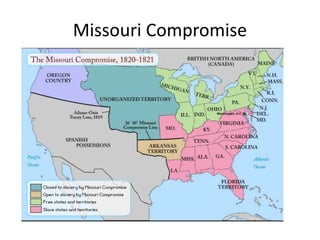
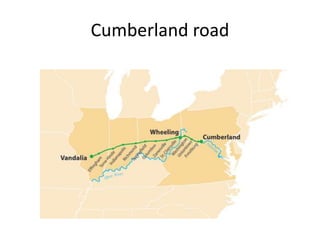
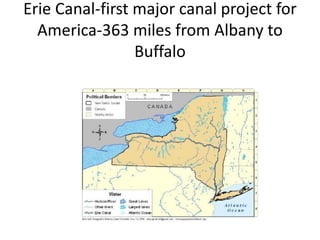
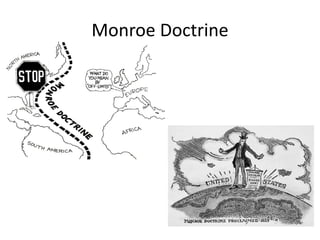
During the Era of Good Feelings from 1813-1824, both nationalism and sectionalism existed simultaneously in the United States. The Missouri Compromise of 1820 temporarily resolved the issue of the expansion of slavery but Thomas Jefferson predicted it would continue to divide the country along regional lines. At the same time, there was a political movement led by Henry Clay to promote economic nationalism through internal improvements, tariffs, and a national bank. Westward expansion also contributed to growth, but internal improvements faced opposition over constitutional authority. The Era of Good Feelings ended with the controversial 1824 presidential election and rise of the Democratic Party under Andrew Jackson.