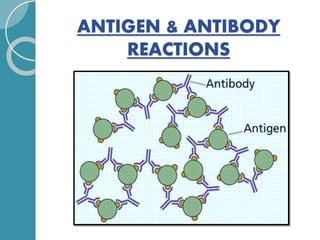
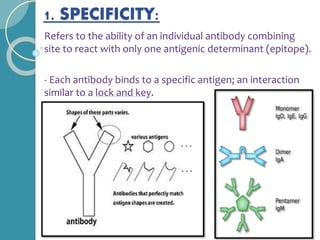
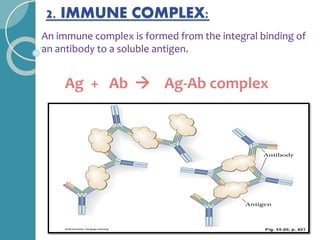
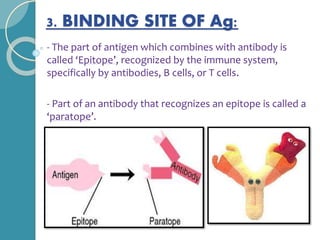
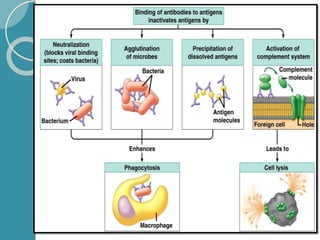
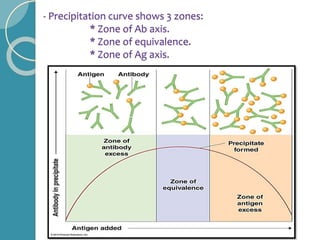
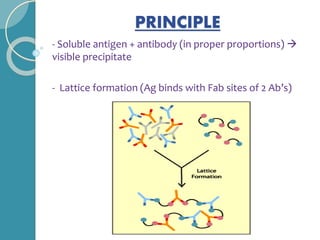
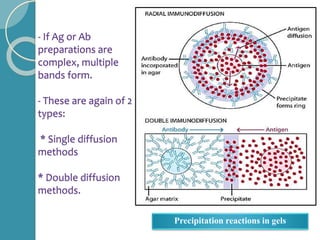
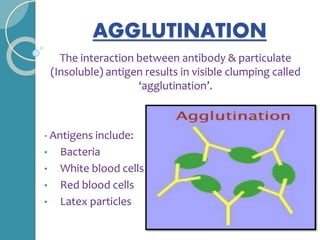
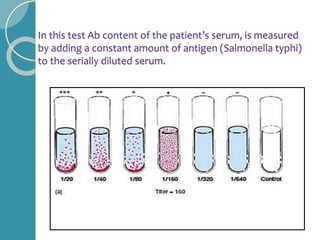
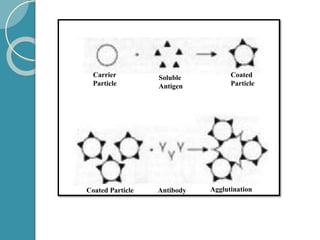
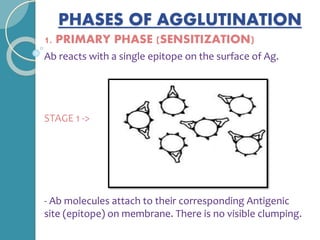
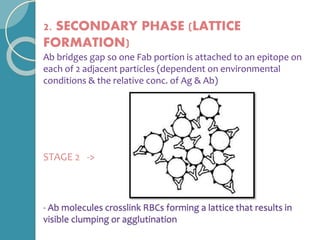
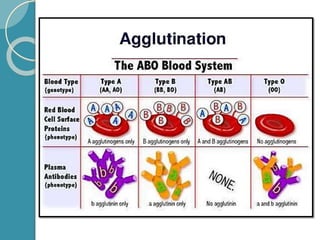
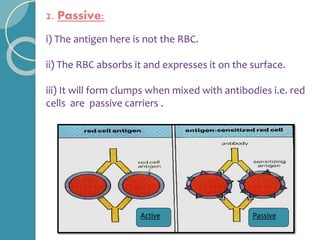
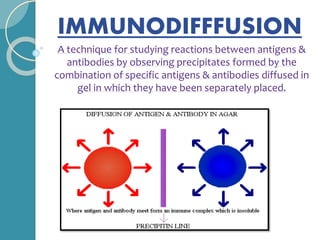
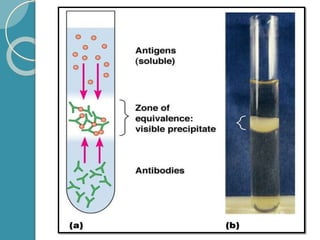
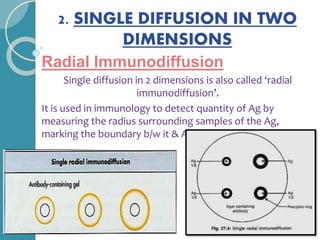
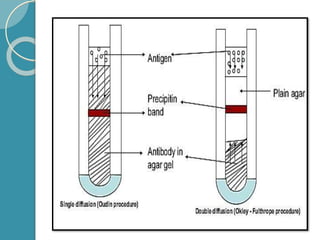
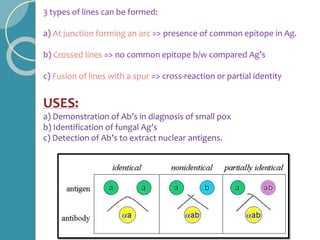
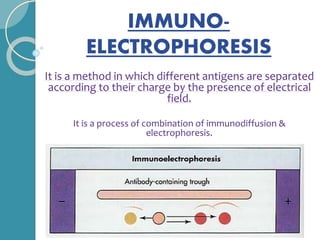
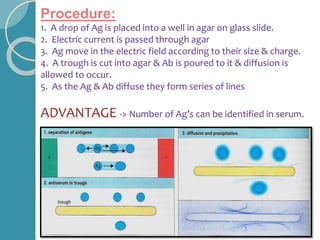
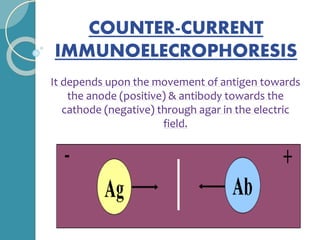
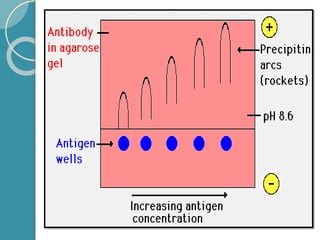
The document discusses antigen-antibody reactions. It begins by introducing antigens and antibodies and how they specifically combine in antigen-antibody reactions. The reactions occur in three stages: formation of an antigen-antibody complex, leading to visible events like precipitation or agglutination, and destruction or neutralization of the antigen. Key features of antigen-antibody reactions are their specificity, the formation of immune complexes, antigen binding sites called epitopes, and the binding force between antigens and antibodies. Common types of antigen-antibody reactions include precipitation, agglutination, complement fixation, ELISA, and immunofluorescence.