The document discusses several key concepts related to culture:
- Culture is learned, shared, and symbolic. It provides rules and meaning systems that are distinct from biological instincts.
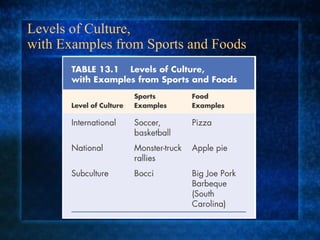
- Culture is integrated and adaptive. Changes in one aspect of culture can influence other aspects as the culture aims to maintain equilibrium.
- Theories of culture include cultural materialism, which sees culture as adapting to the environment, and symbolic theories, which see culture as systems of meaning and symbols.