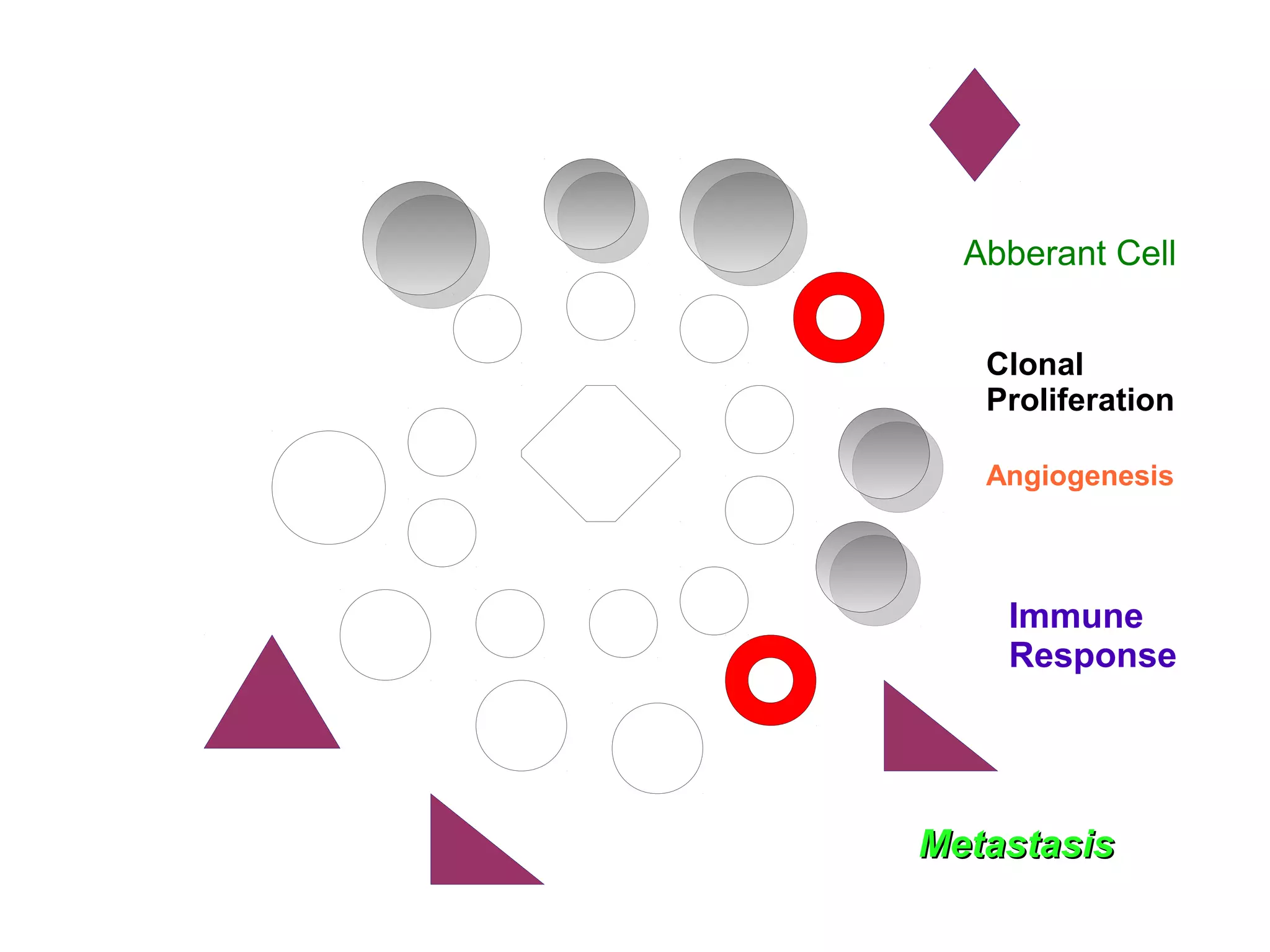
