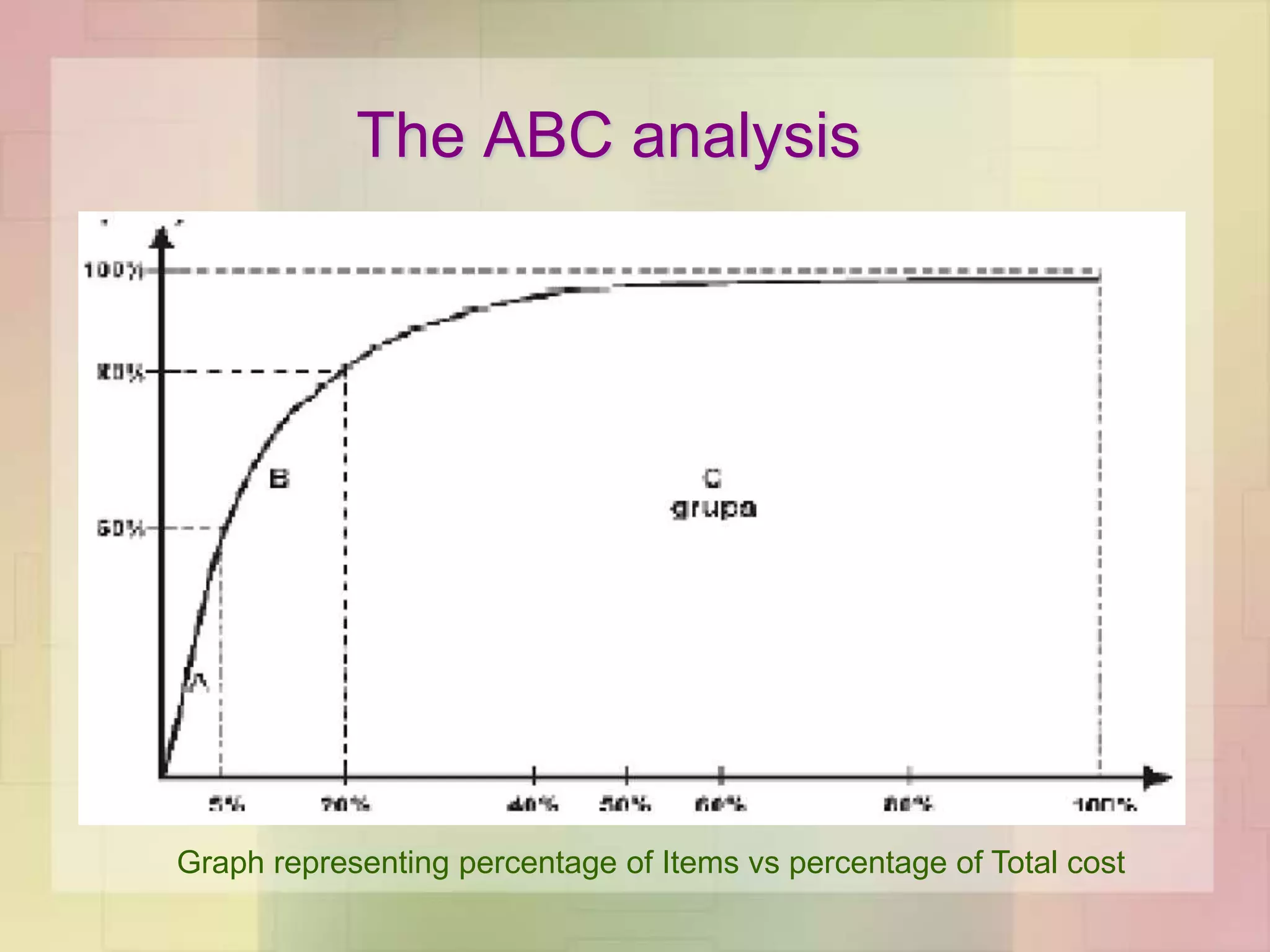
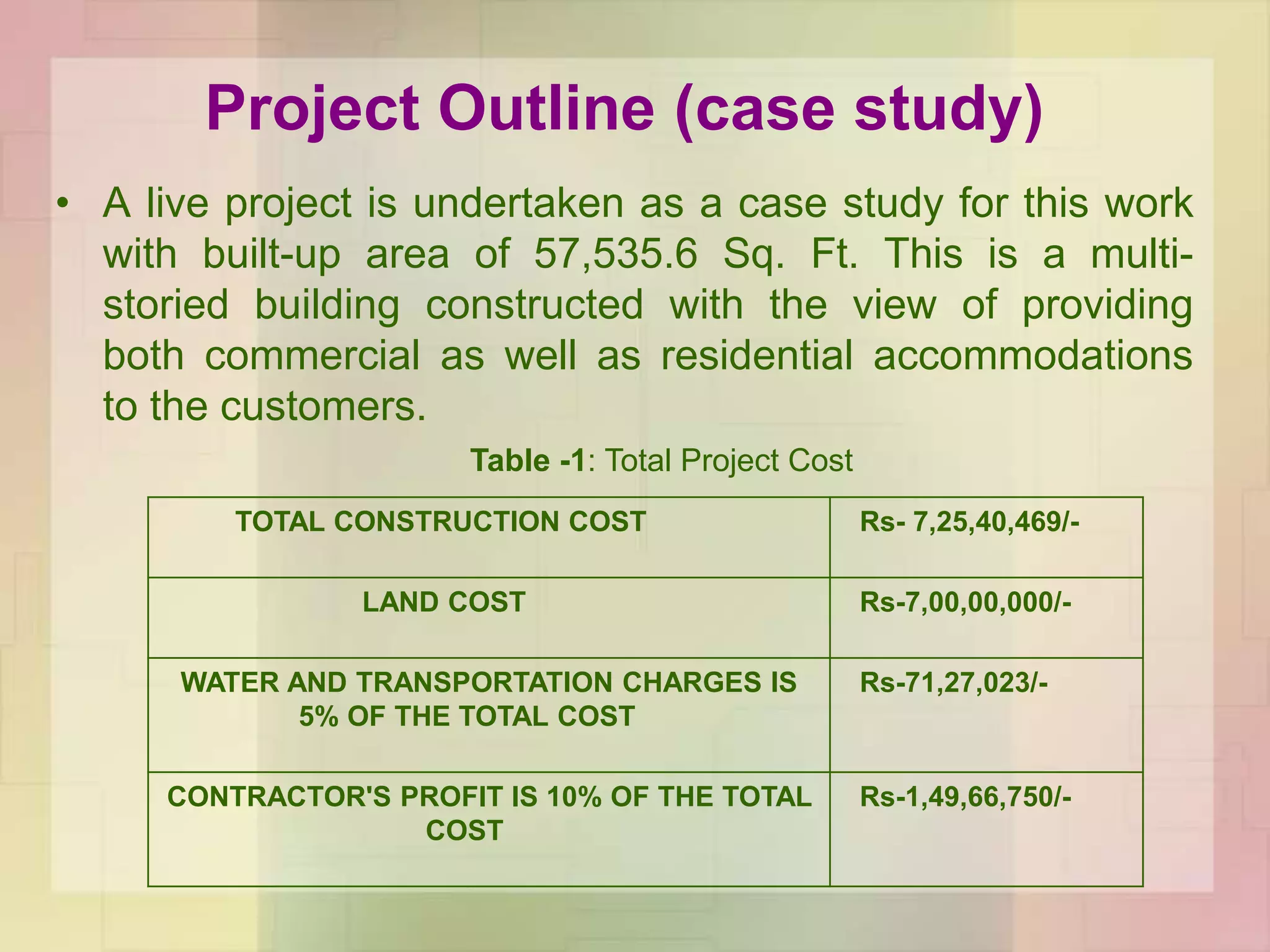
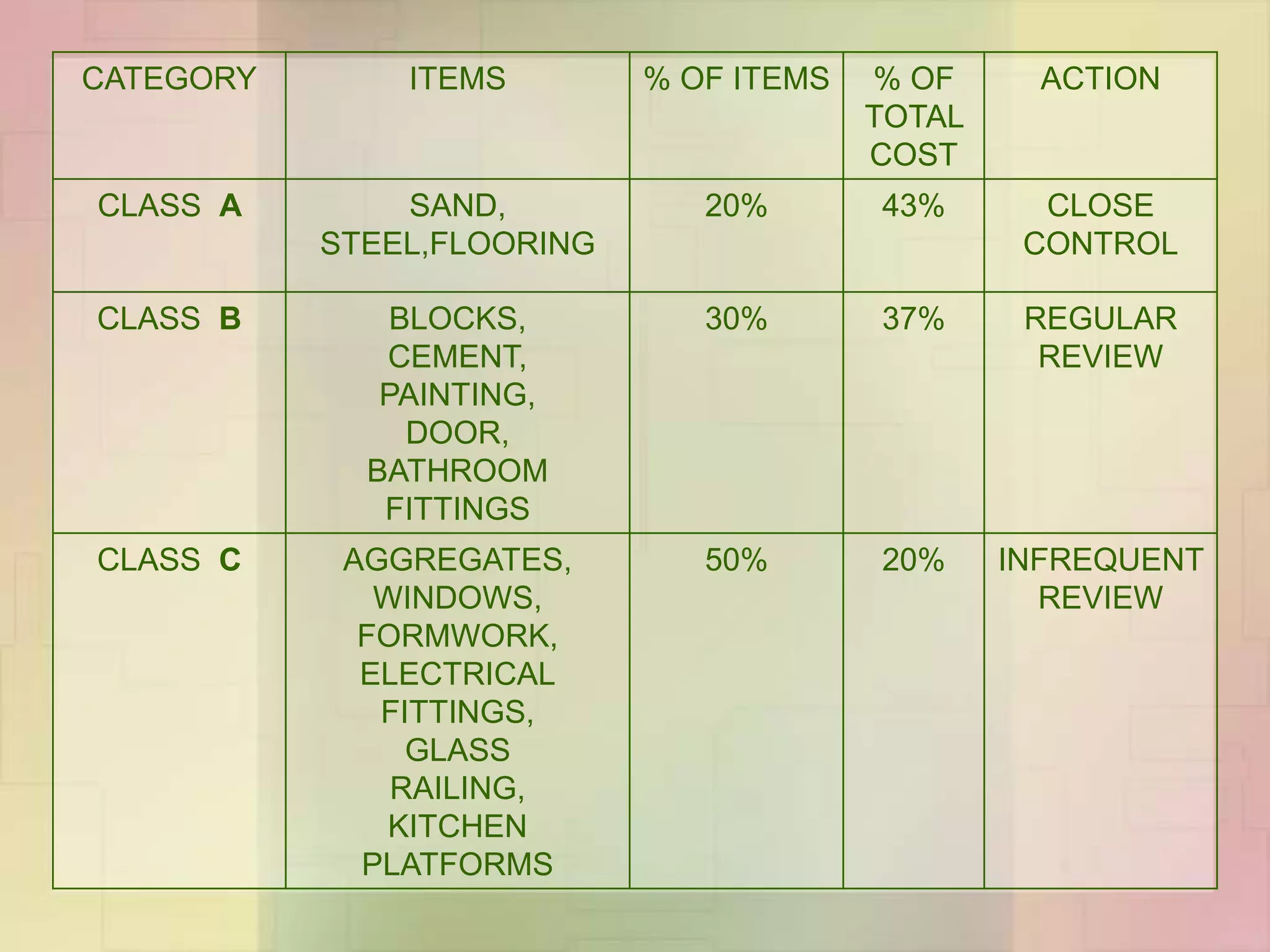
