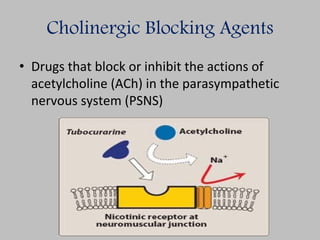
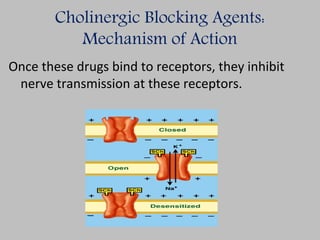
This document discusses cholinergic antagonist agents, which block the actions of acetylcholine in the parasympathetic nervous system. It describes their uses in conditions like myasthenia gravis and drug overdoses. The document outlines the agents' mechanisms of action as competitive antagonists that bind muscarinic receptors. It also details their therapeutic uses in treating conditions of the CNS, cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal and genitourinary systems. Potential side effects and interactions are presented.