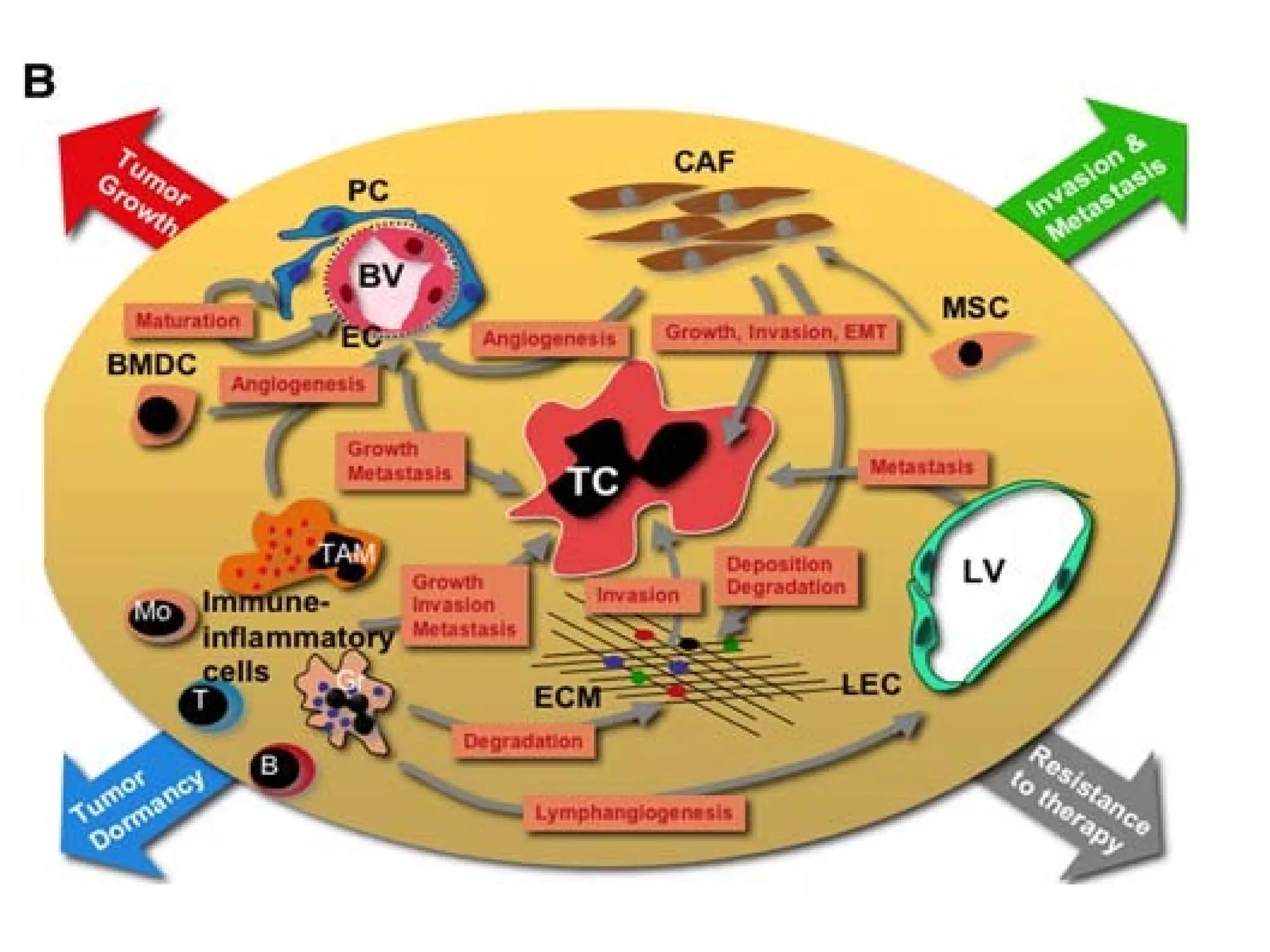
