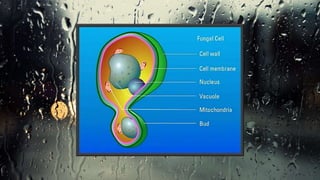
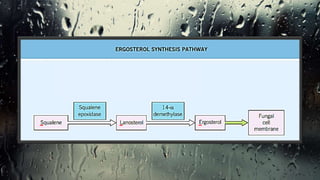
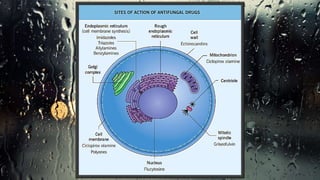
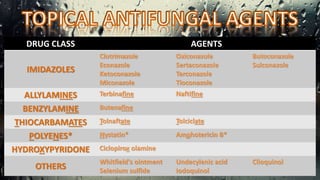
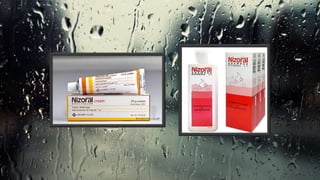
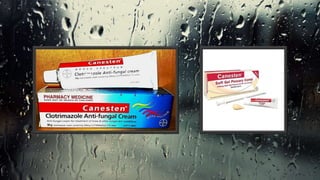
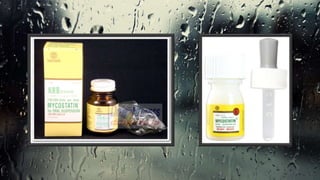
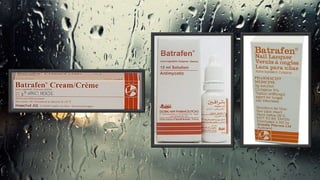
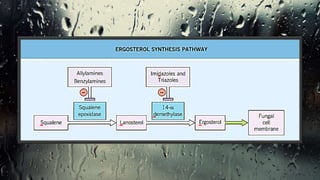
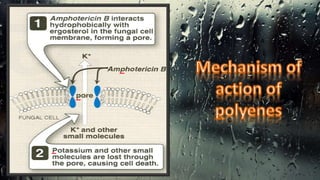
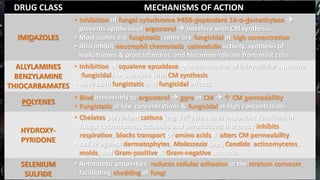
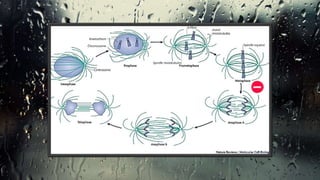
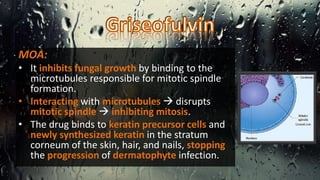
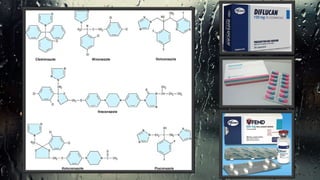
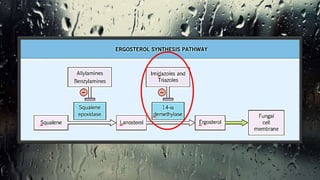
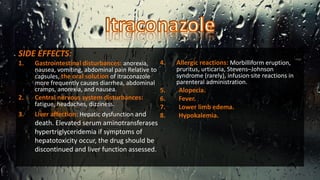
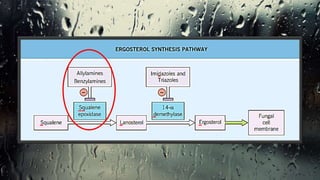
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms with complex structures that differ from bacteria, including a chitin-based cell wall and unique membrane components. Various antifungal agents target different aspects of fungal biology, such as cell membrane synthesis and permeability, with some effective for superficial infections and others necessary for systemic conditions. Drug treatments can vary based on the infection type, patient condition, and drug mechanisms, with emerging concerns about safety and side effects of specific agents.