The document outlines the architecture, design, and execution of SystemML, a declarative machine learning language designed to work with Hadoop and Spark. It discusses key components such as APIs, the compilation chain, runtime execution plans, and includes examples of DML expressions and linear regression operations. Additionally, it highlights important links for further exploration and contributions to the SystemML project.



![SystemML Design
5
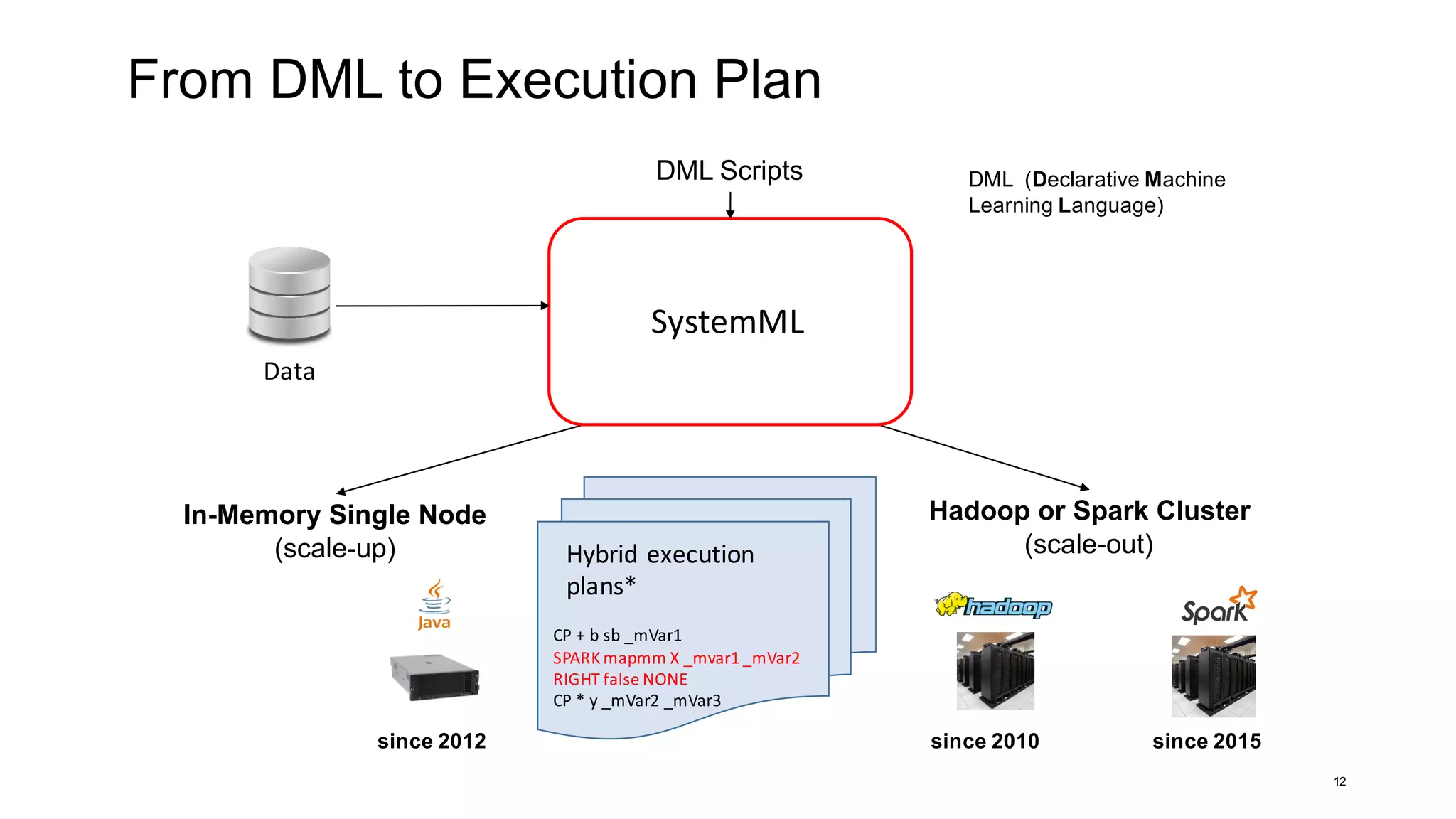
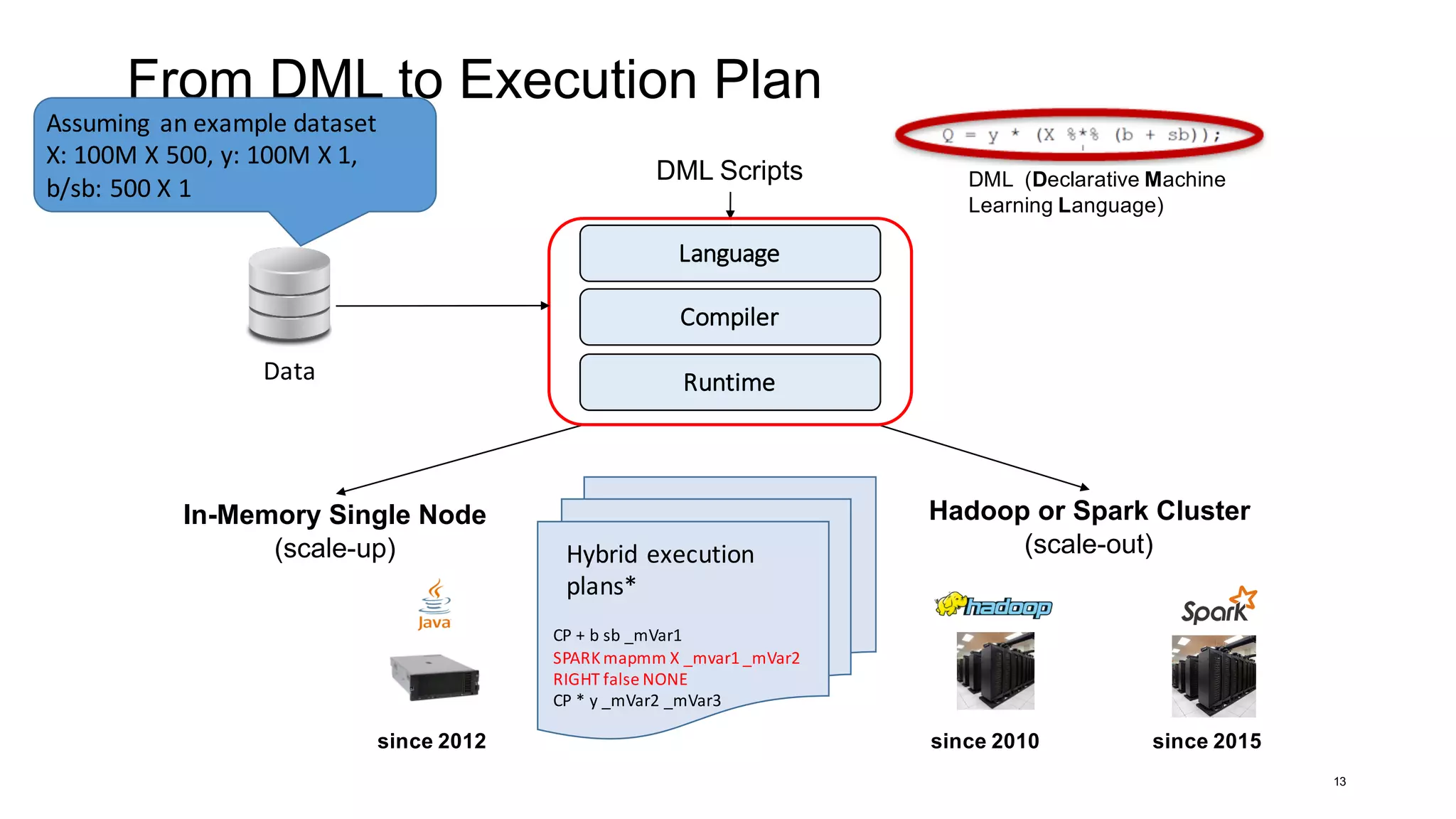
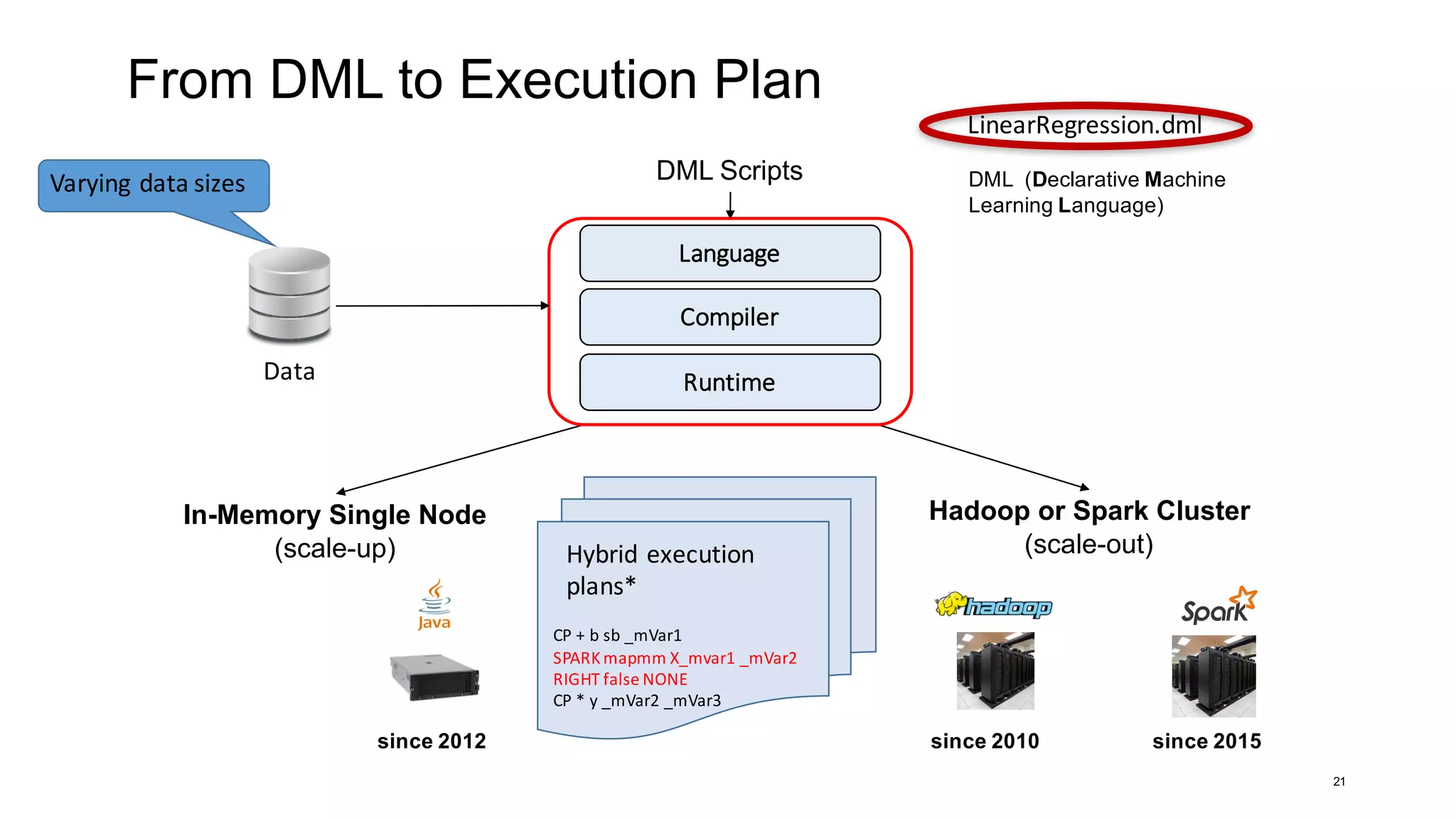
DML (Declarative Machine
Learning Language)
Hadoop or Spark Cluster
(scale-out)
since 2010
