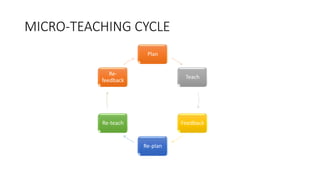
Micro-teaching is a teacher training technique developed by Dwight Allen at Stanford University in the 1960s. It involves teaching a short lesson to a small group of 5-10 students while being observed. The lesson is then followed by feedback to help the teacher improve specific teaching skills. Some key skills practiced through micro-teaching include introducing a lesson, using examples, questioning techniques, and reinforcement. The micro-teaching process follows a cycle of planning, teaching, receiving feedback, re-planning, and re-teaching to refine skills. It allows teacher trainees to learn and practice new skills in a low-stakes environment before student teaching.