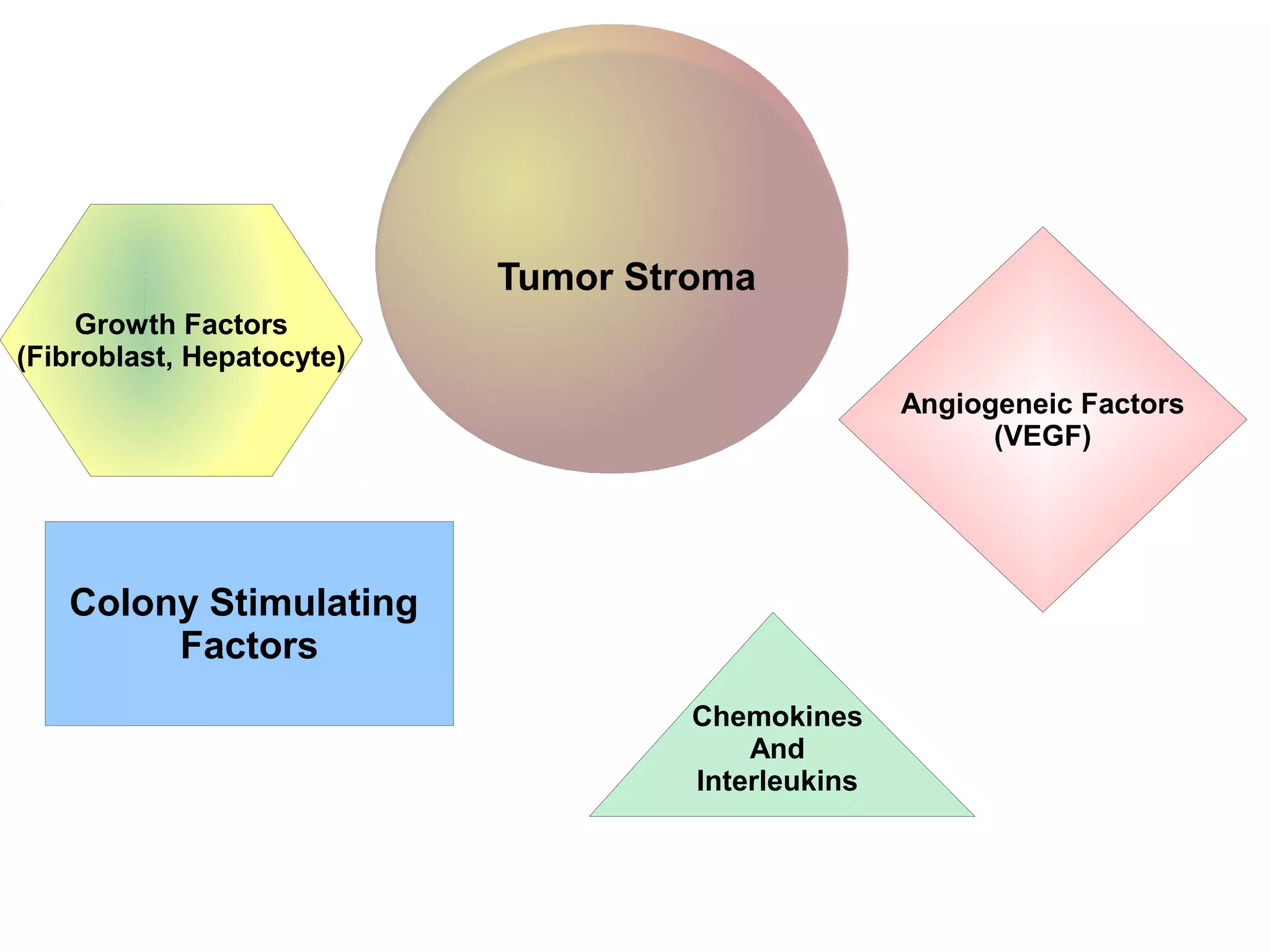
