Embed presentation
Downloaded 105 times



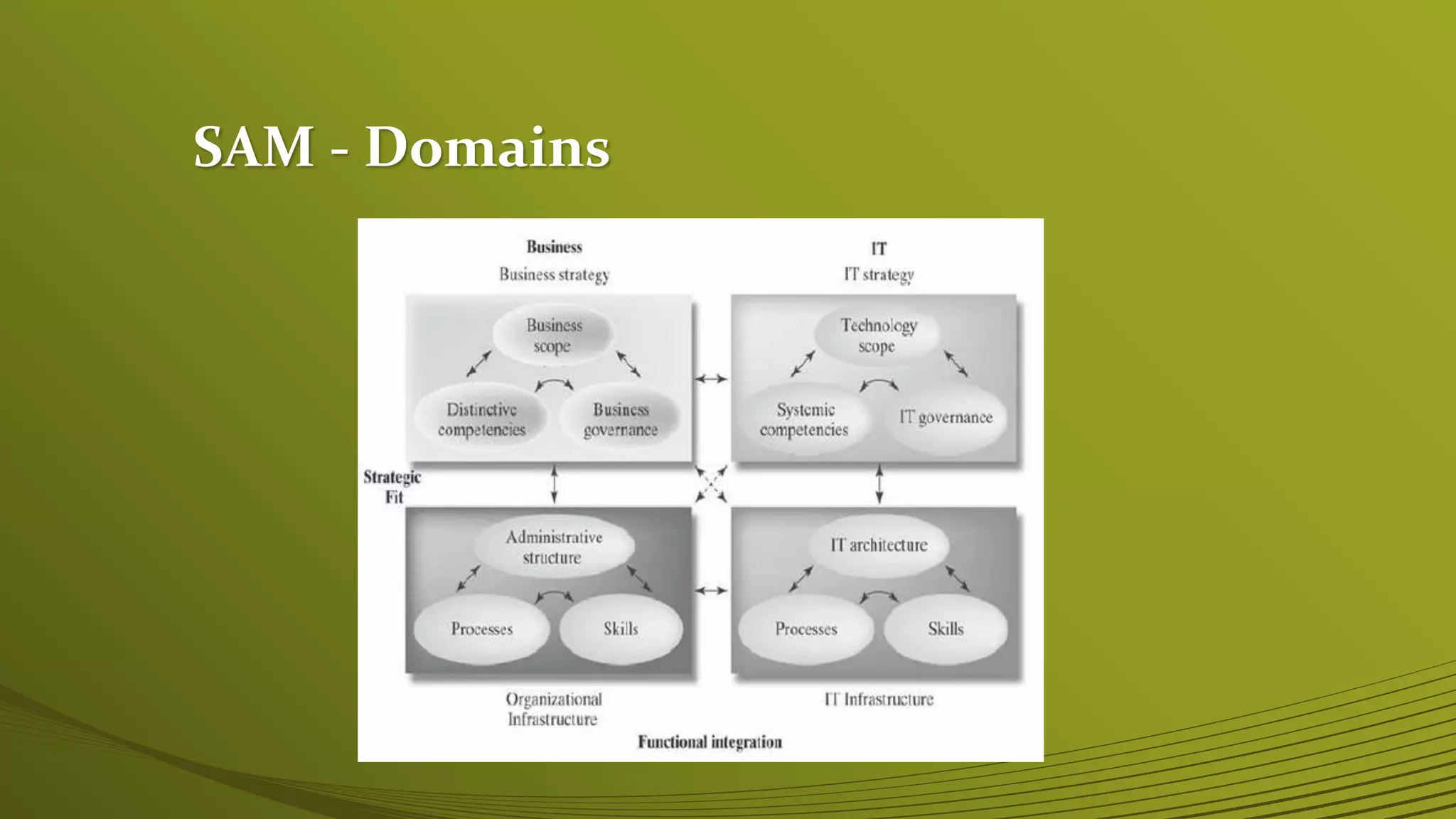


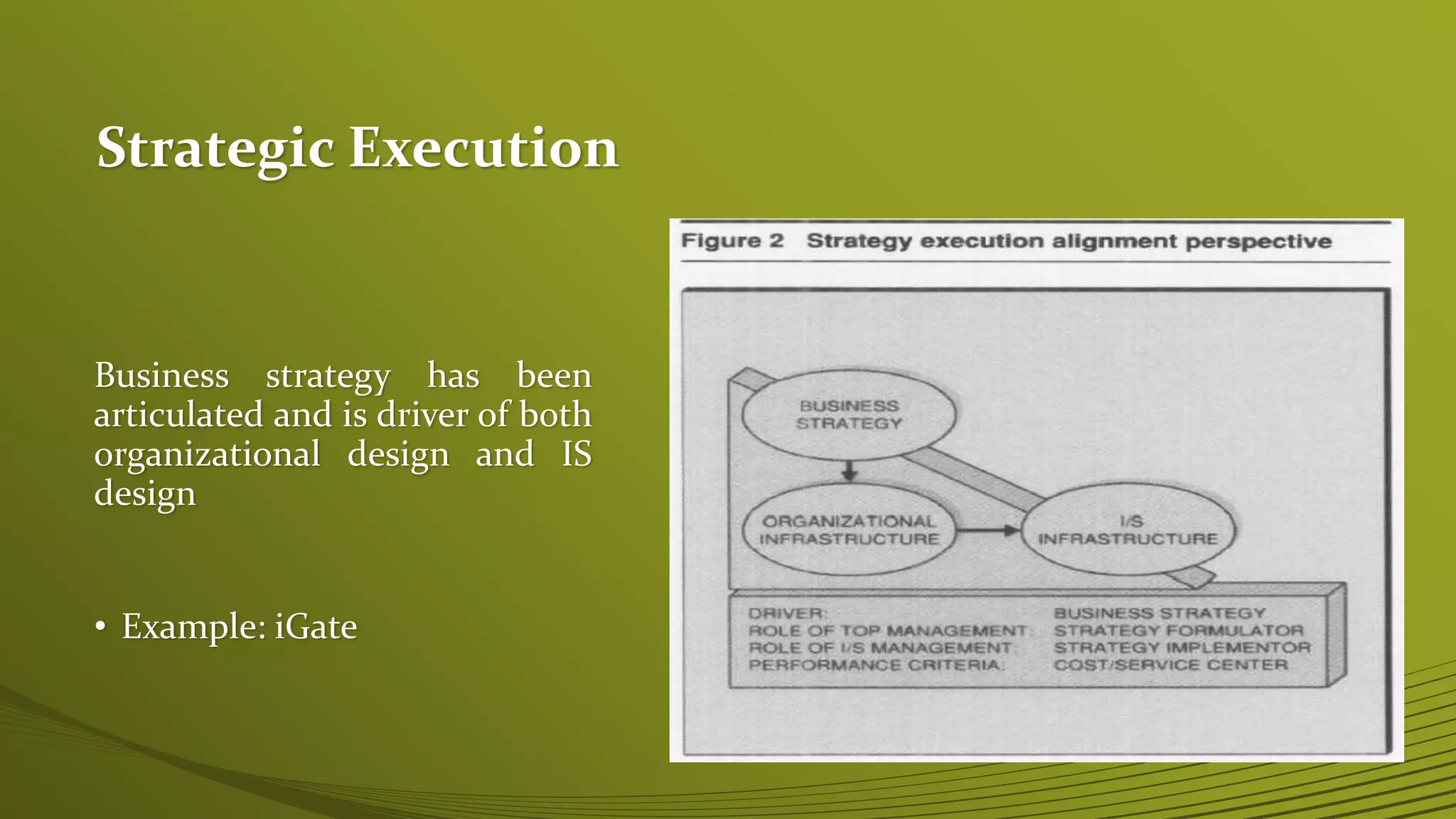
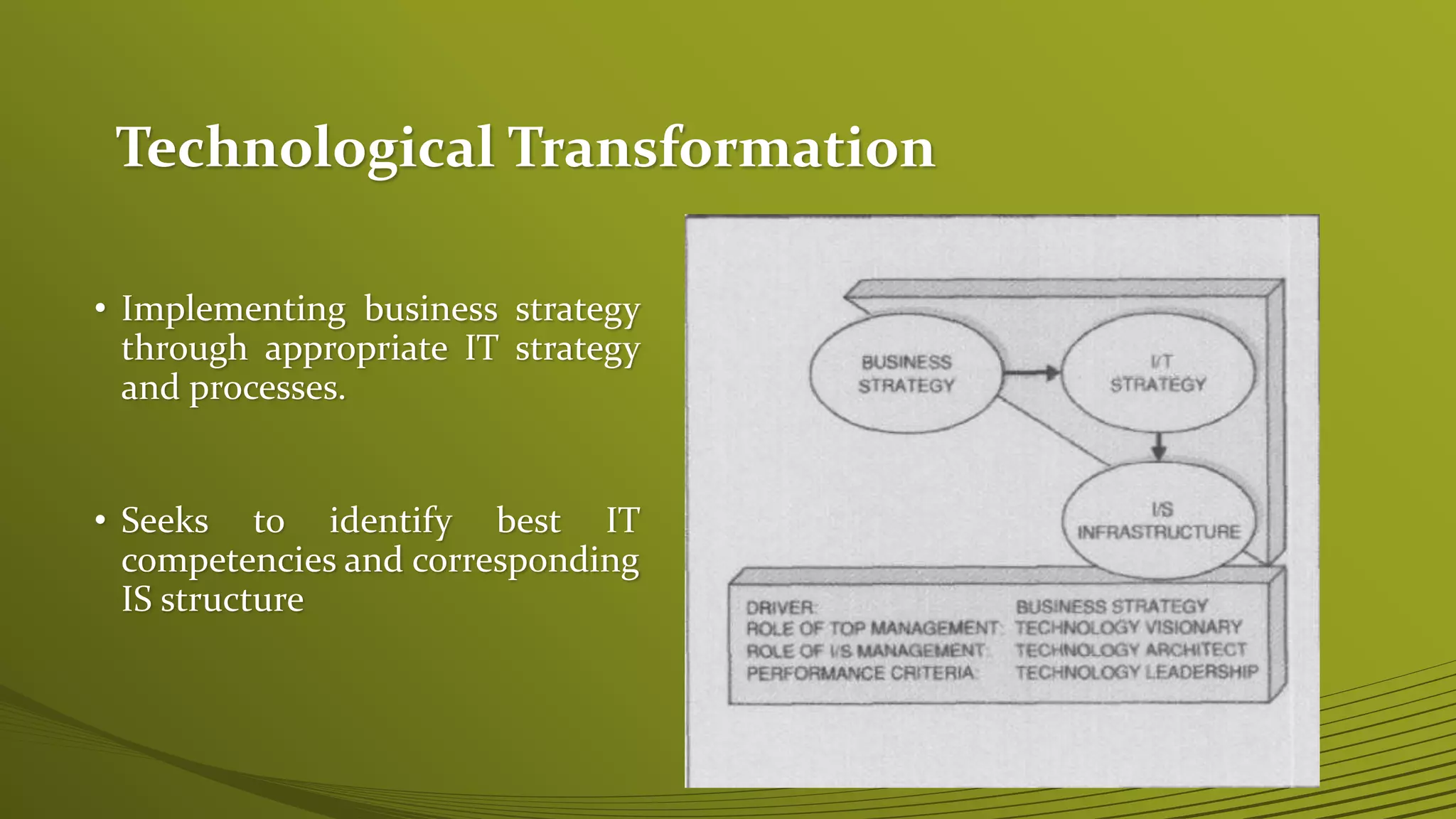

