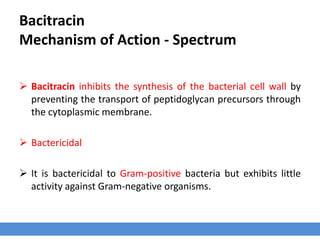
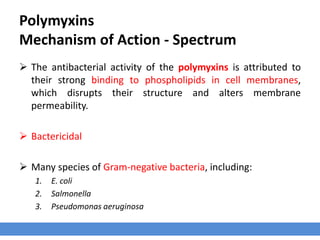
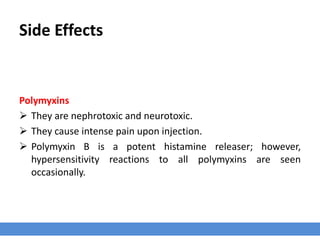
The polypeptides antibiotics group includes bacitracin A, colistin, novobiocin, and polymyxin B. Bacitracin inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis while polymyxins disrupt cell membranes. Bacitracin is effective against gram-positive bacteria but not gram-negatives. Polymyxins are effective against many gram-negative species like E. coli and Pseudomonas. Resistance can develop to bacitracin and novobiocin but is rare for polymyxins. Bacitracin is used to improve growth and feed efficiency in livestock while novobiocin treats mastitis in dairy cattle. However, polymyxins are nephrotoxic,