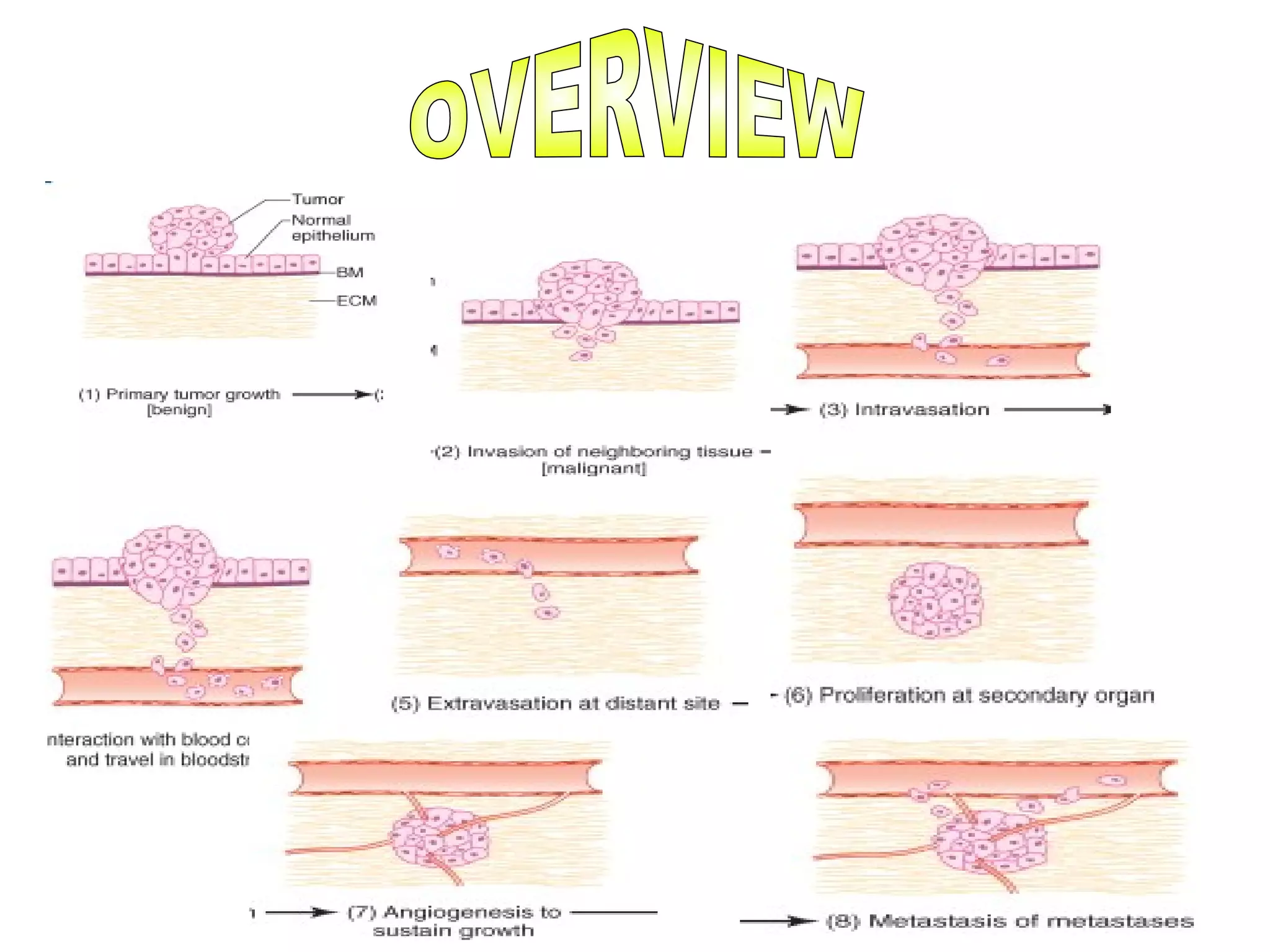
