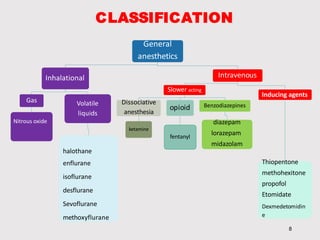
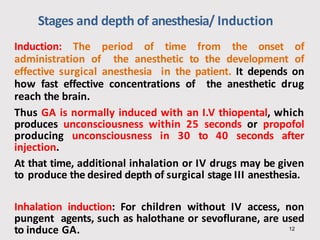
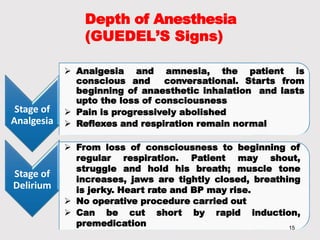
General anesthetics provide amnesia, analgesia, muscle relaxation and sedation, placing the patient in a reversible state of unconsciousness. There are inhalational agents like nitrous oxide, halothane, enflurane and isoflurane, and intravenous agents like propofol, ketamine and thiopental. They work mainly by enhancing the effect of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA at GABAA receptors. Different agents have advantages and disadvantages related to their potency, metabolism, effects on vital organs and side effects. Careful selection of agents and monitoring is required for safe anesthesia.