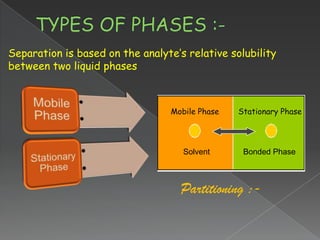
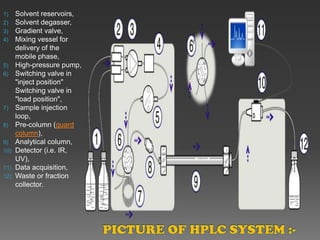
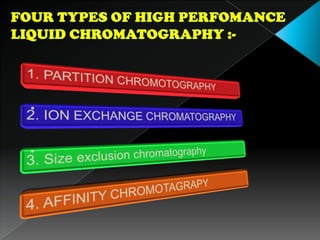
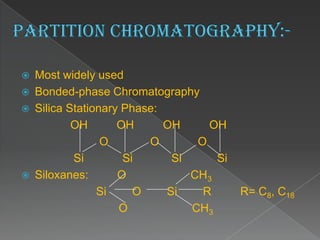
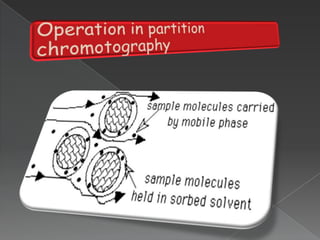
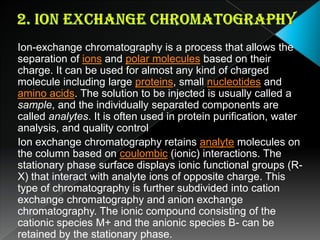
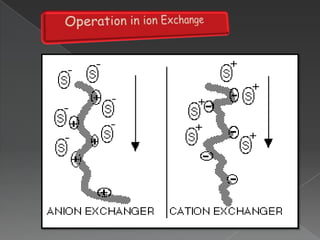
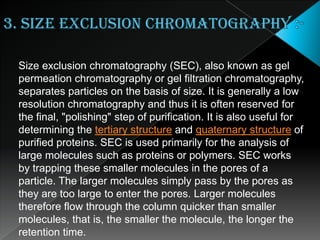
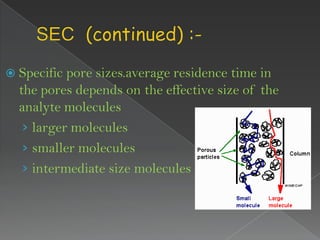
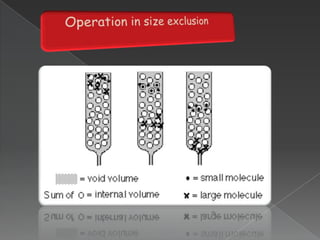
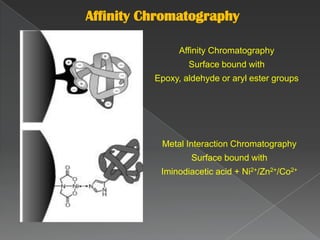
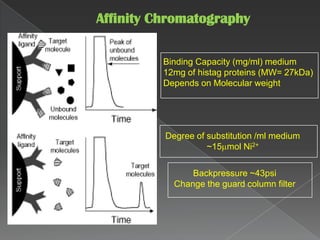
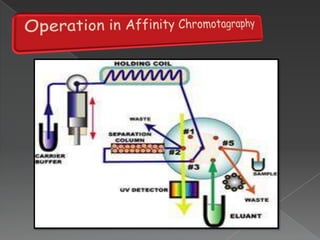
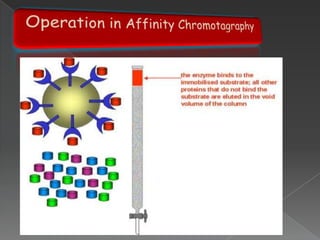
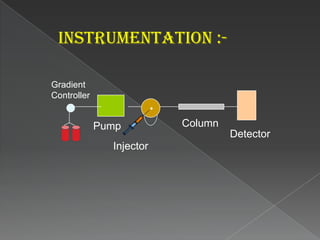
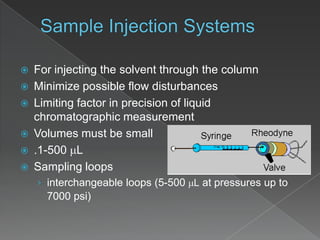
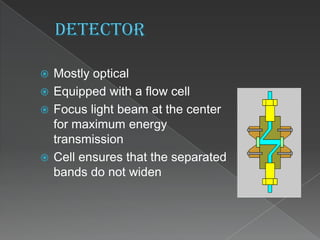
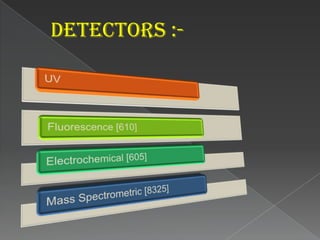
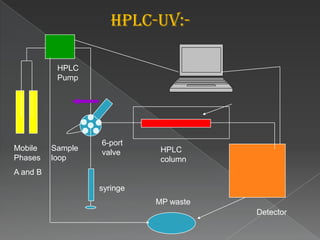
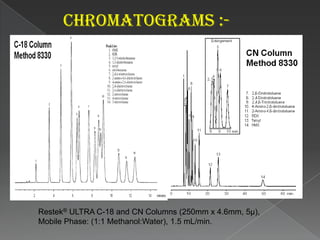
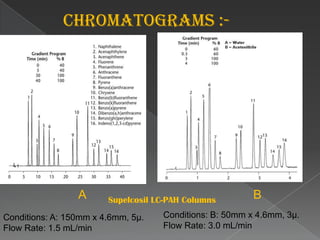
La cromatografía líquida de alto rendimiento (HPLC) es una técnica para separar compuestos disueltos en soluciones, utilizando diferentes fases líquidas y principios como la partición, intercambio iónico, exclusión por tamaño y afinidad. HPLC se emplea en investigación química, control de calidad y análisis de contaminantes, asegurando la pureza de compuestos. Se requiere un equipo especializado que incluye columnas, bombas y detectores para lograr separaciones precisas.