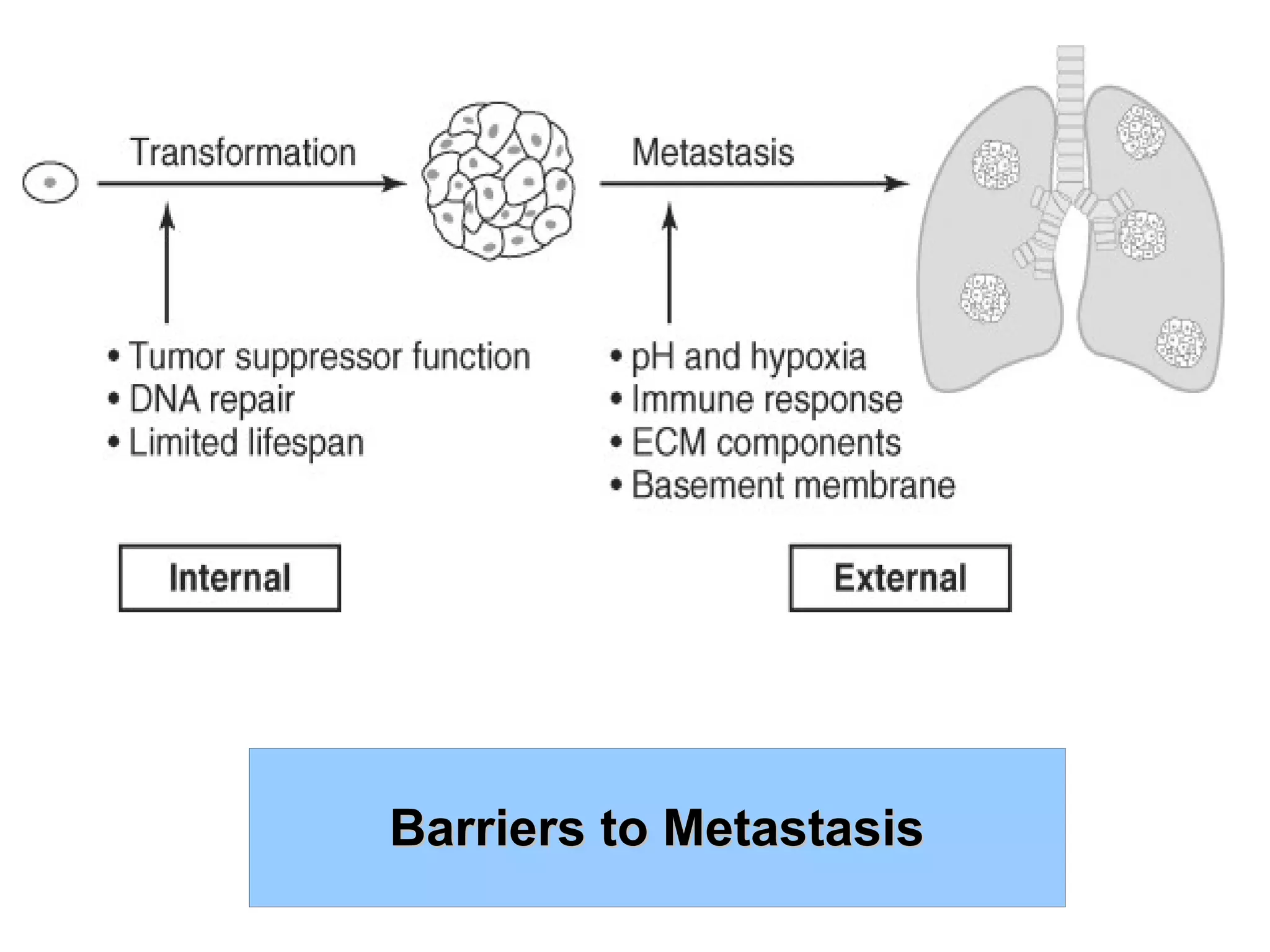
