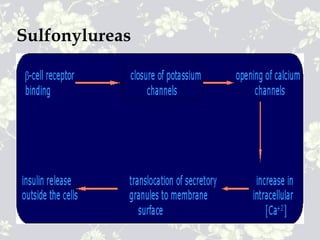
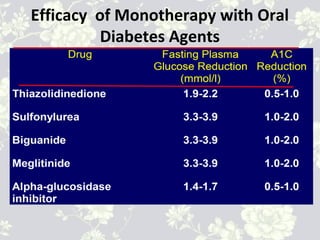
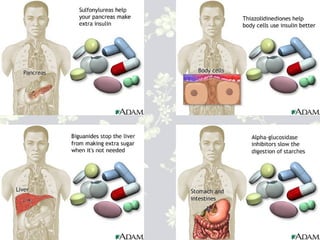
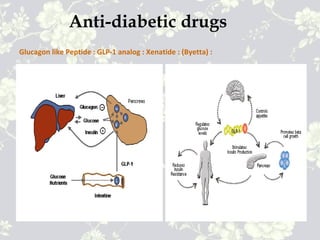
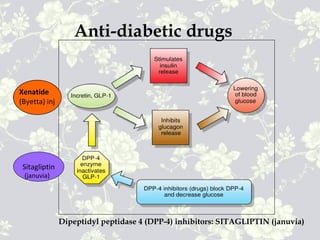
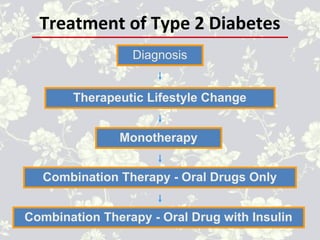
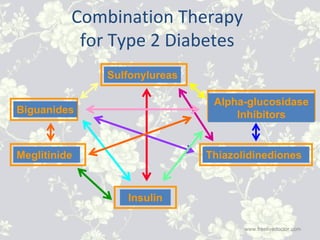
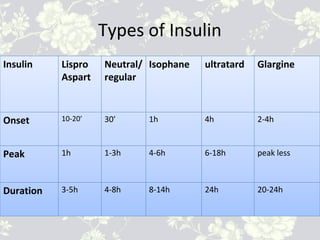
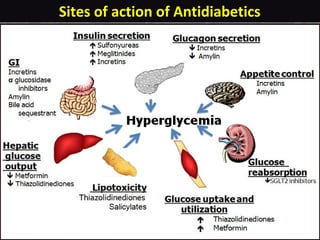
This document provides an overview of antidiabetic agents including insulin and oral medications used to treat type 2 diabetes. It discusses the aims of diabetes management including achieving near-normal glycemia to prevent short and long-term complications. It then describes the types of insulin including rapid, short, intermediate and long-acting varieties. The document also summarizes the classes of oral medications including their mechanisms of action, efficacy, side effects and examples of drugs from each class. Combination therapy approaches are briefly outlined.











![• Other Effects
– Weight gain, oedema
– Hypoglycemia (if taken with insulin or agents that
stimulate insulin release)
– Improves HDL cholesterol and plasma triglycerides ;
usually LDL neutral
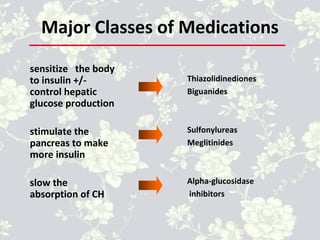
• Medications in this Class: pioglitazone (Actos),
rosiglitazone (Avandia), troglitazone (Rezulin) - taken
off market due to liver toxicity]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/022600235910antidiabeticagents-170225174457/85/Antidiabetic-agent-18-320.jpg)