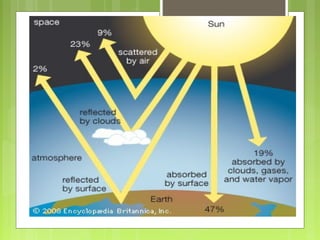
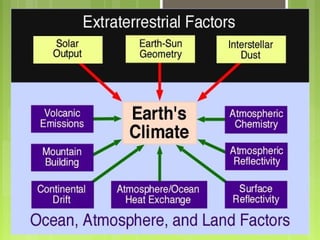
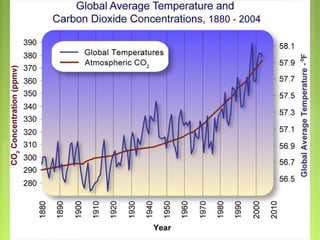
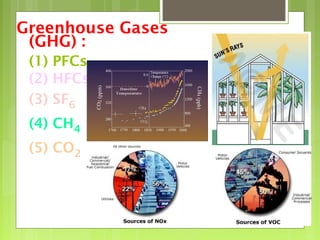
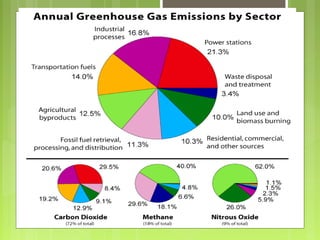
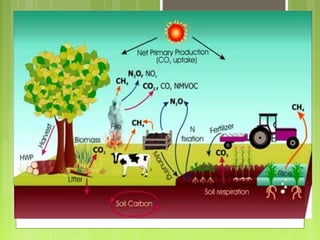
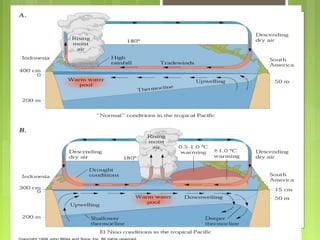
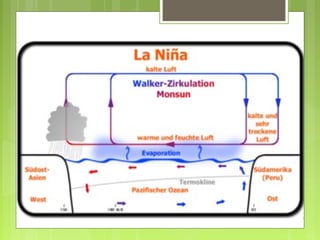
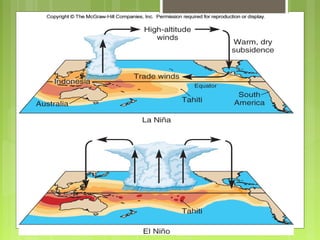
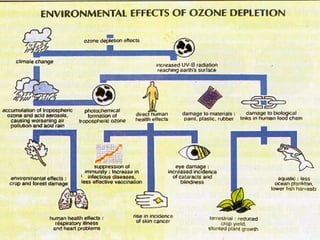
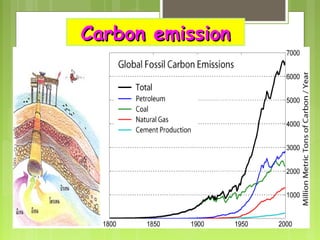
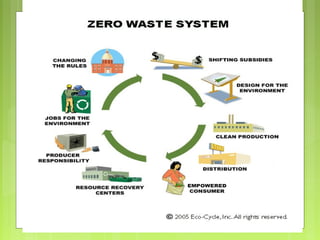
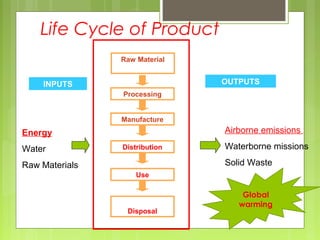
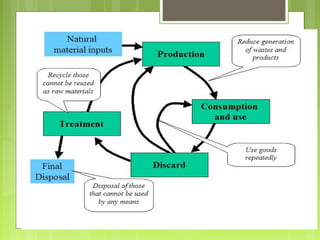
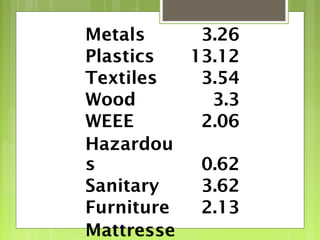
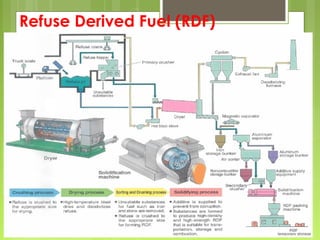
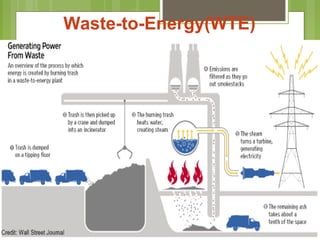
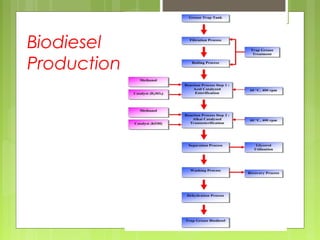
This document discusses global warming and the greenhouse effect. It explains that Earth's temperature is balanced by incoming and outgoing energy. Greenhouse gases like CO2 trap heat in the atmosphere and cause the greenhouse effect. Since the industrial revolution, human activities like burning fossil fuels have increased CO2 levels and contributed to climate change. The main greenhouse gases are identified. The document discusses how climate change is affecting different regions of the world through impacts like rising sea levels, stronger storms, and changing weather patterns. It concludes that humans are largely responsible for the recent warming trend due to emissions from activities like burning fossil fuels.