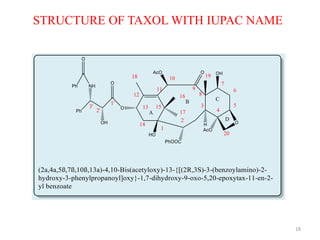
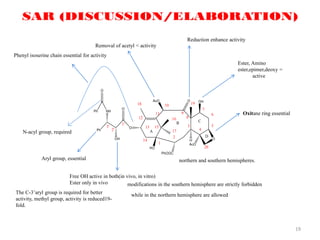
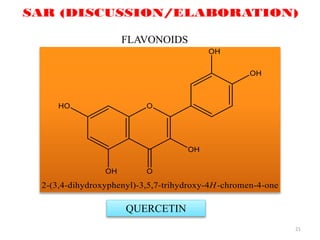
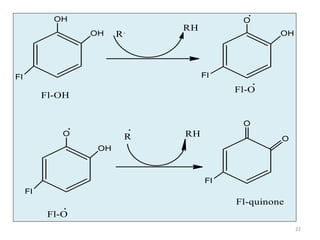
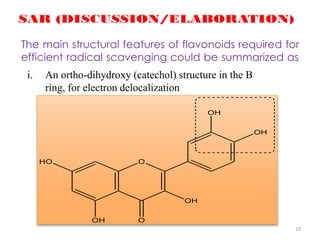
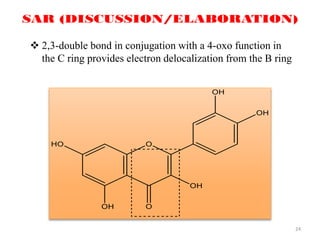
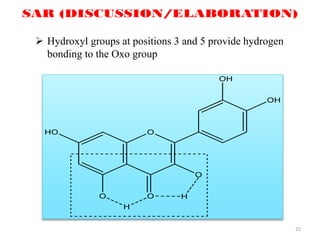
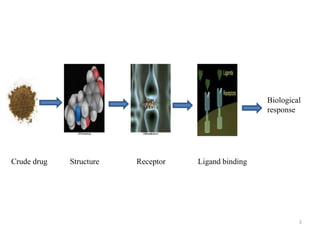
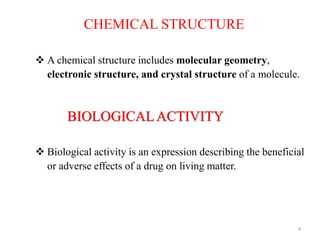
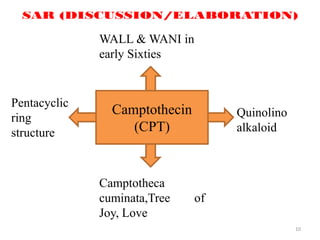
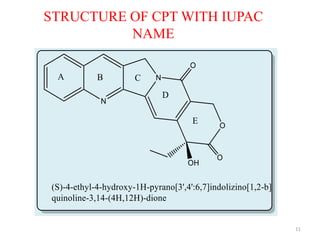
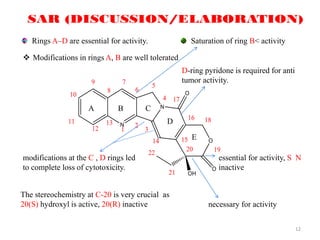
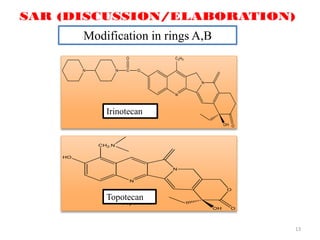
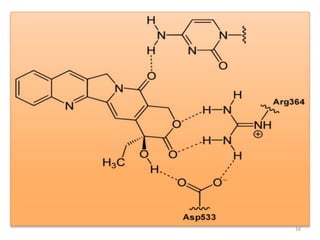
This document discusses structure-activity relationships (SAR) through examples of different drug molecules. It provides details on the chemical structures of camptothecin (CPT), taxol, and the flavonoid quercetin and how specific structural features relate to their biological activities. For CPT, rings A-D and the stereochemistry at C-20 are essential for anti-tumor activity, while modifications to rings C and D eliminate activity. The ester linkage and phenylisoserine chain of taxol are required for its anticancer effects. For flavonoids like quercetin, features important for radical scavenging include a catechol structure in ring B and hydroxyl groups that enable hydrogen bonding and electron de







![17
TAXOL
Taxol, paclitaxel, trade name taxol,
by Dr. WALL and Dr. WANI
Complex
polyoxygenated
diterpenoid
Pacific yew, Taxus
brevifolia
basic [9.3.1.0]
Pentadecane, tetracyclic
ring system.
N-benzoyl-b-phenyl
isoserine side chain, at
the C-13 hydroxyl as an
ester linkage.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureactivityrelationship6-150124020043-conversion-gate01/85/Structure-activity-relationship-6-17-320.jpg)