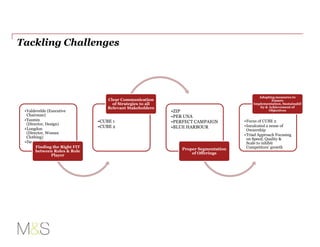
Marks & Spencer adopted a business model focused on creating value for customers and employees. It pioneered social services for employees and adopted merchandising practices from Sears. It began directly buying from manufacturers. Over time it expanded globally but faced challenges like high costs, outdated stores, and changing fashion trends. A 1991 reorganization focused on cutting costs in clothing, improving food access, and growing financial services. A later recovery plan segmented offerings, found the right leaders, improved communication, sourced products faster at lower cost, and strengthened customer relationships to rebuild the brand.