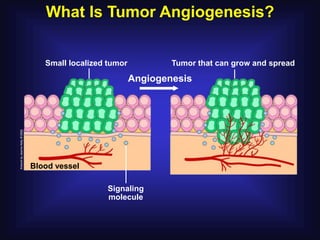
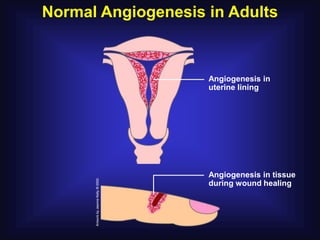
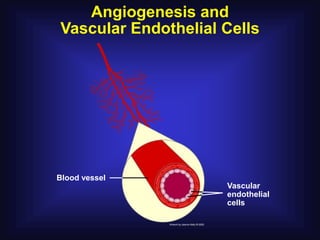
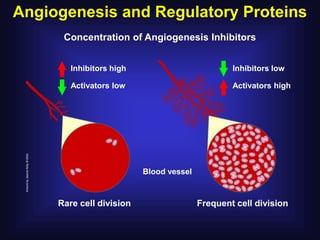
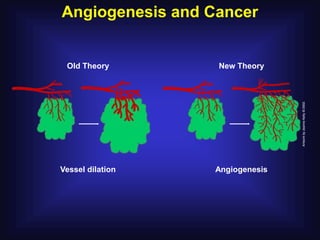
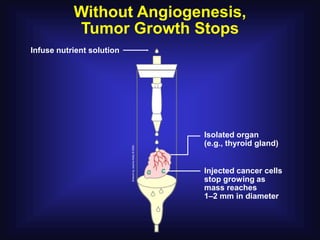
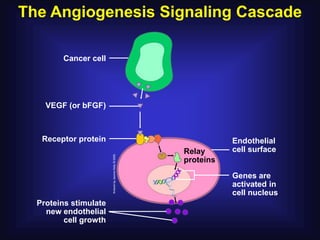
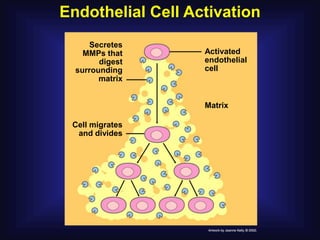
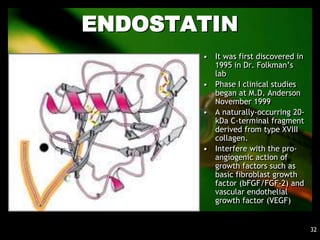
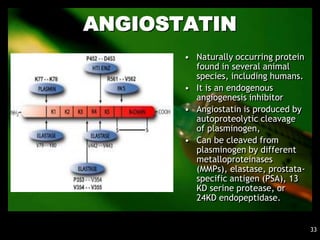
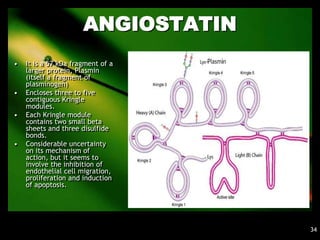
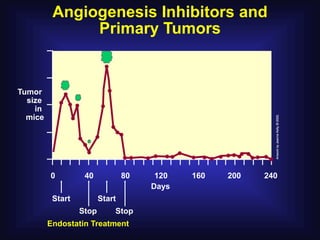
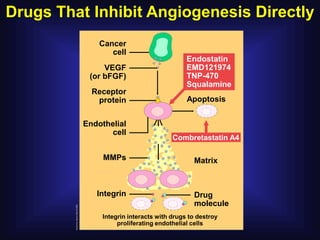
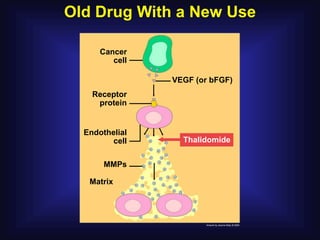
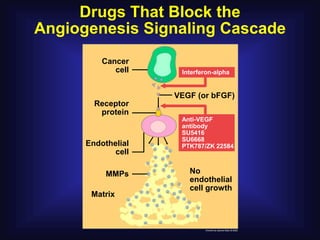
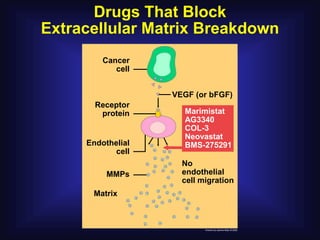
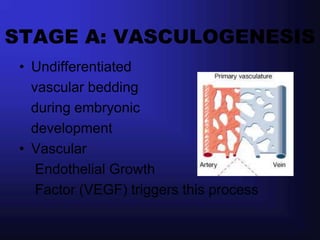
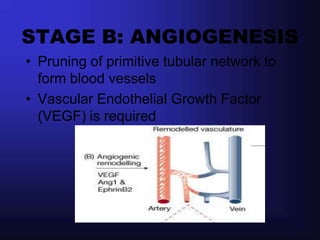
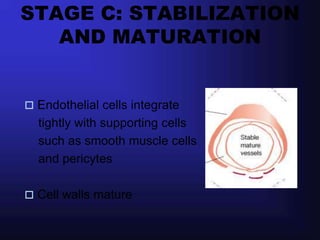
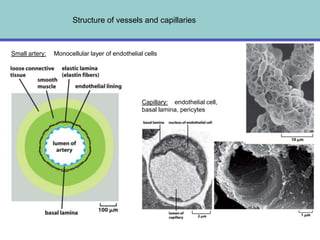
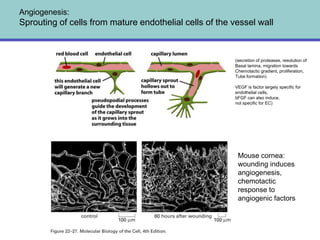
