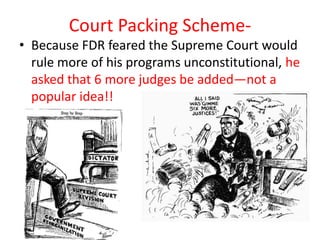
Franklin D. Roosevelt was elected president in 1932, promising a "New Deal" to address the Great Depression. His New Deal policies aimed to provide relief through immediate aid programs, promote recovery of the economy, and reform the financial system. FDR pushed many programs through Congress in his first 100 days, including the CCC to employ young men in conservation projects, the PWA to fund public works projects, and the AAA to support farmers. The New Deal expanded the role of the federal government and established programs and agencies like the SEC, FDIC, and Social Security.