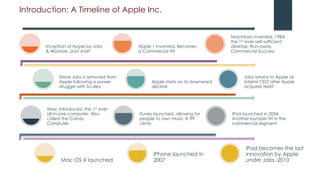
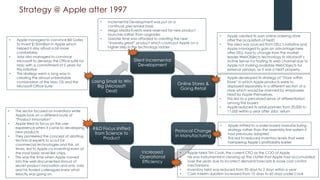
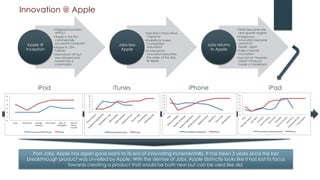
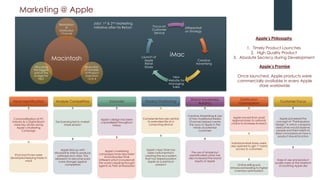
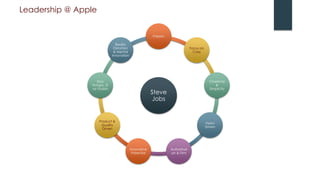
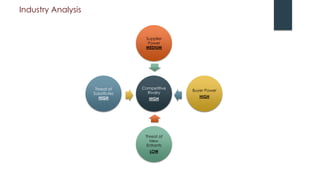
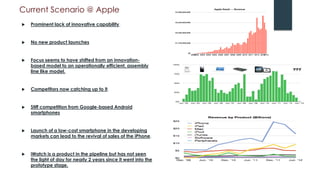
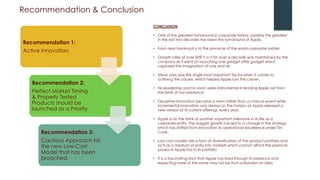
Apple underwent a remarkable turnaround under Steve Jobs from 1997-2011:
- When Jobs returned as CEO in 1997, Apple was struggling but he transformed it by focusing on innovative new products.
- Over the next 13 years, Apple launched hugely successful products like the iMac, iPod, iTunes, iPhone, and iPad that changed their industries.
- After Jobs' death in 2011, Apple has struggled to maintain the same level of innovation and has seen its share price decline as competitors like Samsung gained ground.