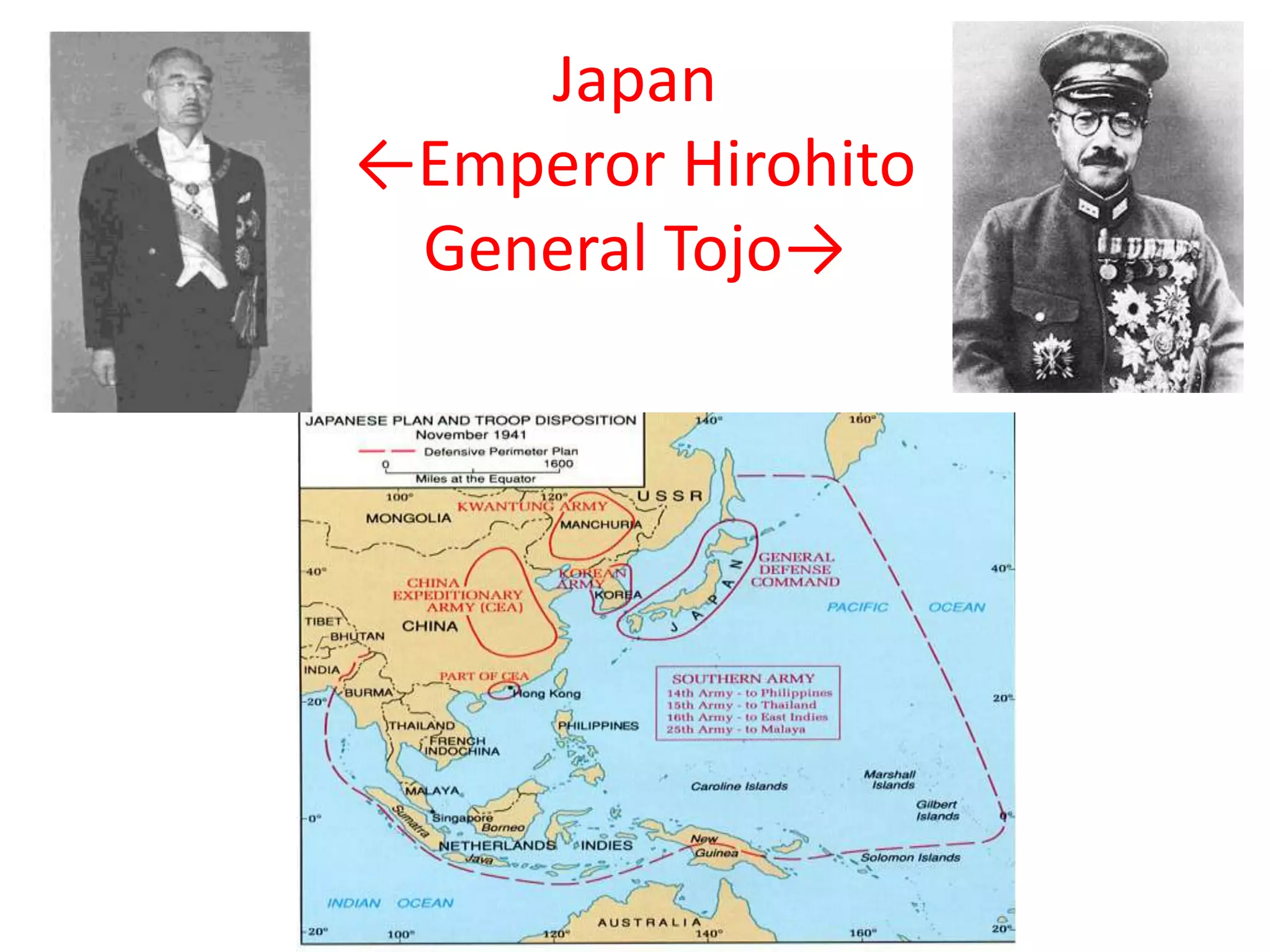
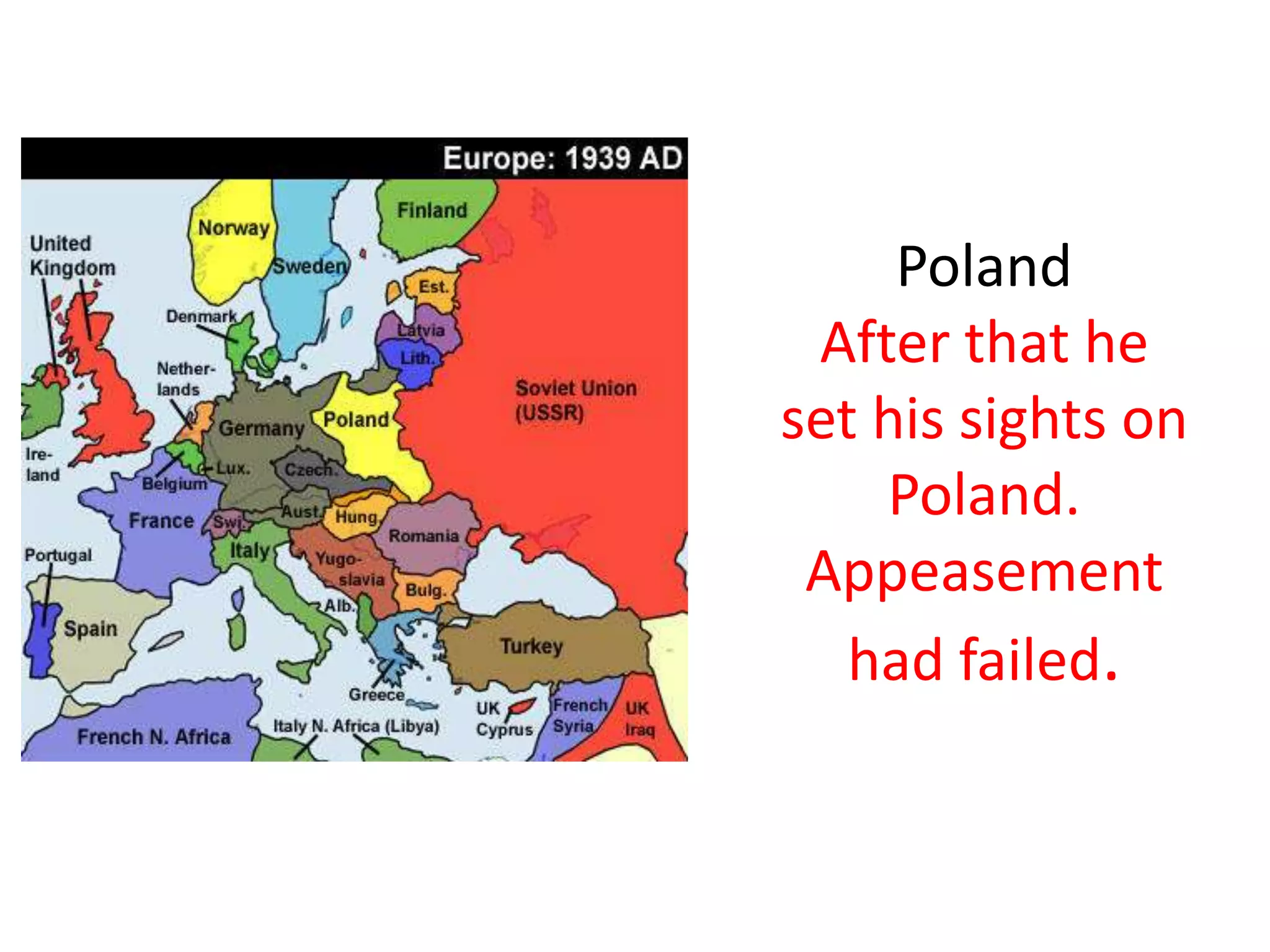
The document summarizes the rise of fascist and totalitarian regimes in Europe and Asia in the aftermath of WWI. It describes how leaders like Mussolini in Italy, Stalin in Russia, and Hitler in Germany rose to power amid economic struggles and unrest over territorial losses from WWI. Hitler violated the Treaty of Versailles and began invading neighboring countries like Austria and Czechoslovakia, prompting Britain and France to pursue a failed policy of appeasement. When Germany invaded Poland in 1939, Britain and France declared war on Germany, marking the start of World War II.