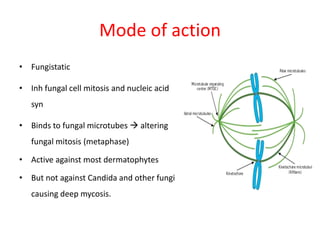
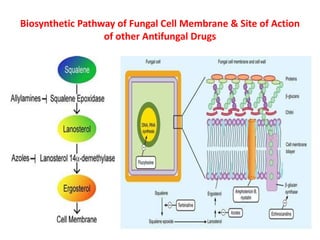
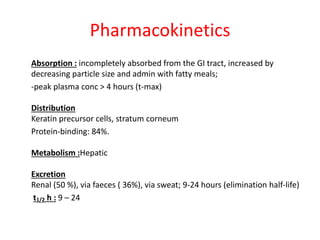
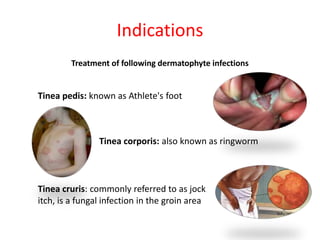
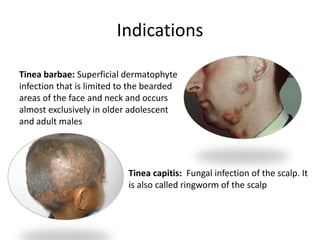
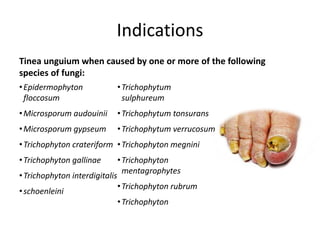
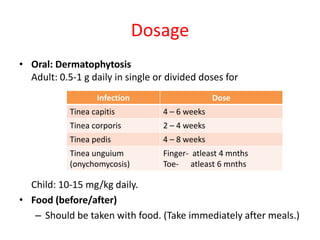
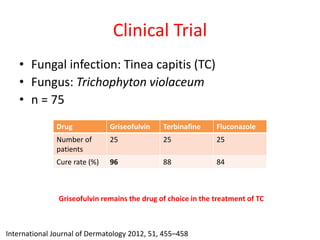
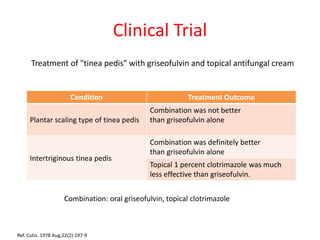
Griseofulvin is an antifungal antibiotic produced by the fungus Penicillium griseofulvum. It works by inhibiting fungal cell mitosis and nucleic acid synthesis. It is indicated for several types of dermatophyte infections including ringworm, athlete's foot, jock itch, and nail fungus. Griseofulvin is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and distributed to keratin-containing tissues. It has a long half-life of 9-24 hours. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and photosensitivity. Clinical trials have shown griseofulvin to be effective against tinea capitis and tinea pedis, though a topical antifungal may provide