In-Memory Single Node
(scale-up)
since 2012 since 2015
DML Scripts
Data
CP + b sb _mVar1
SPARK mapmm X _mvar1 _mVar2
RIGHT false NONE
CP * y _mVar2 _mVar3
Hybrid execution
plans*
SystemML3. double [] []
1. On disk/HDFS
2. RDD/DataFrame](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s6systemmlarchitecture-160913183627/75/Apache-SystemML-Architecture-by-Niketan-Panesar-5-2048.jpg)
![SystemML Design
6
Hadoop or Spark Cluster
(scale-out)
since 2010
In-Memory Single Node
(scale-up)
since 2012
DML Scripts
Data
SystemML
1. On disk/HDFS
2. RDD/DataFrame
3. double [] []
Command line API*
(also MLContext*)
-exec hadoop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s6systemmlarchitecture-160913183627/75/Apache-SystemML-Architecture-by-Niketan-Panesar-6-2048.jpg)
![SystemML Design
7
Hadoop or Spark Cluster
(scale-out)
In-Memory Single Node
(scale-up)
since 2012
DML Scripts
Data
SystemML
1. On disk/HDFS
2. RDD/DataFrame
3. double [] []
Two options:
1. –exec singlenode
2. Use standalone jar (preserves rewrites, but
may spawn Local MR jobs)
Command line API*
(also MLContext*)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s6systemmlarchitecture-160913183627/75/Apache-SystemML-Architecture-by-Niketan-Panesar-7-2048.jpg)
![SystemML Design
8
Spark Cluster
(scale-out)
In-Memory Single Node
(scale-up)
since 2012 since 2015
DML Scripts
Data
SystemML