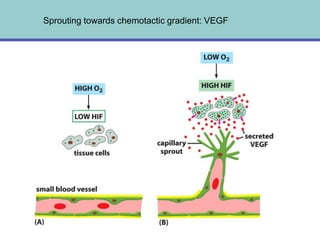
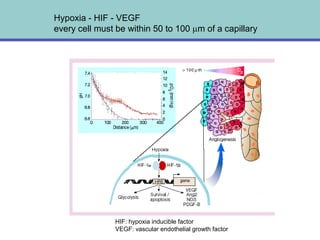
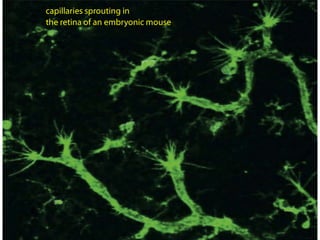
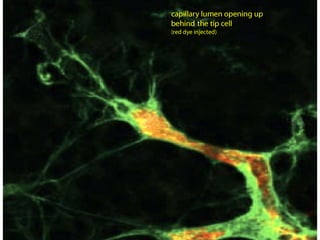
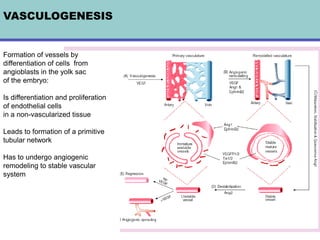
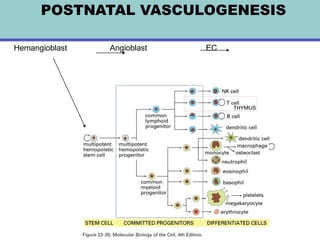
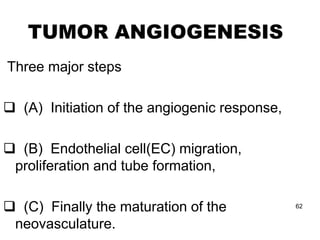
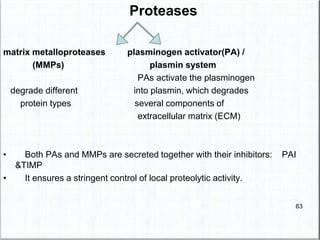
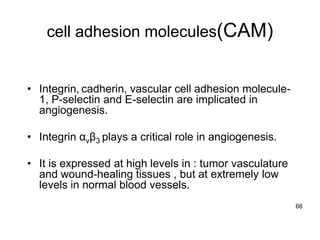
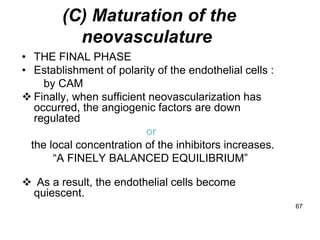
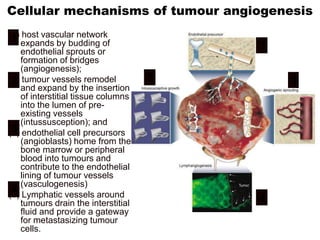
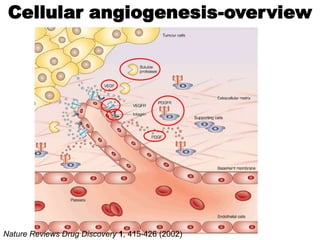
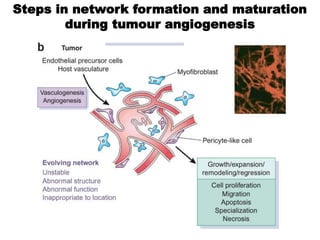
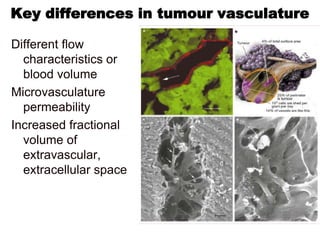
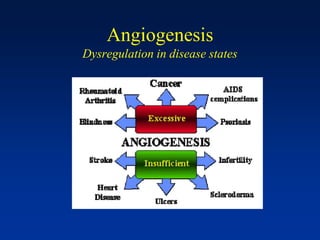
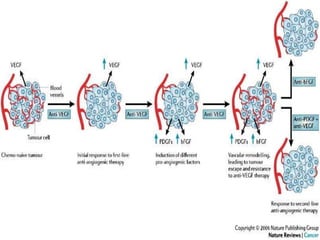
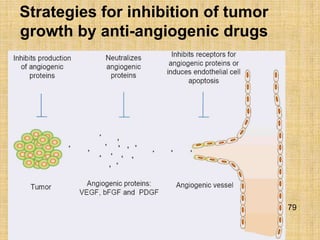
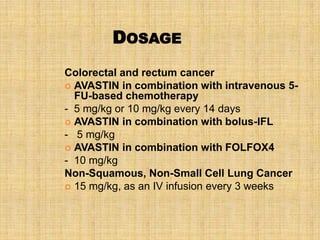
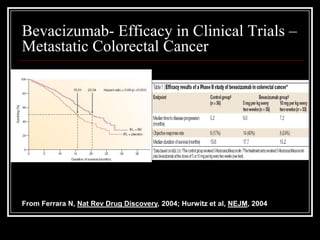
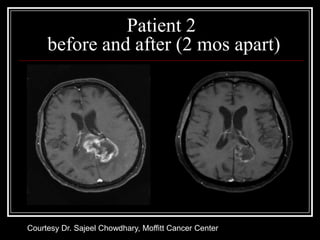
