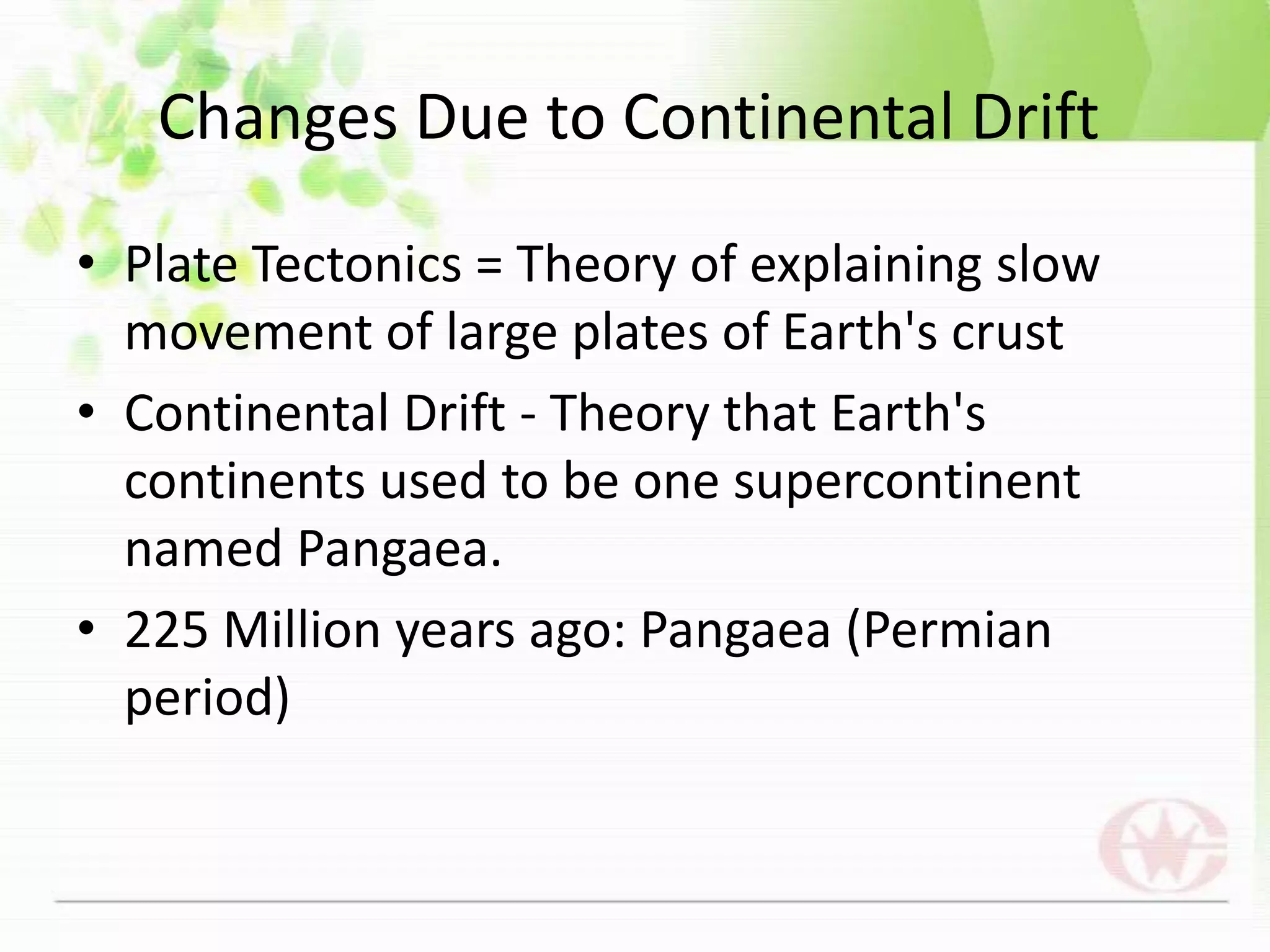
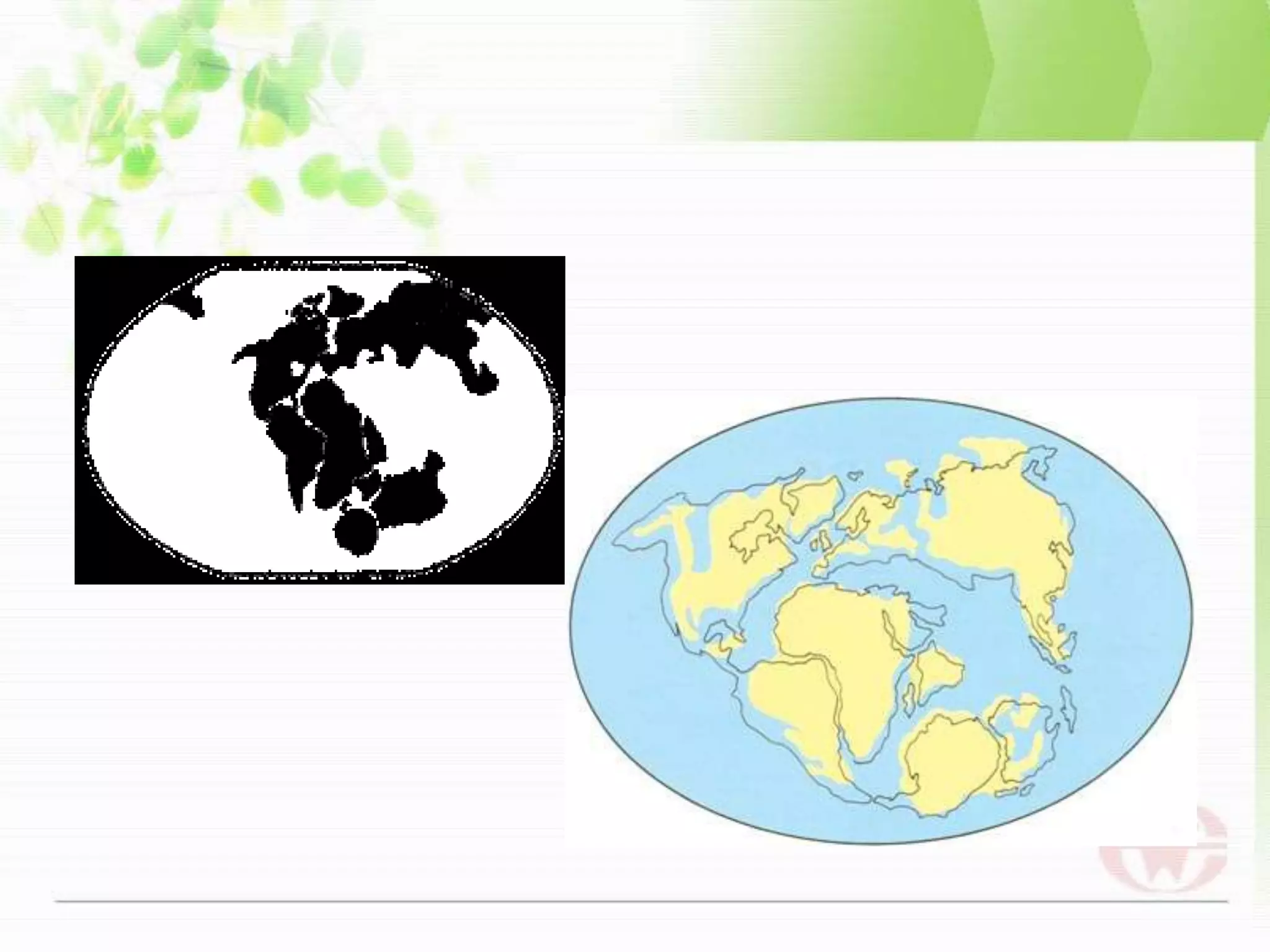
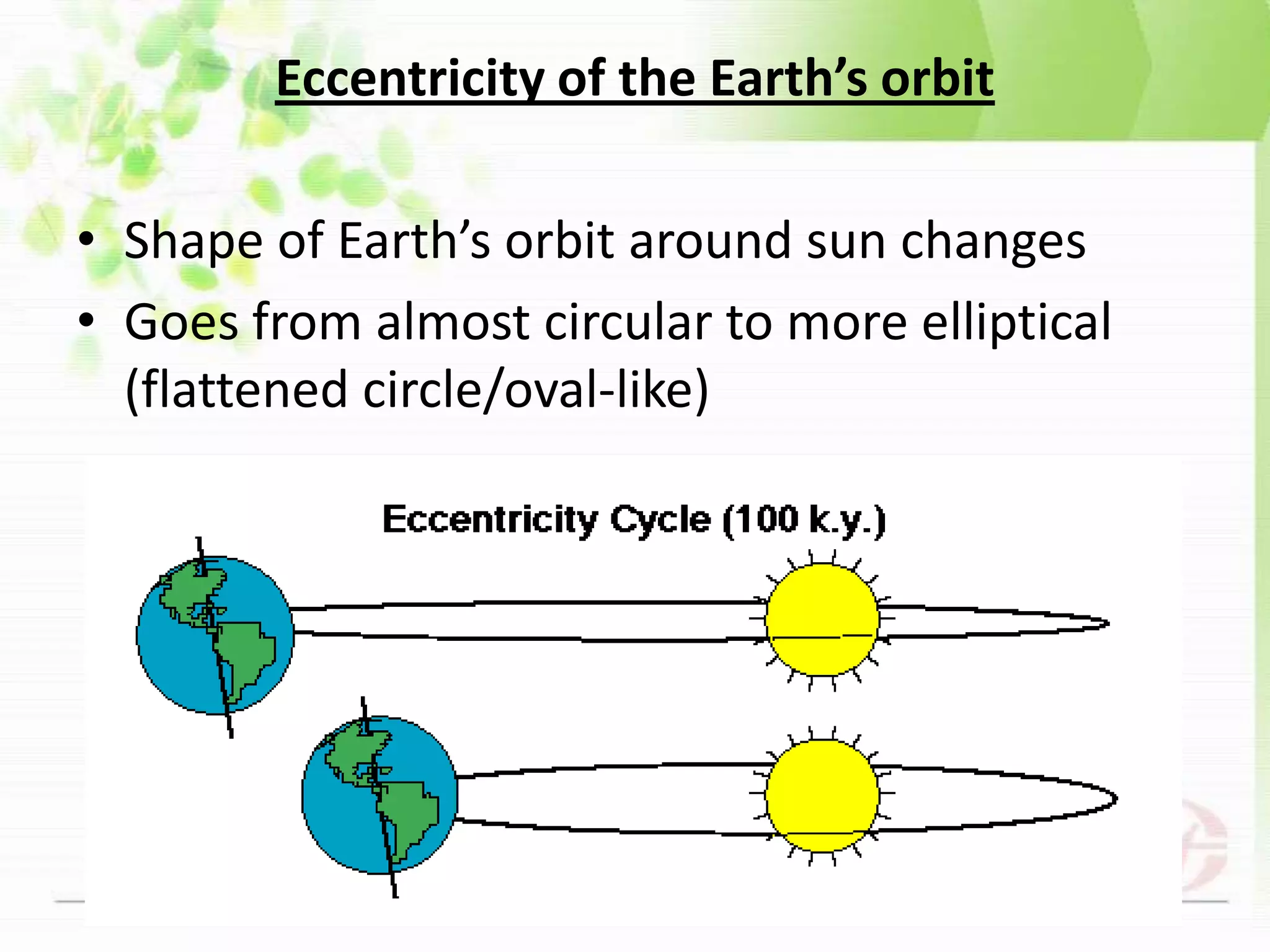
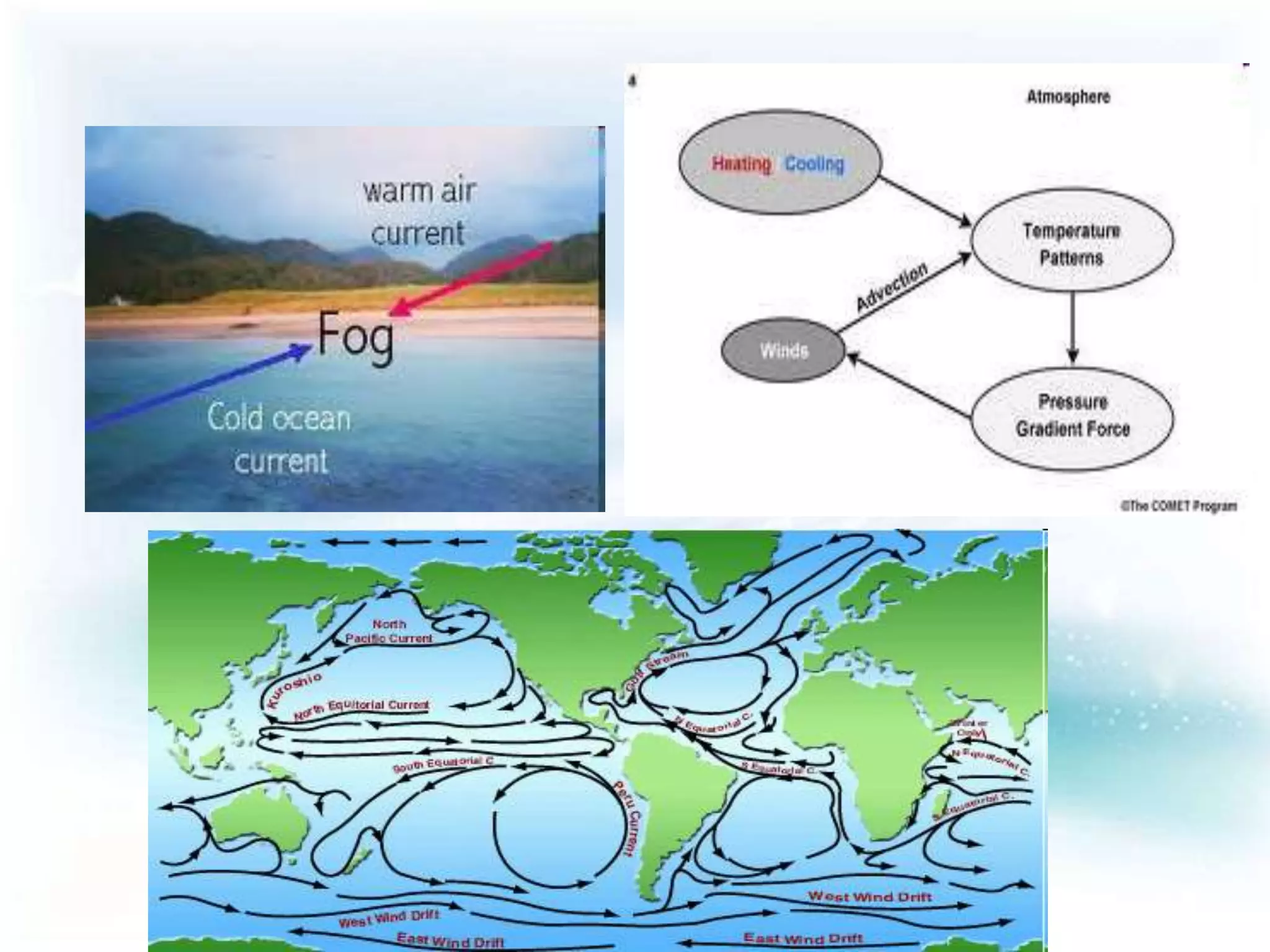
This document discusses both long-term and short-term causes of climate change. Long-term causes occurring over millions of years include continental drift, changes in Earth's orbit and tilt, which affect ocean currents and temperatures. Short-term causes operating over decades to thousands of years include volcanic eruptions, which eject particles that block sunlight, and shifts in ocean and air currents driven by wind and temperature changes. Together, these natural factors have triggered shifts between ice ages and warmer periods throughout Earth's history.