1. On disk/HDFS
2. RDD/DataFrame
3. double [] []
Command line API*
(also MLContext*)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s6systemmlarchitecture-160913183627/75/Apache-SystemML-Architecture-by-Niketan-Panesar-8-2048.jpg)
![SystemML Design
9
Spark Cluster
(scale-out)
In-Memory Single Node
(scale-up)
since 2012 since 2015
DML Scripts
Data
SystemML
1. On disk/HDFS
2. RDD/DataFrame
3. double [] []
MLContext API
- Java/Python/Scala
https://apache.github.io/incubator-systemml/spark-mlcontext-programming-guide.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s6systemmlarchitecture-160913183627/75/Apache-SystemML-Architecture-by-Niketan-Panesar-9-2048.jpg)
![SystemML Design
10
In-Memory Single Node
(scale-up)
since 2012
DML Scripts
Data
SystemML
1. On disk/HDFS
2. RDD/DataFrame
3. double [] []
JMLC API
https://apache.github.io/incubator-systemml/jmlc.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s6systemmlarchitecture-160913183627/75/Apache-SystemML-Architecture-by-Niketan-Panesar-10-2048.jpg)


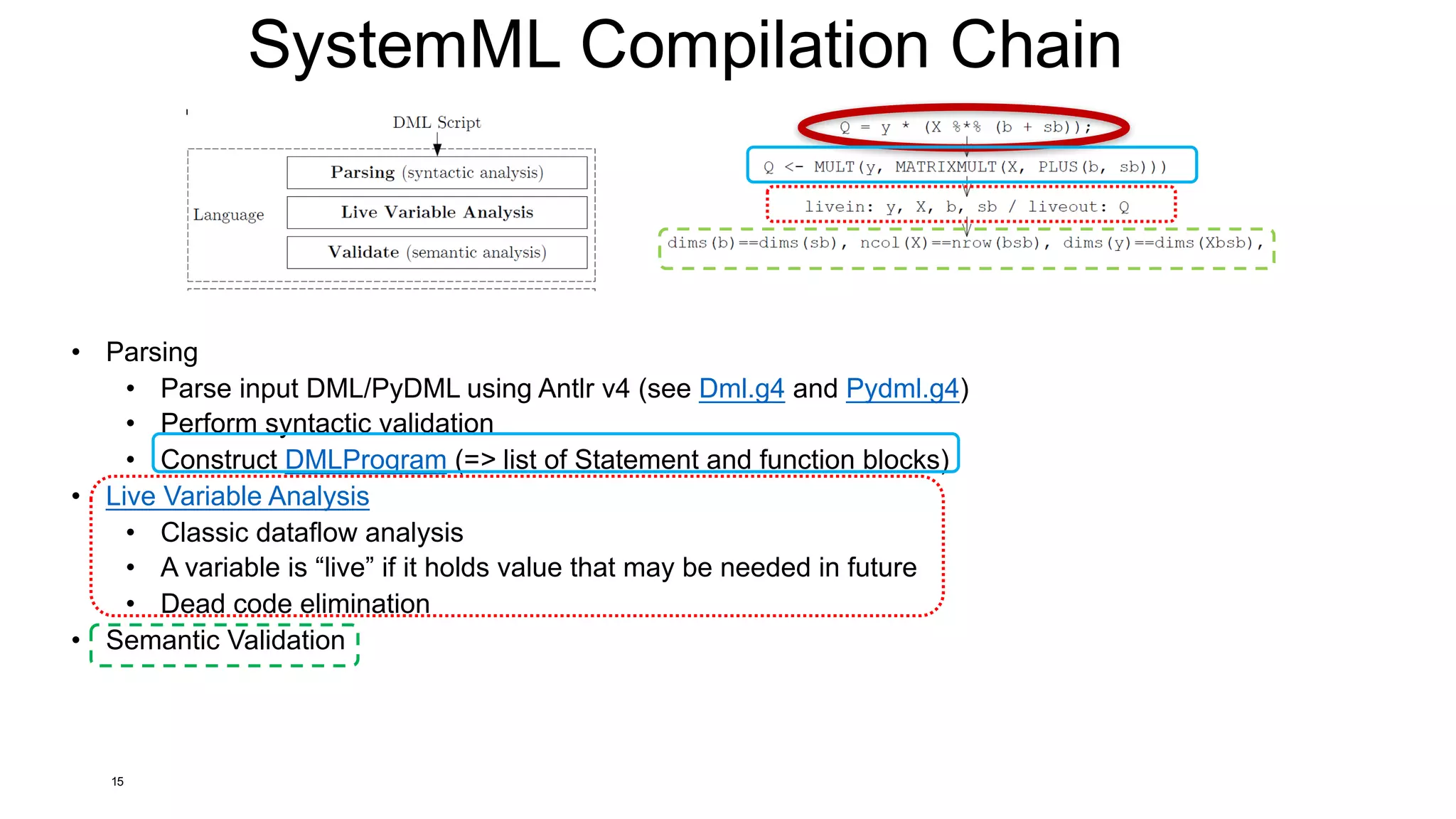
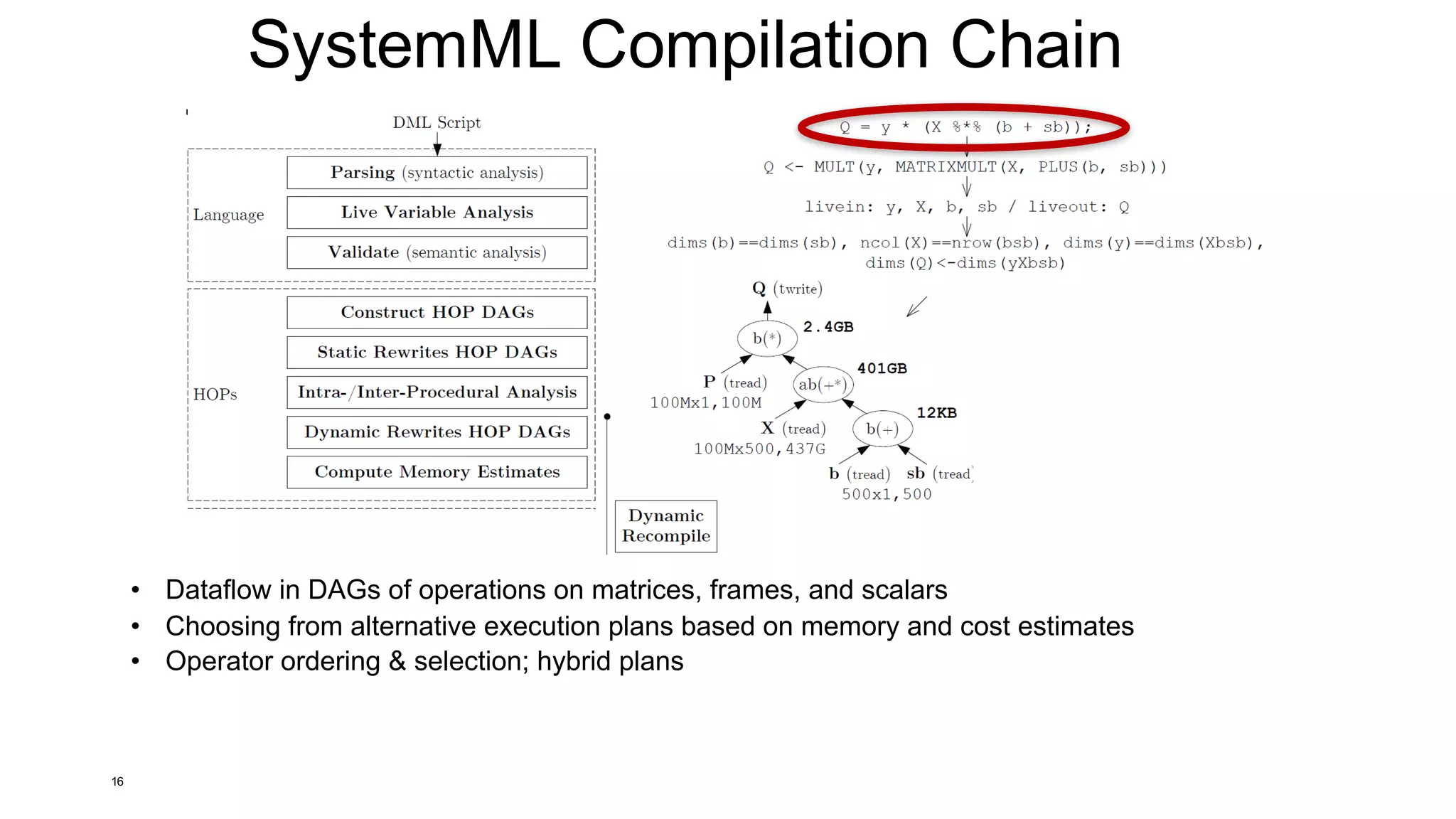
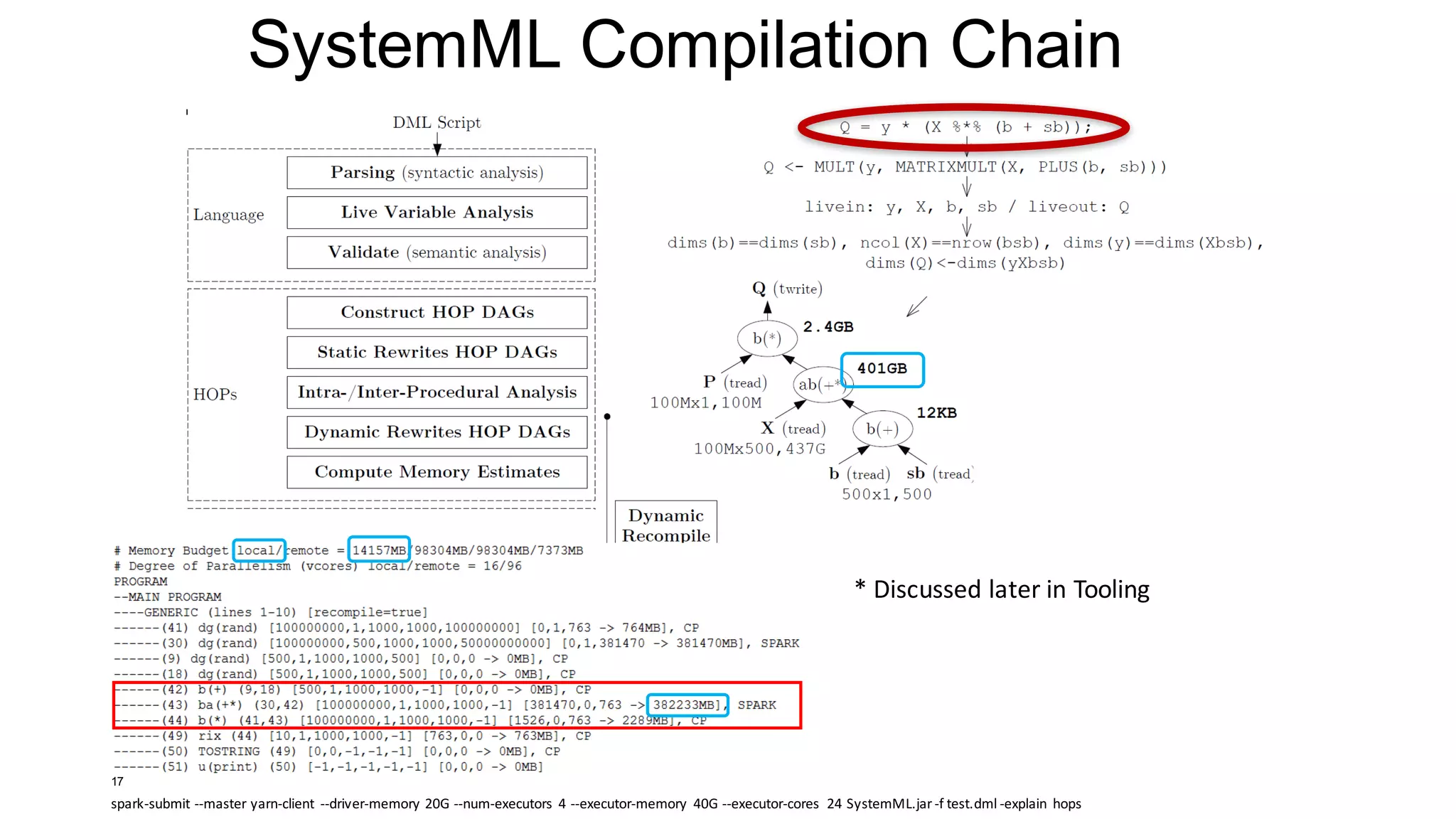
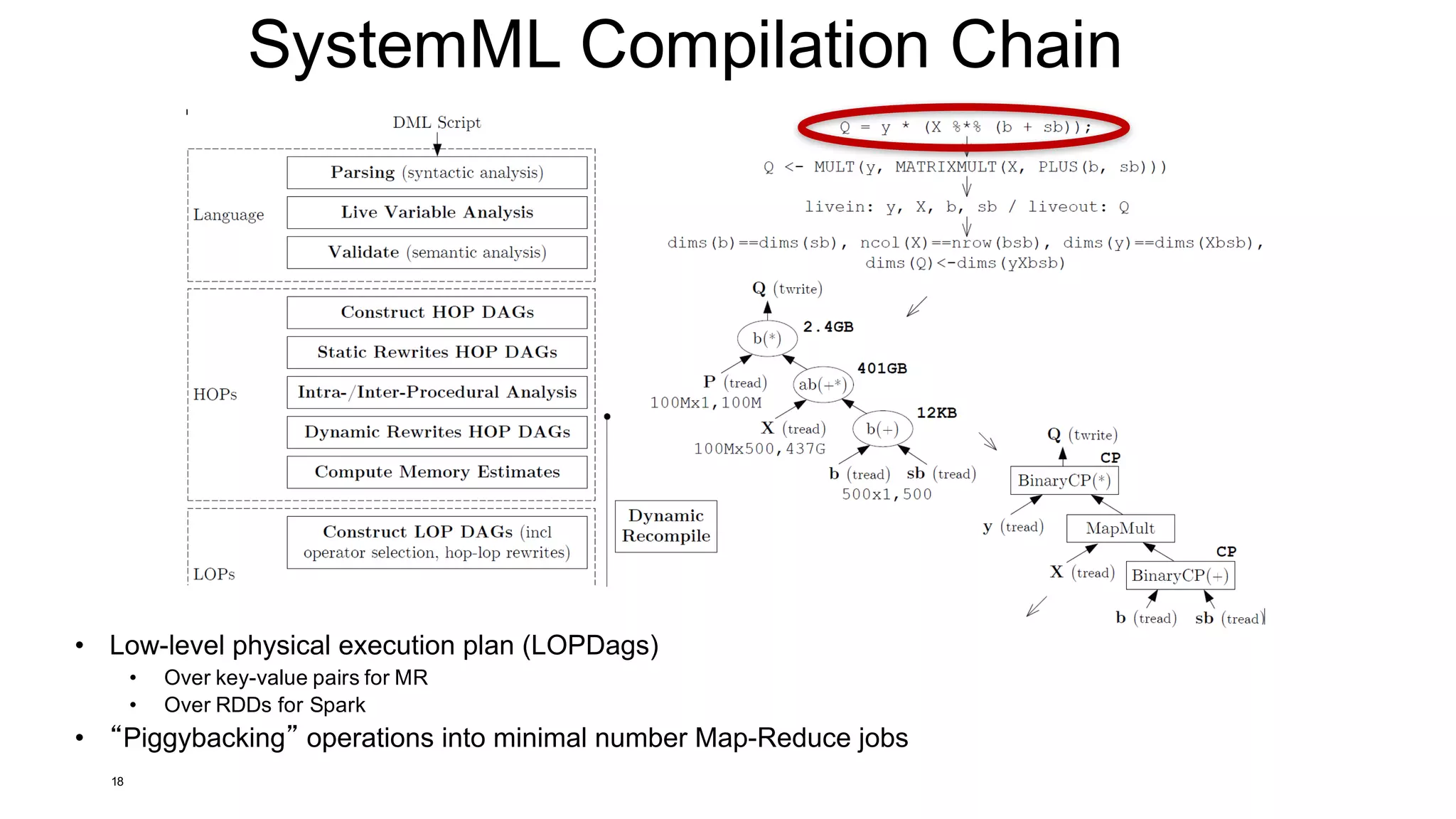
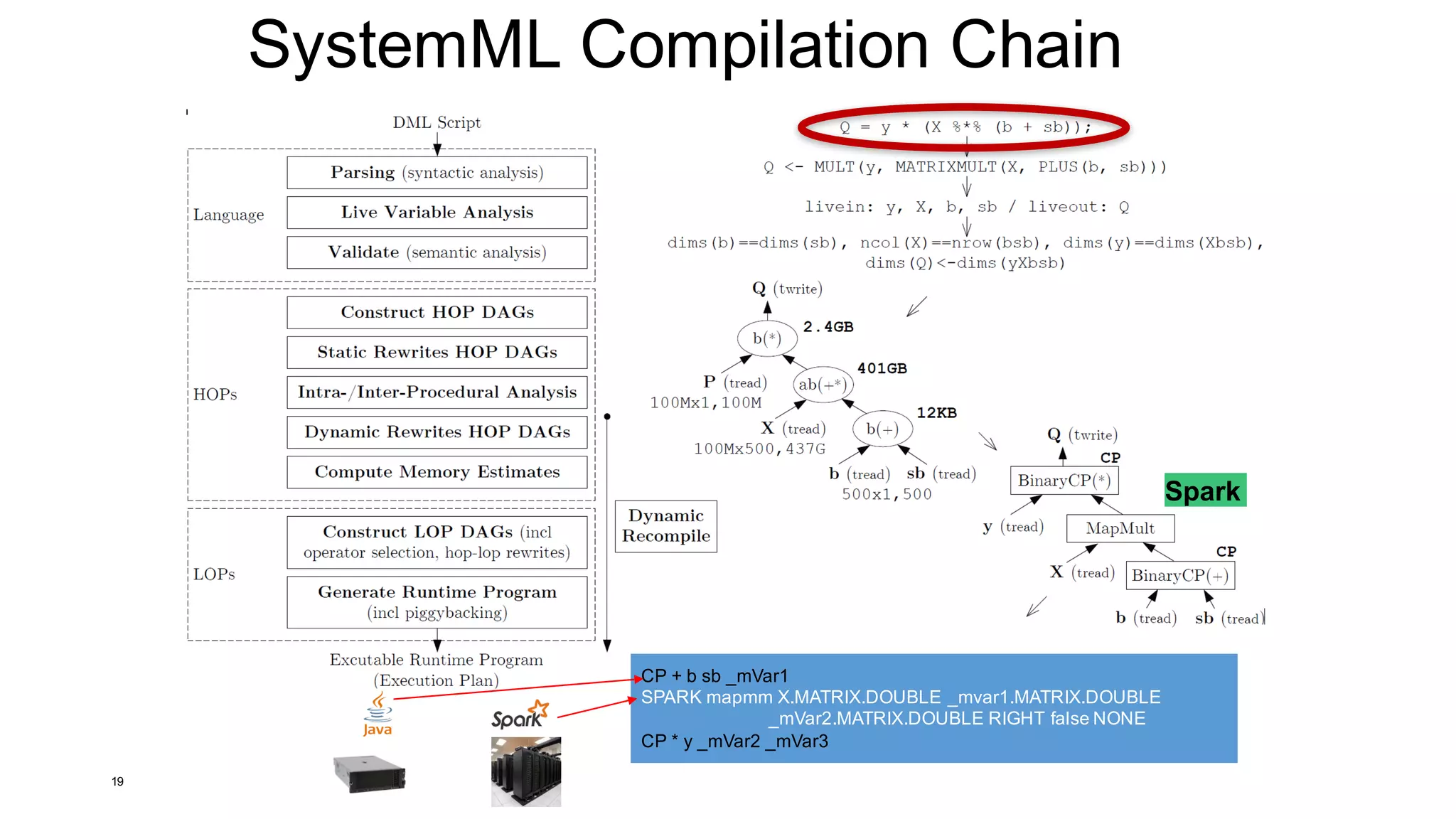

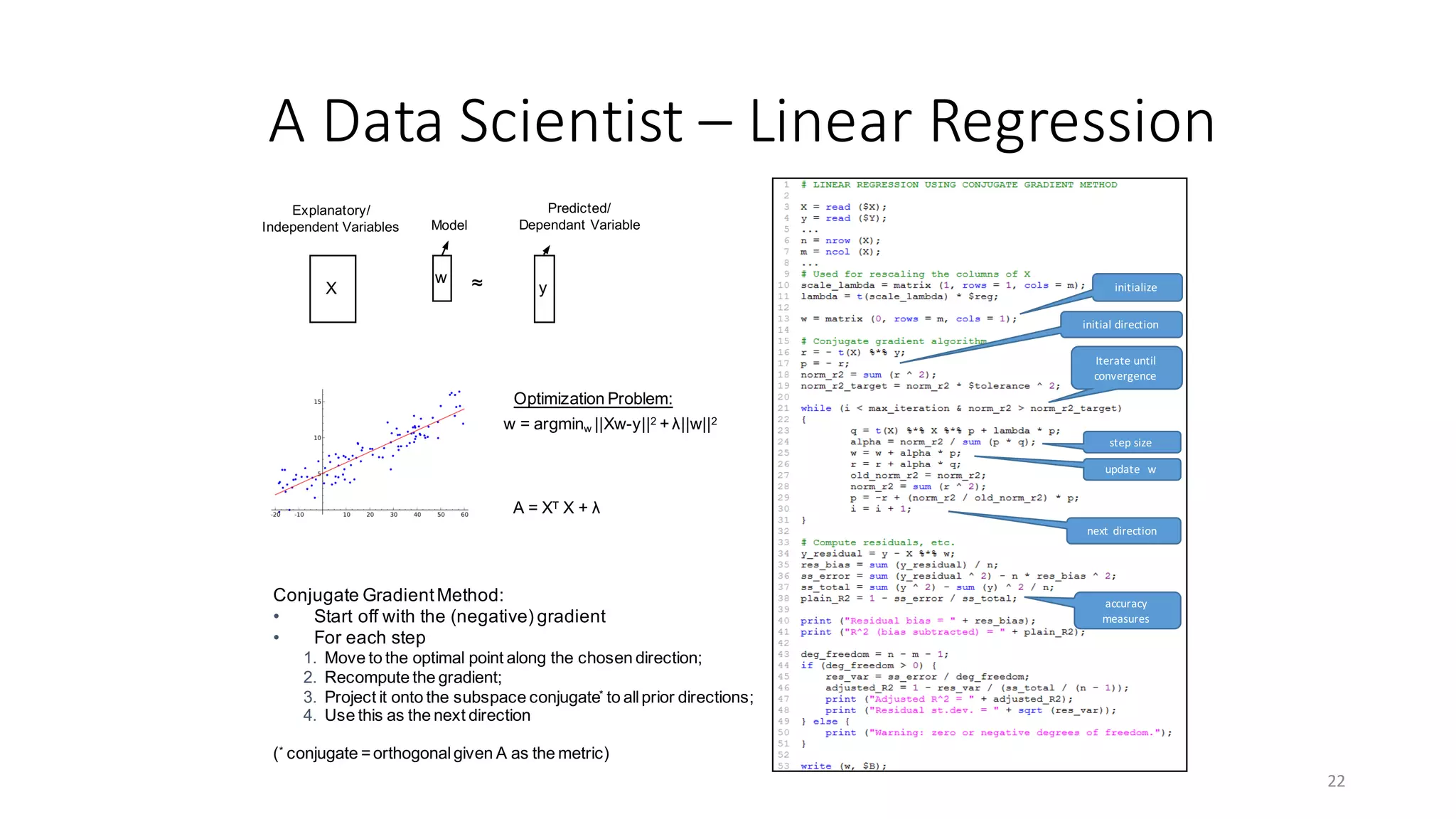
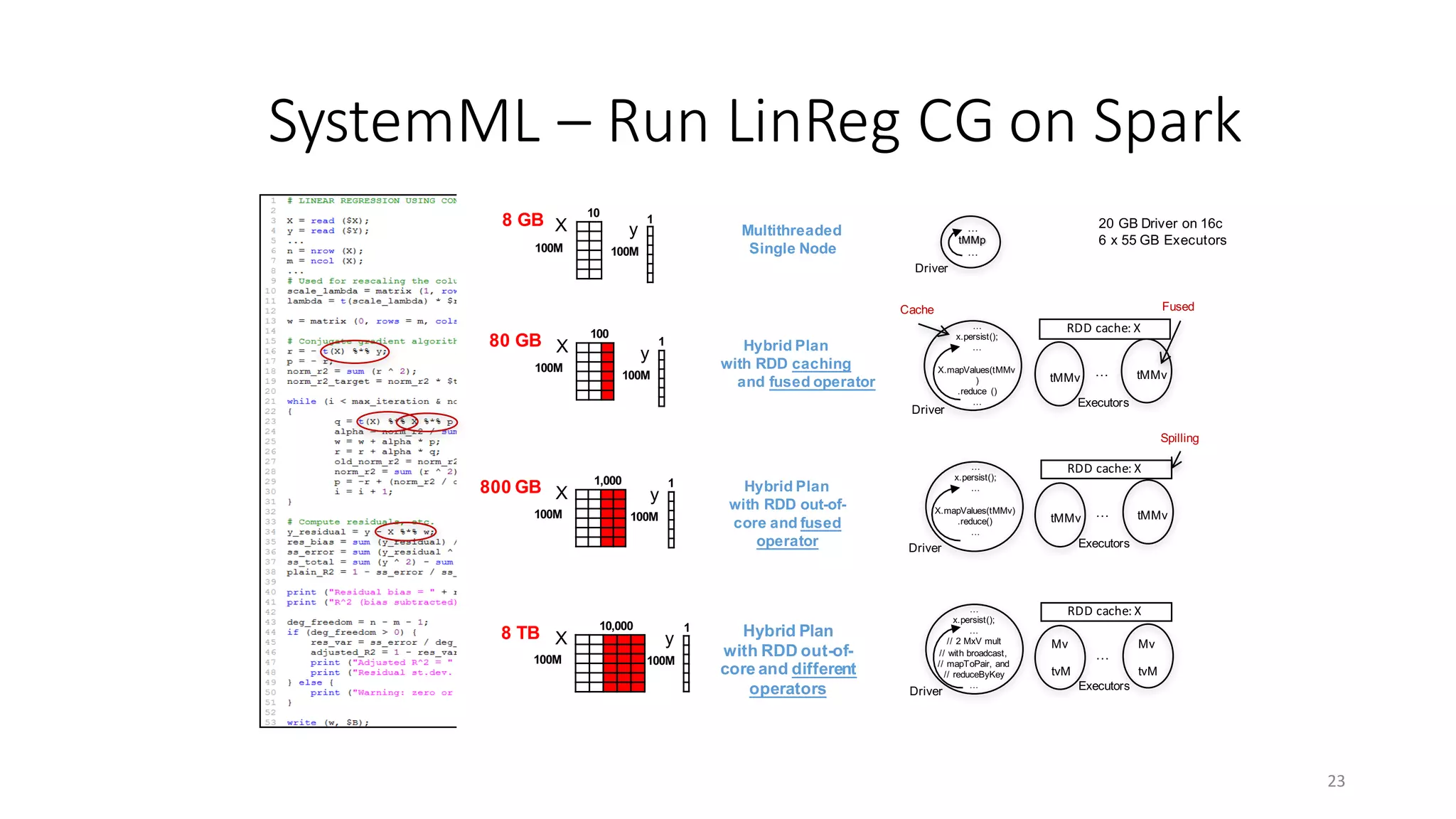

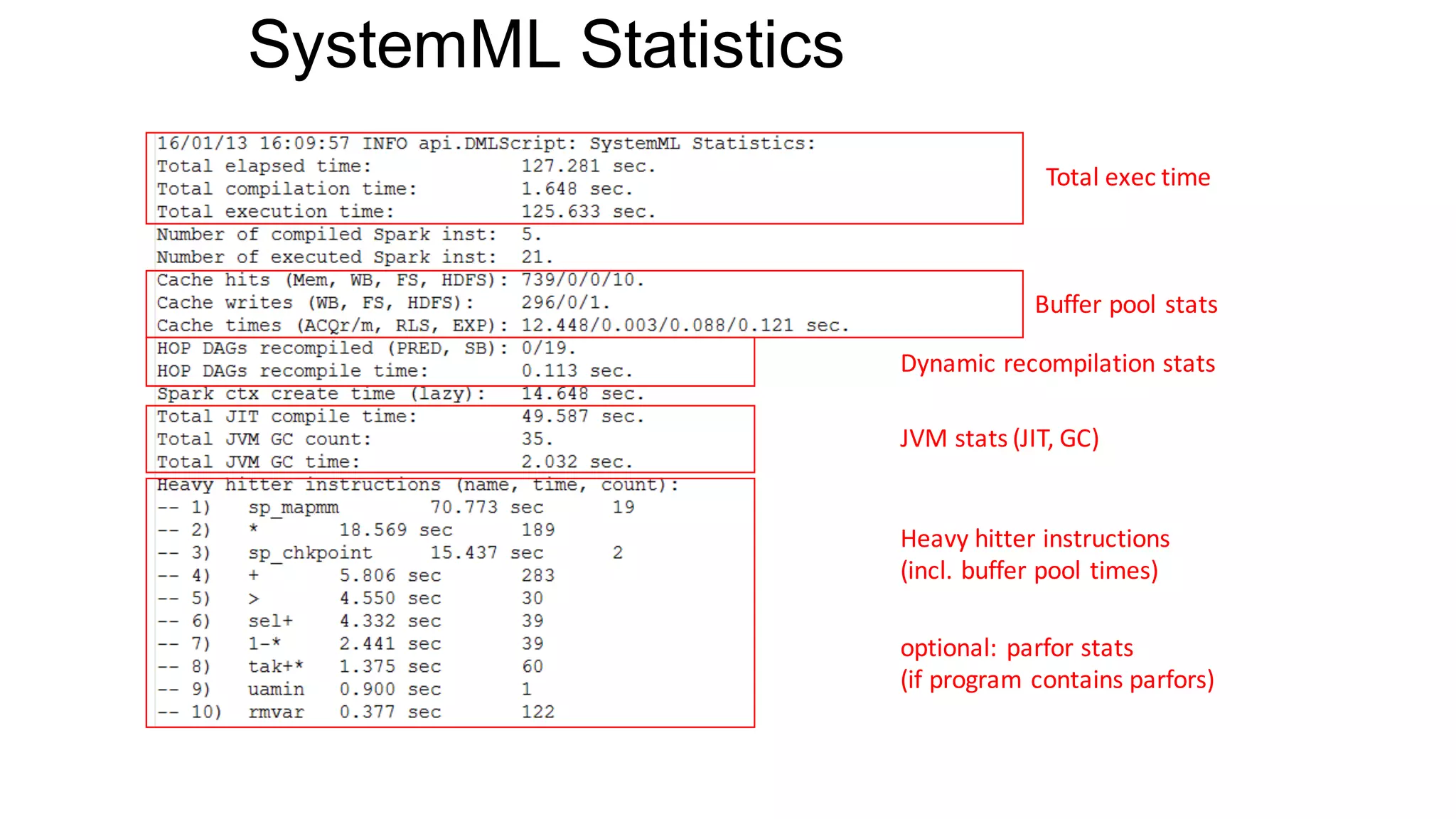
![SystemML’s Compilation Chain / Overview Tools
25
EXPLAIN
hops
STATS
DEBUG
EXPLAIN
runtime
[Matthias Boehm et al:
SystemML's Optimizer: Plan
Generation for Large-Scale
Machine Learning Programs. IEEE
Data Eng. Bull 2014]
HOP (High-level operator)
LOP (Low-level operator)
EXPLAIN
*_recompile](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s6systemmlarchitecture-160913183627/75/Apache-SystemML-Architecture-by-Niketan-Panesar-25-2048.jpg)
![Explain (Understanding Execution Plans)
• Overview
• Shows generated execution plan (at different compilation steps)
• Introduced 05/2014 for internal usage
• Important tool for understanding/debugging optimizer choices!
