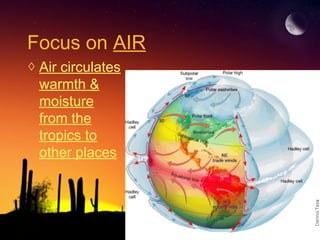
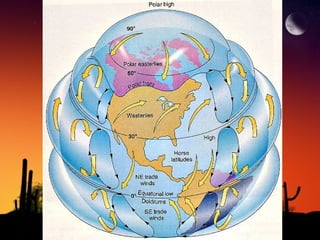
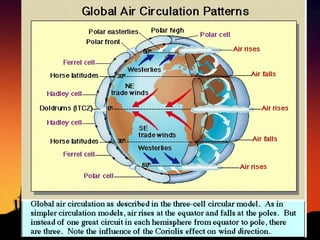
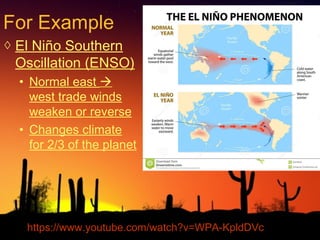
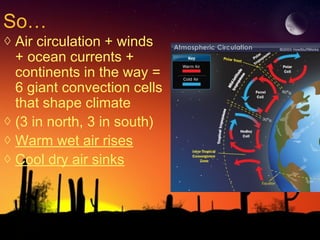
The document discusses factors that influence climate. It describes how air circulation driven by differences in solar heating across the Earth's surface creates global wind patterns. Ocean currents distribute heat around the world and interact with atmospheric circulation. Surface features like mountains also impact climate by influencing precipitation. All of these factors together define the world's major biomes by controlling temperature and rainfall in different regions.