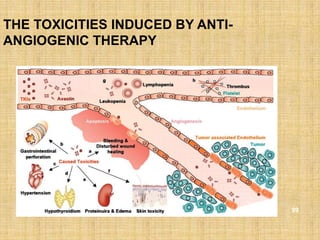
1. Angiogenesis is the process of forming new blood vessels from pre-existing vessels.
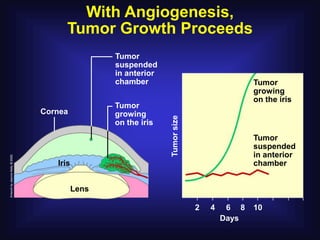
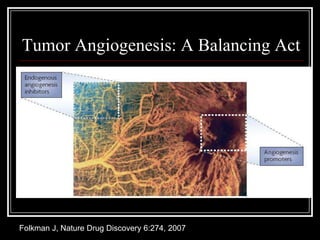
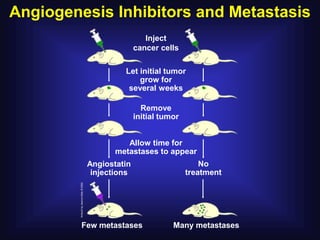
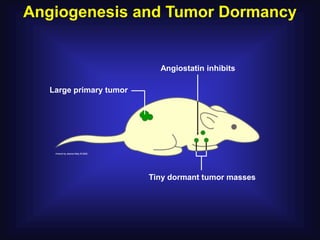
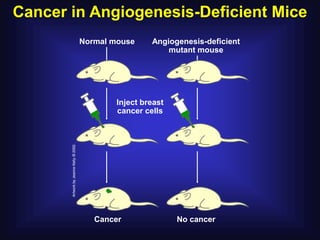
2. In 1971, Dr. Judah Folkman hypothesized that tumor growth depends on angiogenesis and published this theory, which was initially rejected.
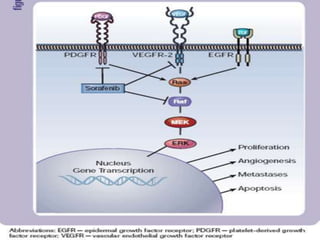
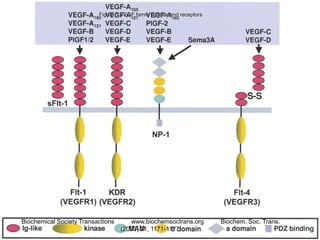
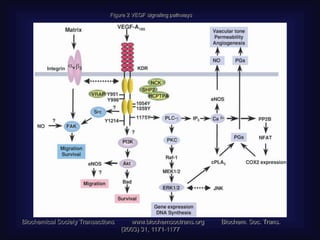
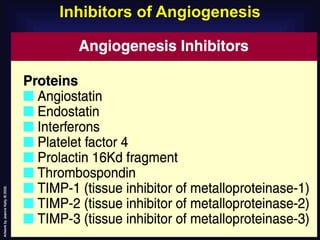
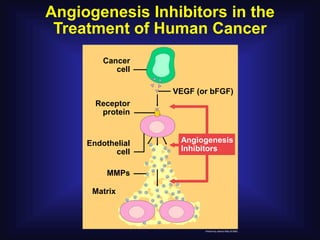
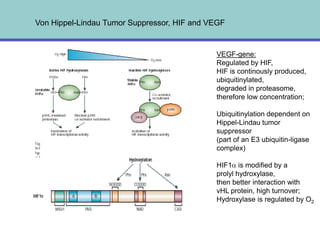
3. Since the 1970s, many important discoveries have been made regarding angiogenic factors like VEGF and angiogenesis inhibitors.