• Usage
• hadoop jar SystemML.jar -f test.dml –explain
[hops | runtime | hops_recompile | runtime_recompile]
• Hops
• Program w/ hop dags after optimization
• Runtime (default)
• Program w/ generated runtime instructions
• Hops_recompile:
• See hops + hop dag after every recompile
• Runtime_recompile:
• See runtime + generated runtime instructions after every recompile
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s6systemmlarchitecture-160913183627/75/Apache-SystemML-Architecture-by-Niketan-Panesar-26-2048.jpg)
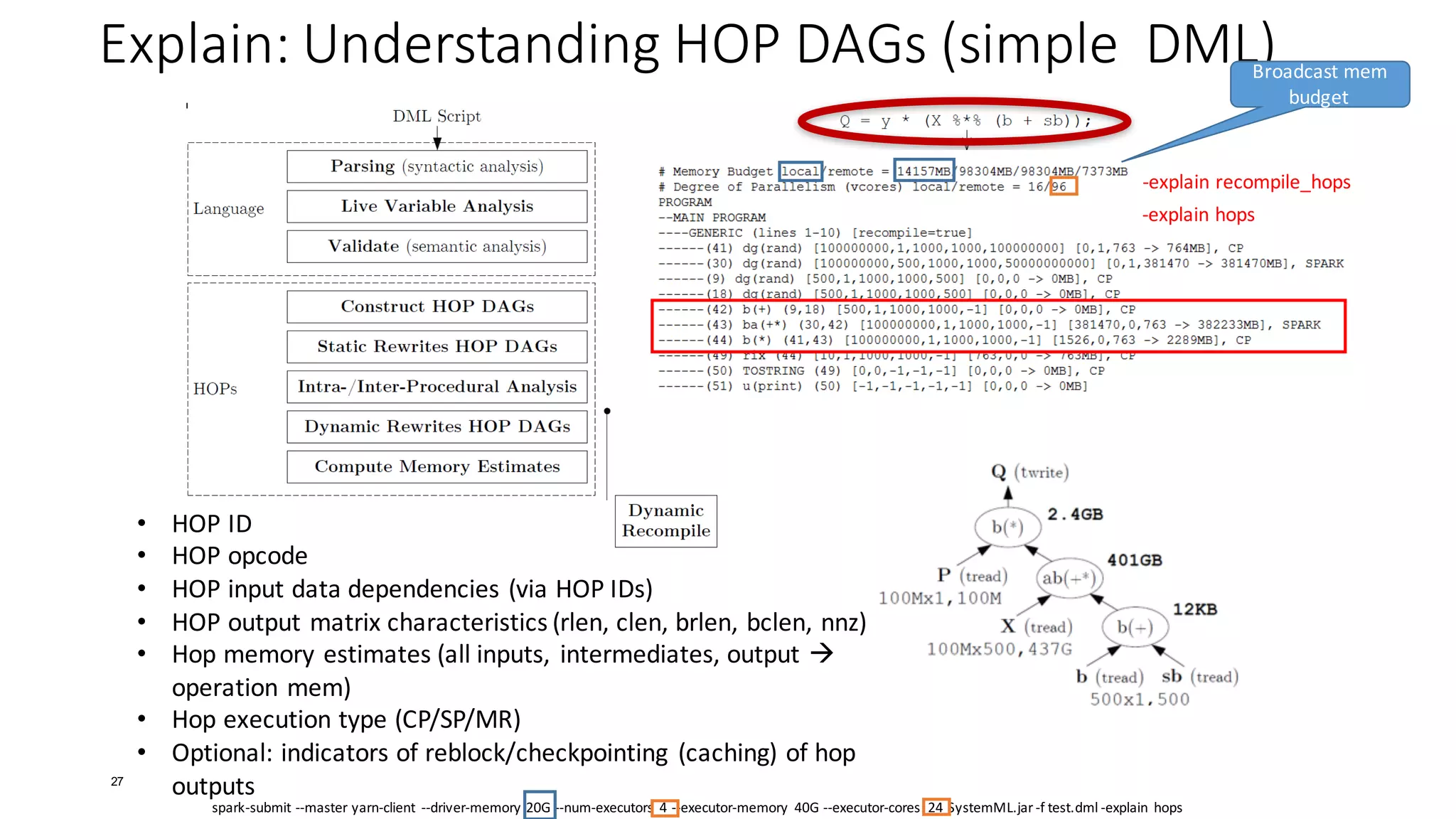
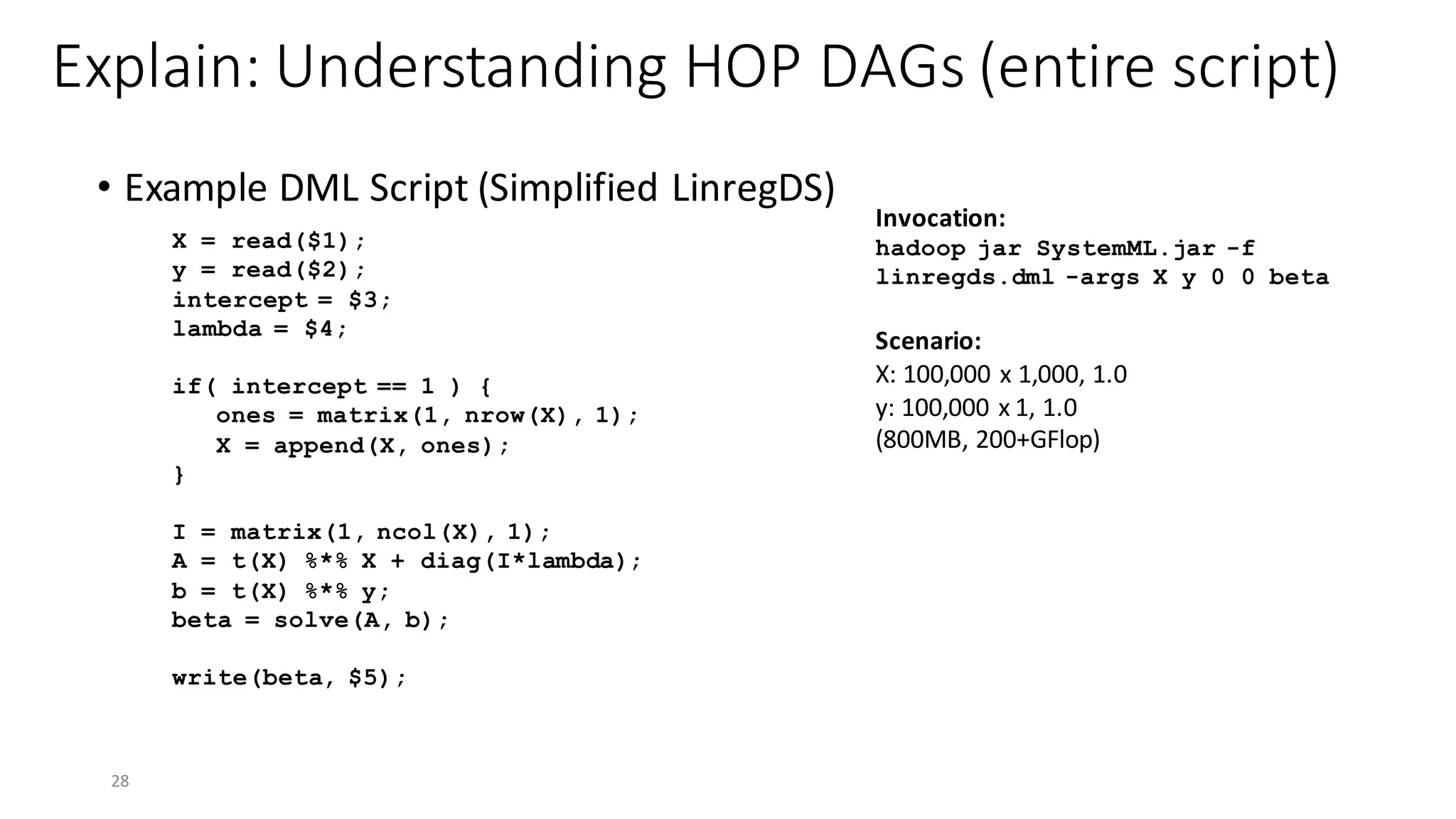
![Explain: Understanding HOP DAGs (2)
• Explain Hops
29
15/07/05 17:18:06 INFO api.DMLScript: EXPLAIN (HOPS):
# Memory Budget local/remote = 57344MB/1434MB/1434MB
# Degree of Parallelism (vcores) local/remote = 24/144/72
PROGRAM
--MAIN PROGRAM
----GENERIC (lines 1-4) [recompile=false]
------(10) PRead X [100000,1000,1000,1000,100000000] [0,0,763 -> 763MB], CP
------(11) TWrite X (10) [100000,1000,1000,1000,100000000] [763,0,0 -> 763MB], CP
------(21) PRead y [100000,1,1000,1000,100000] [0,0,1 -> 1MB], CP
------(22) TWrite y (21) [100000,1,1000,1000,100000] [1,0,0 -> 1MB], CP
------(24) TWrite intercept [0,0,-1,-1,-1] [0,0,0 -> 0MB], CP
------(26) TWrite lambda [0,0,-1,-1,-1] [0,0,0 -> 0MB], CP
----GENERIC (lines 11-16) [recompile=false]
------(42) TRead X [100000,1000,1000,1000,100000000] [0,0,763 -> 763MB], CP
------(52) r(t) (42) [1000,100000,1000,1000,100000000] [763,0,763 -> 1526MB]
------(53) ba(+*) (52,42) [1000,1000,1000,1000,-1] [1526,8,8 -> 1541MB], CP
------(43) TRead y [100000,1,1000,1000,100000] [0,0,1 -> 1MB], CP
------(59) ba(+*) (52,43) [1000,1,1000,1000,-1] [764,0,0 -> 764MB], CP
------(60) b(solve) (53,59) [1000,1,1000,1000,-1] [8,8,0 -> 15MB], CP
------(66) PWrite beta (60) [1000,1,-1,-1,-1] [0,0,0 -> 0MB], CP
Cluster
Characteristics
Program Structure
(incl recompile)
Unrolled
HOP
DAG
