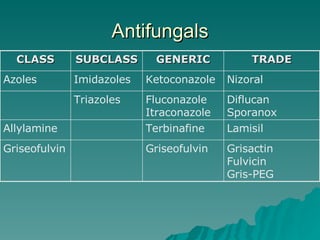
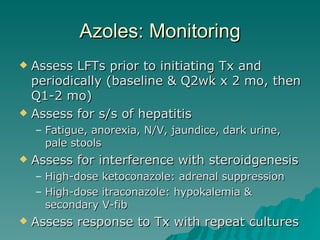
This document discusses antifungal treatment options for both superficial and systemic fungal infections. It covers several classes of antifungals including azoles like fluconazole, itraconazole, and ketoconazole as well as other drugs like terbinafine, griseofulvin. It provides details on indications, pharmacokinetics, drug interactions, monitoring parameters, and adverse effects for common antifungal therapies.