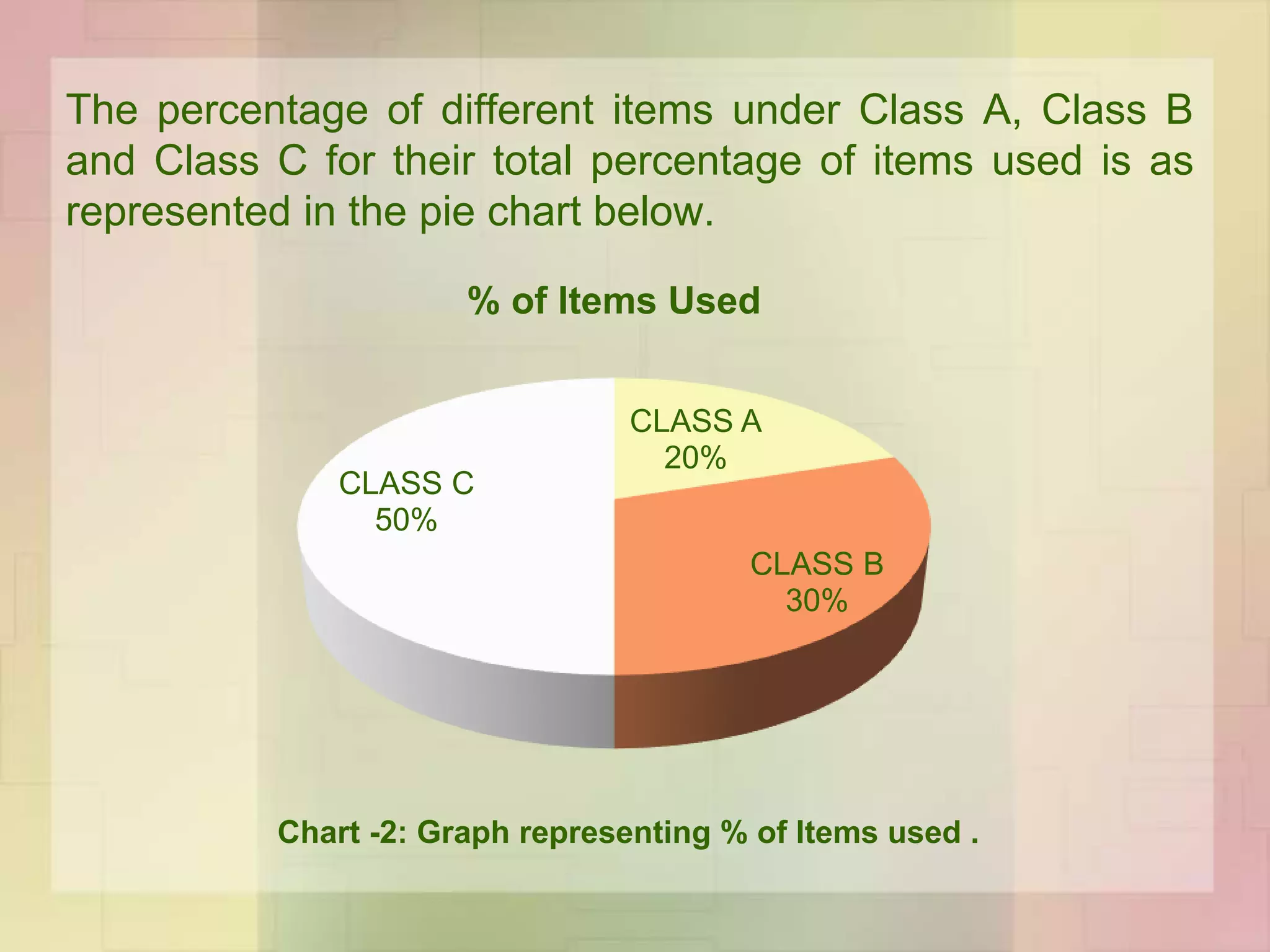
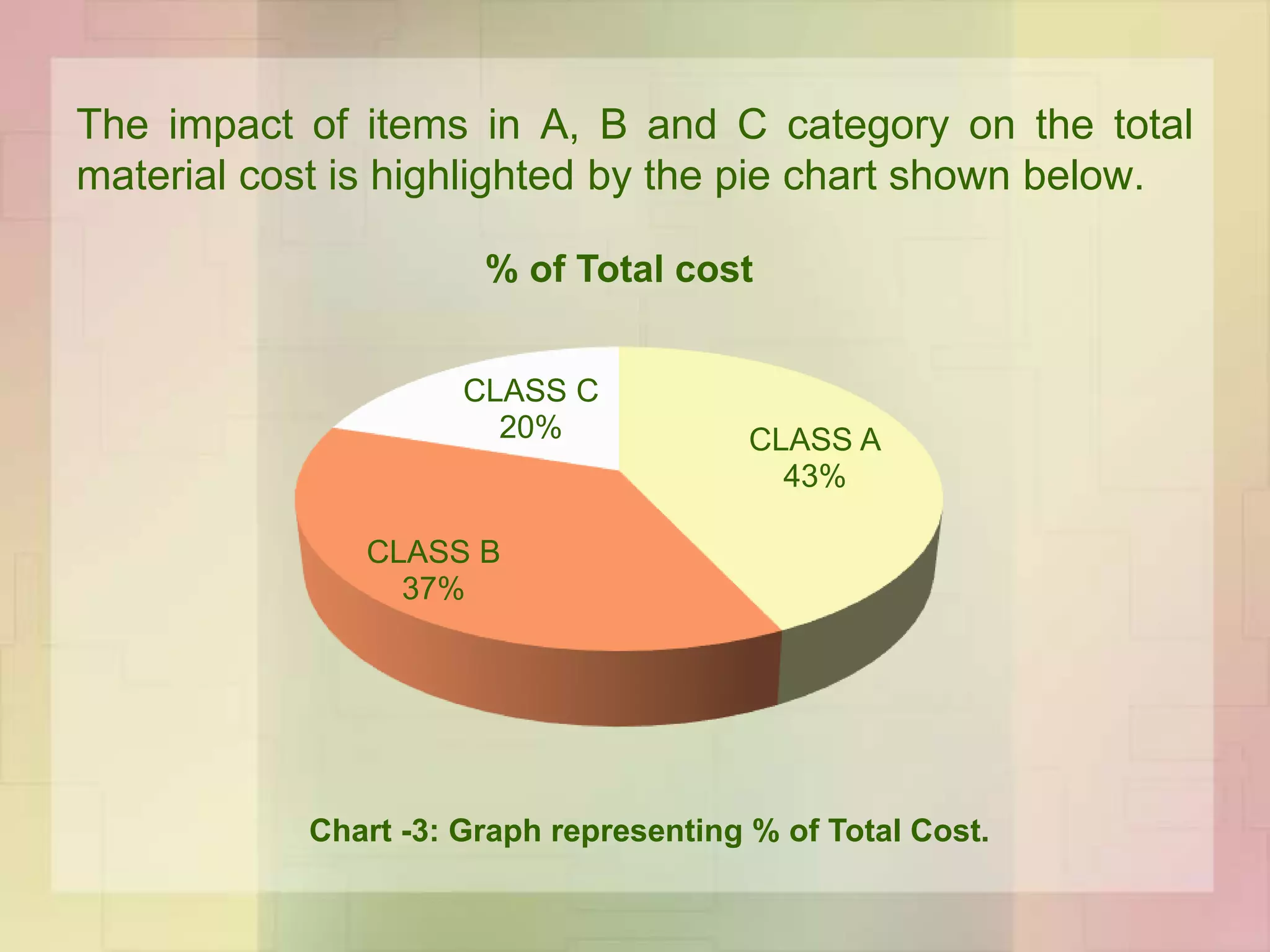
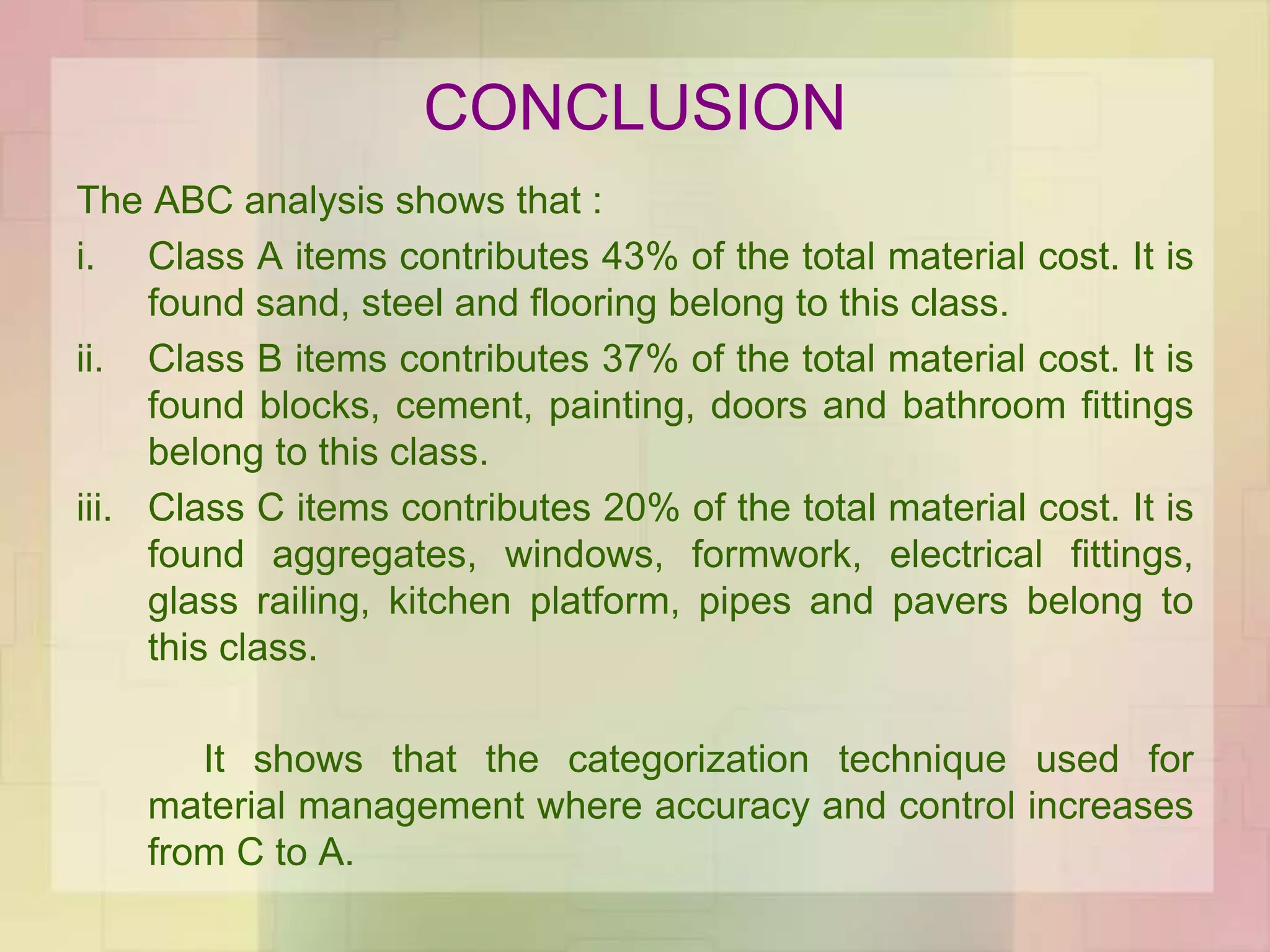
