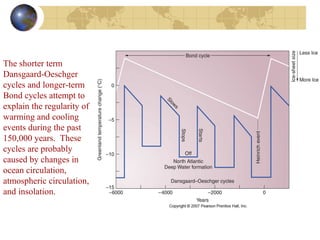
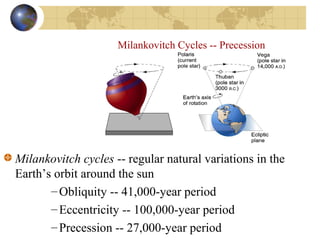
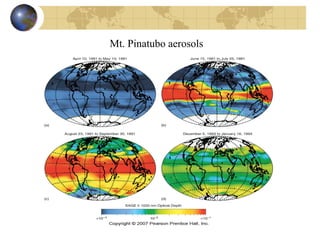
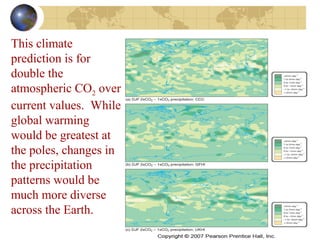
- Climate change occurs on various timescales and is influenced by factors like solar activity, Earth's orbit, atmospheric composition and greenhouse gases, volcanic eruptions, and human activities like fossil fuel burning.
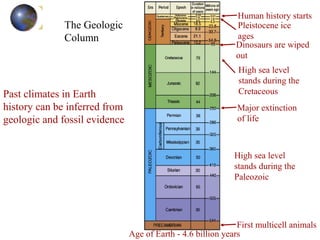
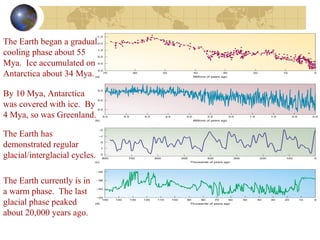
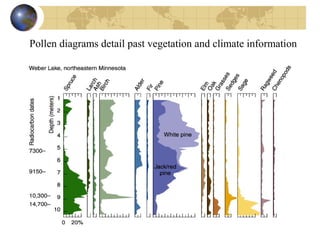
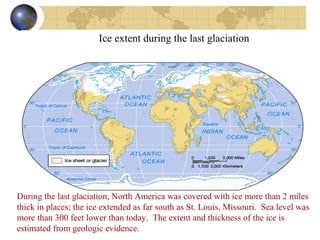
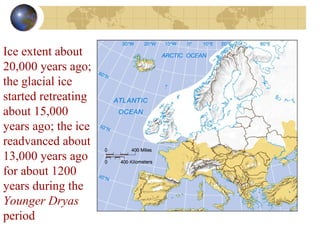
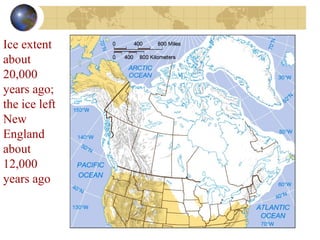
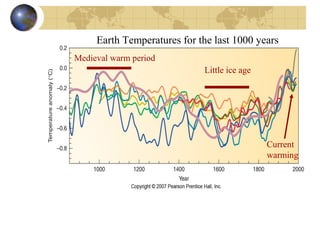
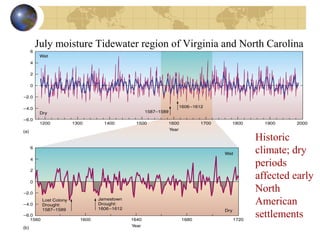
- Evidence from geology and fossils shows past climate changes, including intervals warmer than today and ice ages. The last ice age peaked around 20,000 years ago and glaciers have since retreated.
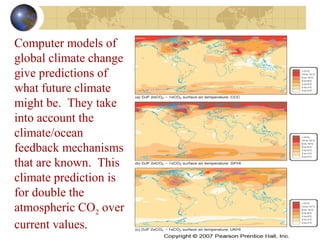
- Future climate is uncertain but computer models predict global warming and changing precipitation patterns if CO2 doubles from current levels due to feedbacks like ice-albedo and water vapor effects. Careful study of past and present helps understand complex climate system.