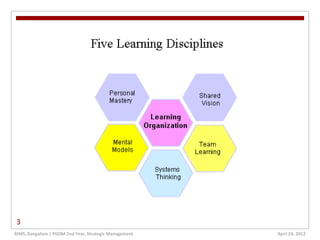
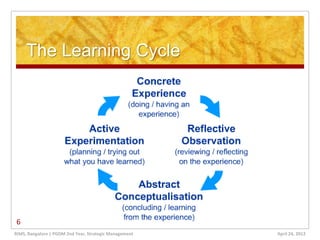
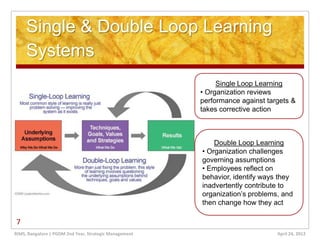
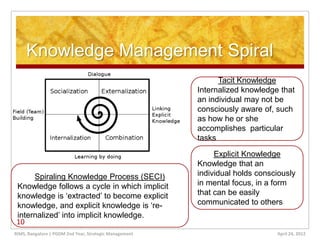
The document discusses learning organizations, which are defined as entities that foster continuous learning and adaptability among their members to remain competitive. It highlights the characteristics of such organizations, including systems thinking, personal mastery, and the necessity of knowledge management to cope with increasing market complexities. Additionally, it addresses the challenges leaders face in creating learning organizations, emphasizing the need for a long-term vision and openness to change.