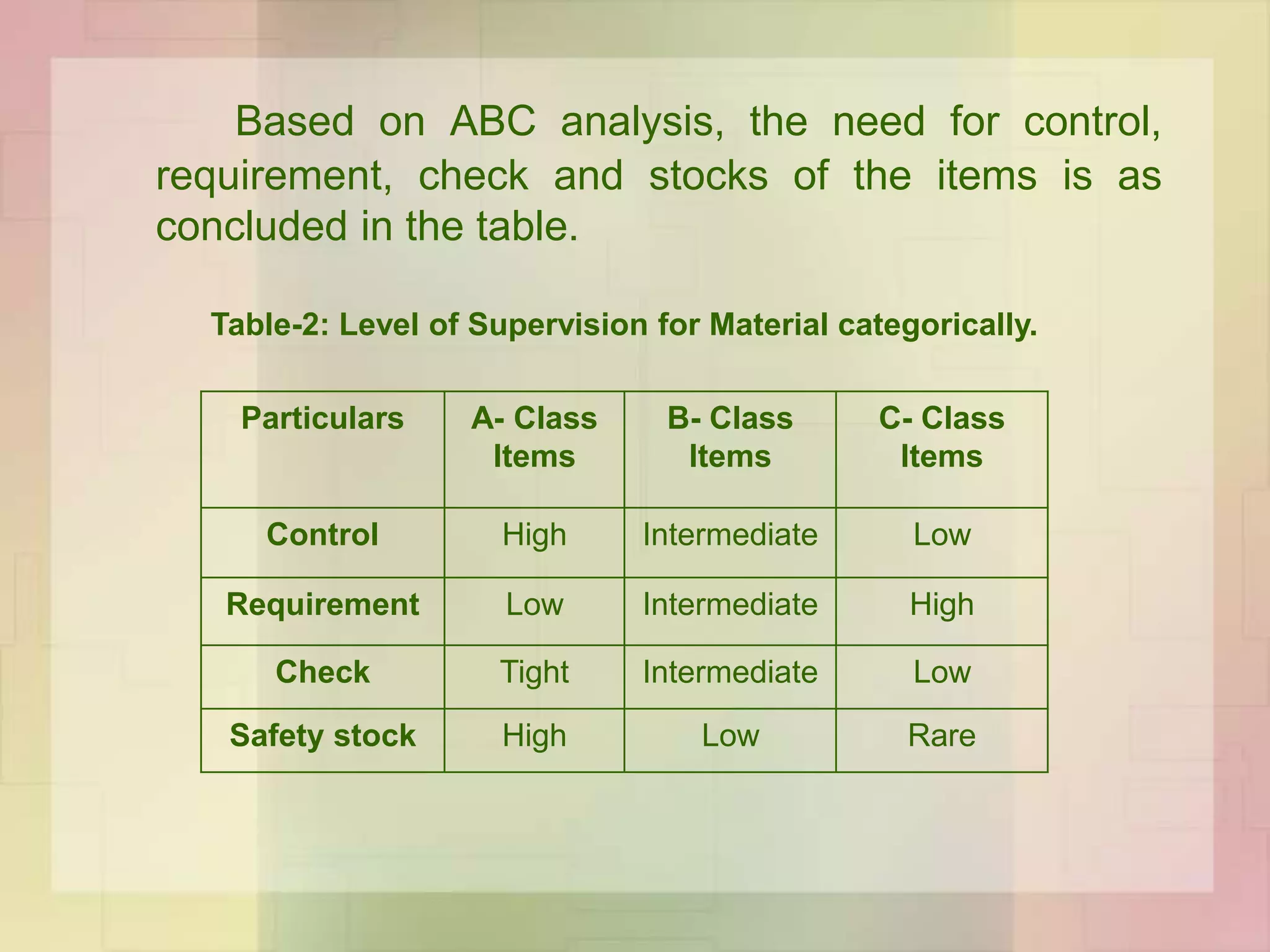
The document discusses the application of ABC analysis in material management specifically for residential building projects, focusing on planning, organizing, and controlling material flow. It outlines the objectives, functions, and benefits of material management, categorizing inventory into A, B, and C classes based on consumption value. A case study illustrates the impact of material categorization on project cost, showing that material management significantly contributes to reducing overall costs.