Notes: if branch (6-9) and regularization removed by rewrites](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s6systemmlarchitecture-160913183627/75/Apache-SystemML-Architecture-by-Niketan-Panesar-29-2048.jpg)
![Explain: Understanding Runtime Plans (1)
• Explain Runtime (simplified filenames, removed rmvar)
30 IBM Research
15/07/05 17:18:53 INFO api.DMLScript: EXPLAIN (RUNTIME):
# Memory Budget local/remote = 57344MB/1434MB/1434MB
# Degree of Parallelism (vcores) local/remote = 24/144/72
PROGRAM ( size CP/MR = 25/0 )
--MAIN PROGRAM
----GENERIC (lines 1-4) [recompile=false]
------CP createvar pREADX X false binaryblock 100000 1000 1000 1000 100000000
------CP createvar pREADy y false binaryblock 100000 1 1000 1000 100000
------CP assignvar 0.SCALAR.INT.true intercept.SCALAR.INT
------CP assignvar 0.0.SCALAR.DOUBLE.true lambda.SCALAR.DOUBLE
------CP cpvar pREADX X
------CP cpvar pREADy y
----GENERIC (lines 11-16) [recompile=false]
------CP createvar _mVar2 .../_t0/temp1 true binaryblock 1000 1000 1000 1000 -1
------CP tsmm X.MATRIX.DOUBLE _mVar2.MATRIX.DOUBLE LEFT 24
------CP createvar _mVar3 .../_t0/temp2 true binaryblock 1 100000 1000 1000 100000
------CP r' y.MATRIX.DOUBLE _mVar3.MATRIX.DOUBLE
------CP createvar _mVar4 .../_t0/temp3 true binaryblock 1 1000 1000 1000 -1
------CP ba+* _mVar3.MATRIX.DOUBLE X.MATRIX.DOUBLE _mVar4.MATRIX.DOUBLE 24
------CP createvar _mVar5 .../_t0/temp4 true binaryblock 1000 1 1000 1000 -1
------CP r' _mVar4.MATRIX.DOUBLE _mVar5.MATRIX.DOUBLE
------CP createvar _mVar6 .../_t0/temp5 true binaryblock 1000 1 1000 1000 -1
------CP solve _mVar2.MATRIX.DOUBLE _mVar5.MATRIX.DOUBLE _mVar6.MATRIX.DOUBLE
------CP write _mVar6.MATRIX.DOUBLE .../beta.SCALAR.STRING.true textcell.SCALAR.STRING.true
Literally a string
representation of
runtime instructions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s6systemmlarchitecture-160913183627/75/Apache-SystemML-Architecture-by-Niketan-Panesar-30-2048.jpg)