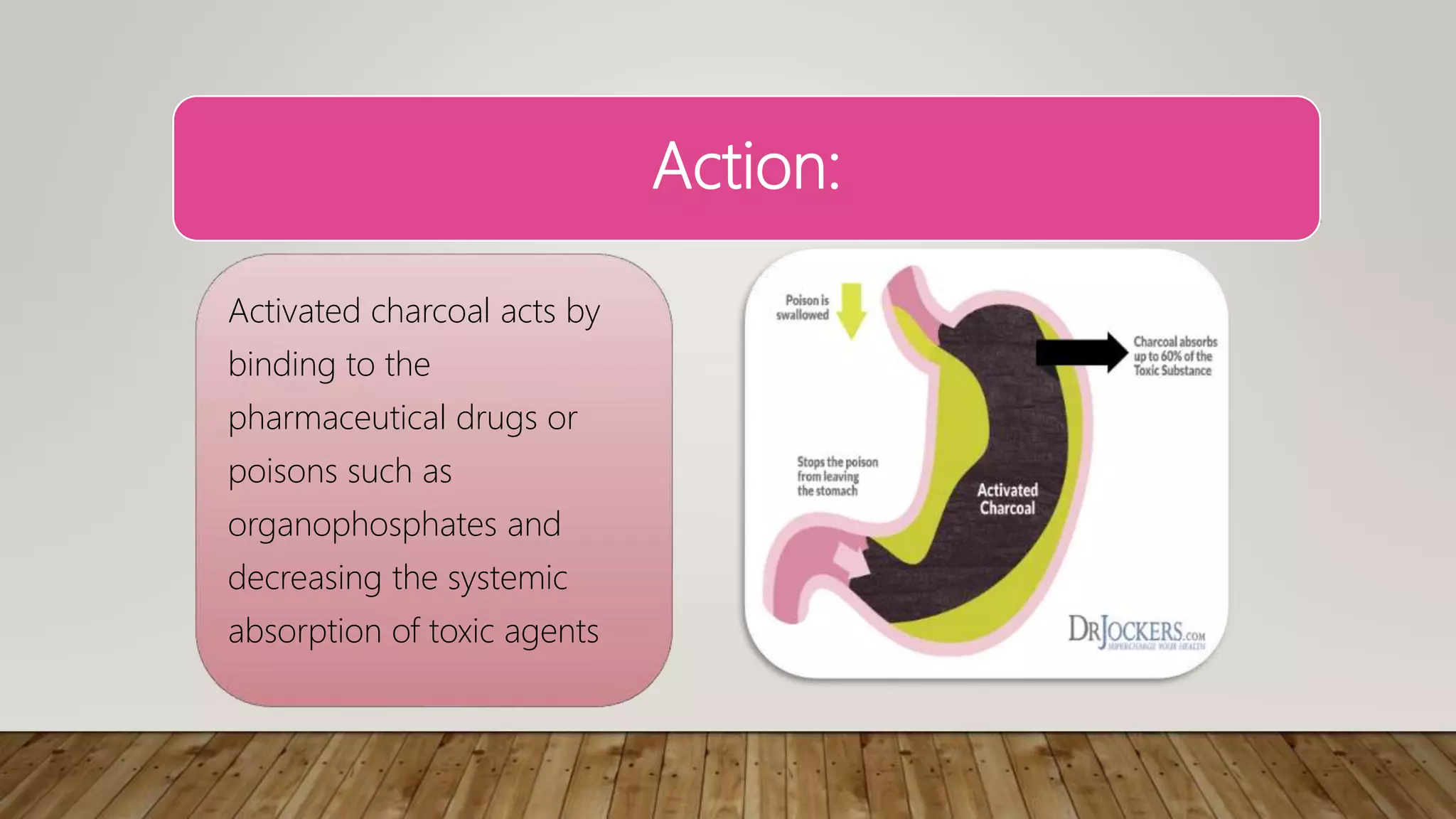
Activated charcoal is a universal antidote used to prevent systemic absorption of drugs when administered within 1-2 hours of ingestion. It acts by binding to pharmaceutical drugs and poisons in the gastrointestinal tract to decrease absorption. The optimal dose is a 40:1 ratio of charcoal to drug. It is contraindicated for some overdoses like iron, lithium, and ethanol. When administering activated charcoal, it is important to monitor the patient for side effects like vomiting or black stools and educate them that stools will turn black after use.