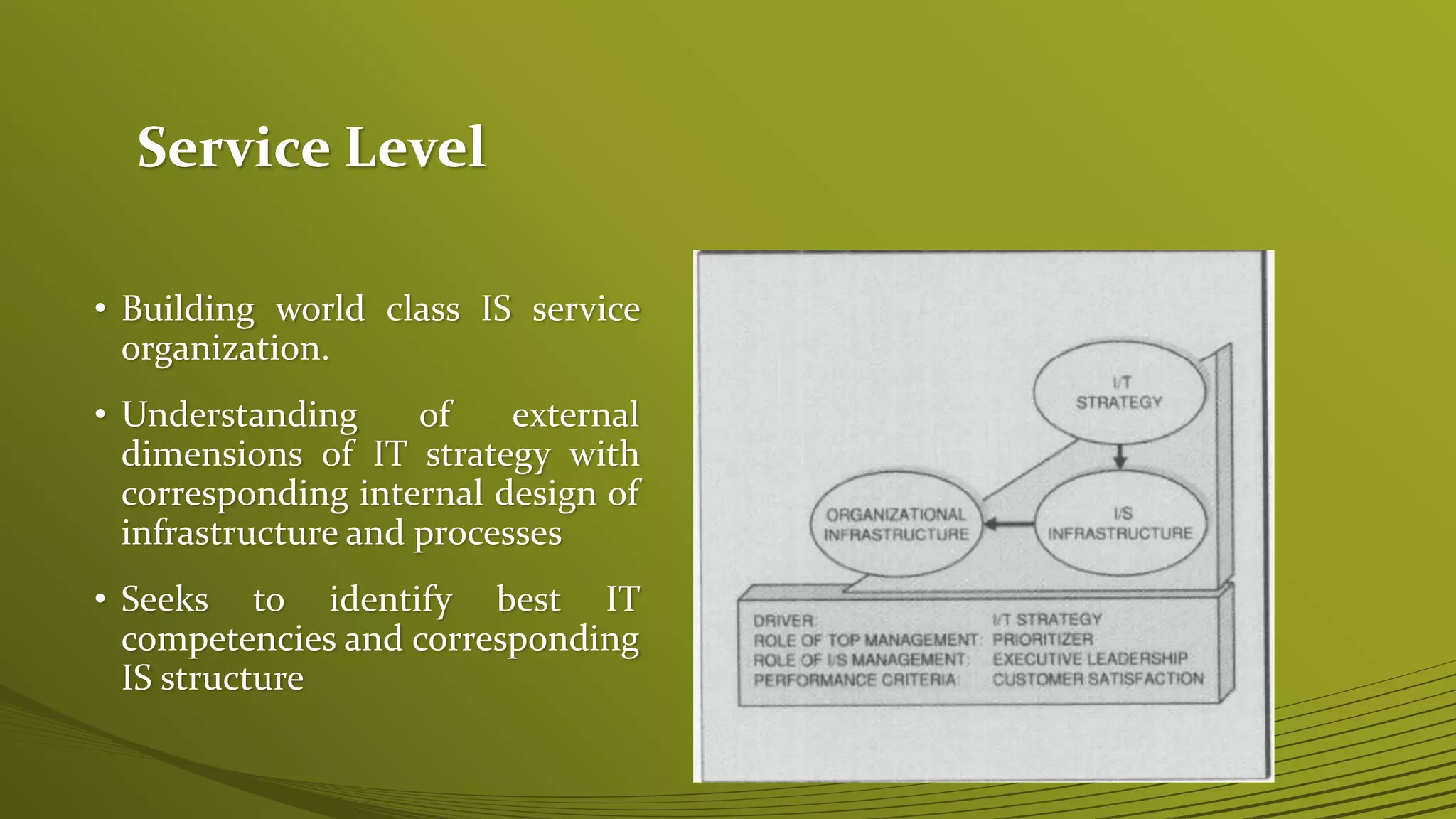

The Strategic Alignment Model (SAM) focuses on the dynamic relationship between business strategies and IT, aiming to create and exploit opportunities through technology. It consists of frameworks that analyze strategic fit and functional integration, emphasizing the need for coordinated IT and business strategies to drive processes and competitive potential. Examples included demonstrate the practical application of SAM, such as Federal Express adapting its strategy through emerging IT capabilities.









