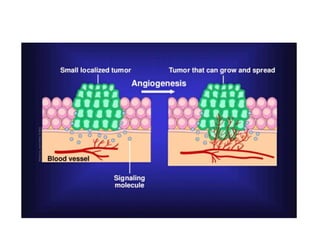
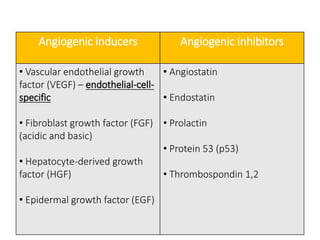
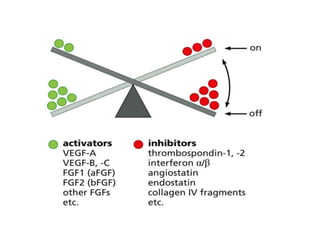
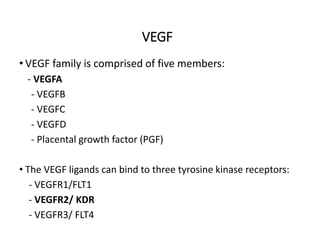
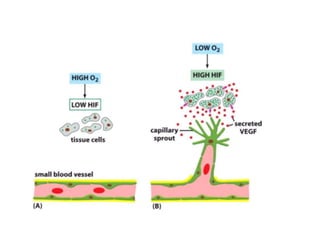
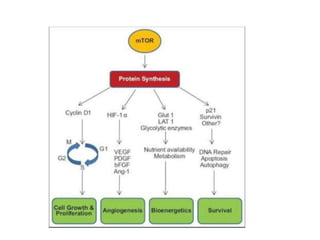
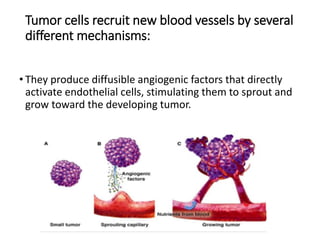
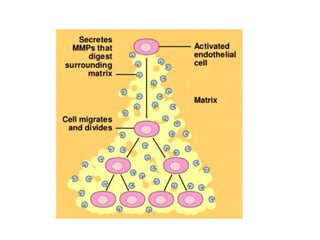
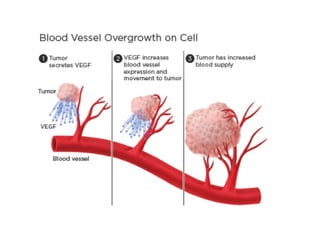
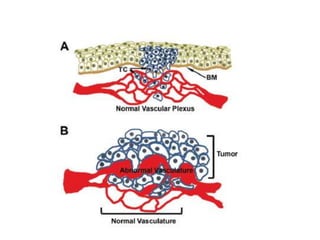
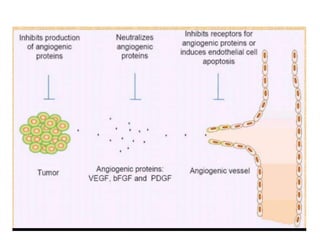
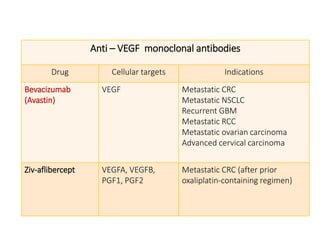
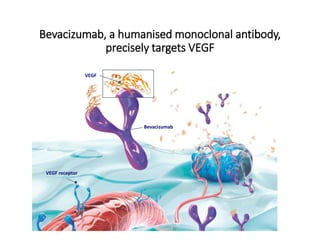
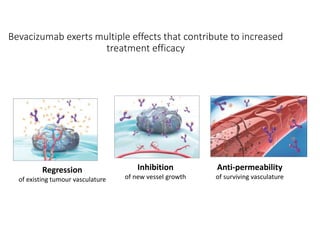
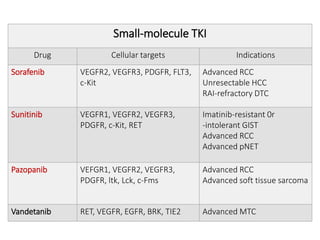
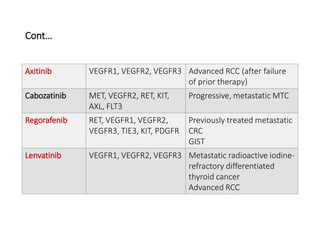
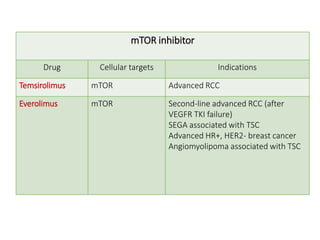
Tumor growth requires angiogenesis to develop new blood vessels. This process is regulated by a balance of pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors. Tumors disrupt this balance by inducing hypoxia and secreting factors like VEGF, which activate the "angiogenic switch" and promote new vessel growth. This allows tumors to recruit blood vessels to supply nutrients and remove waste. Anti-angiogenic therapies aim to block this process by targeting VEGF and its receptors. Drugs like bevacizumab and sorafenib inhibit angiogenesis to limit tumor growth and progression.