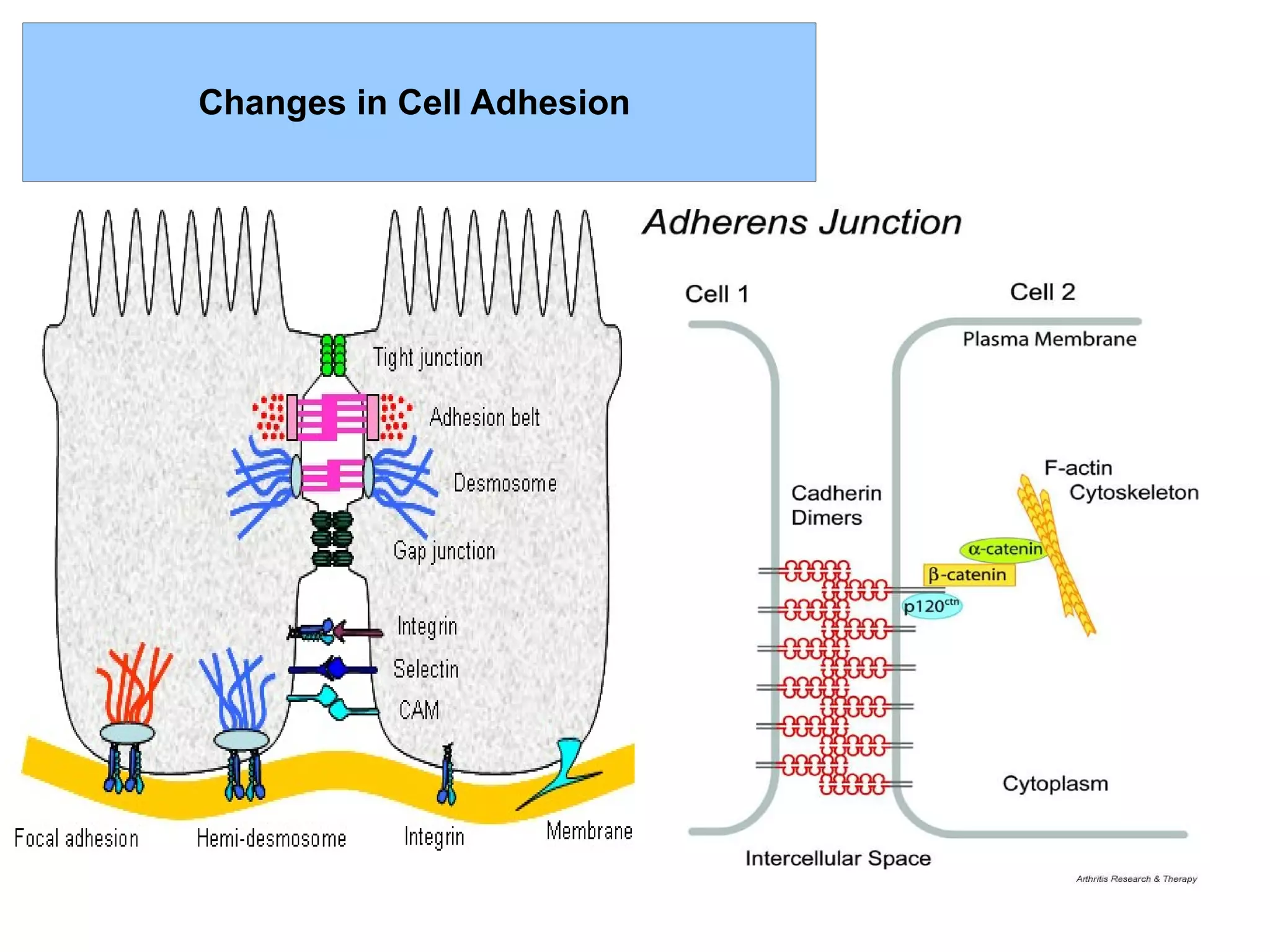
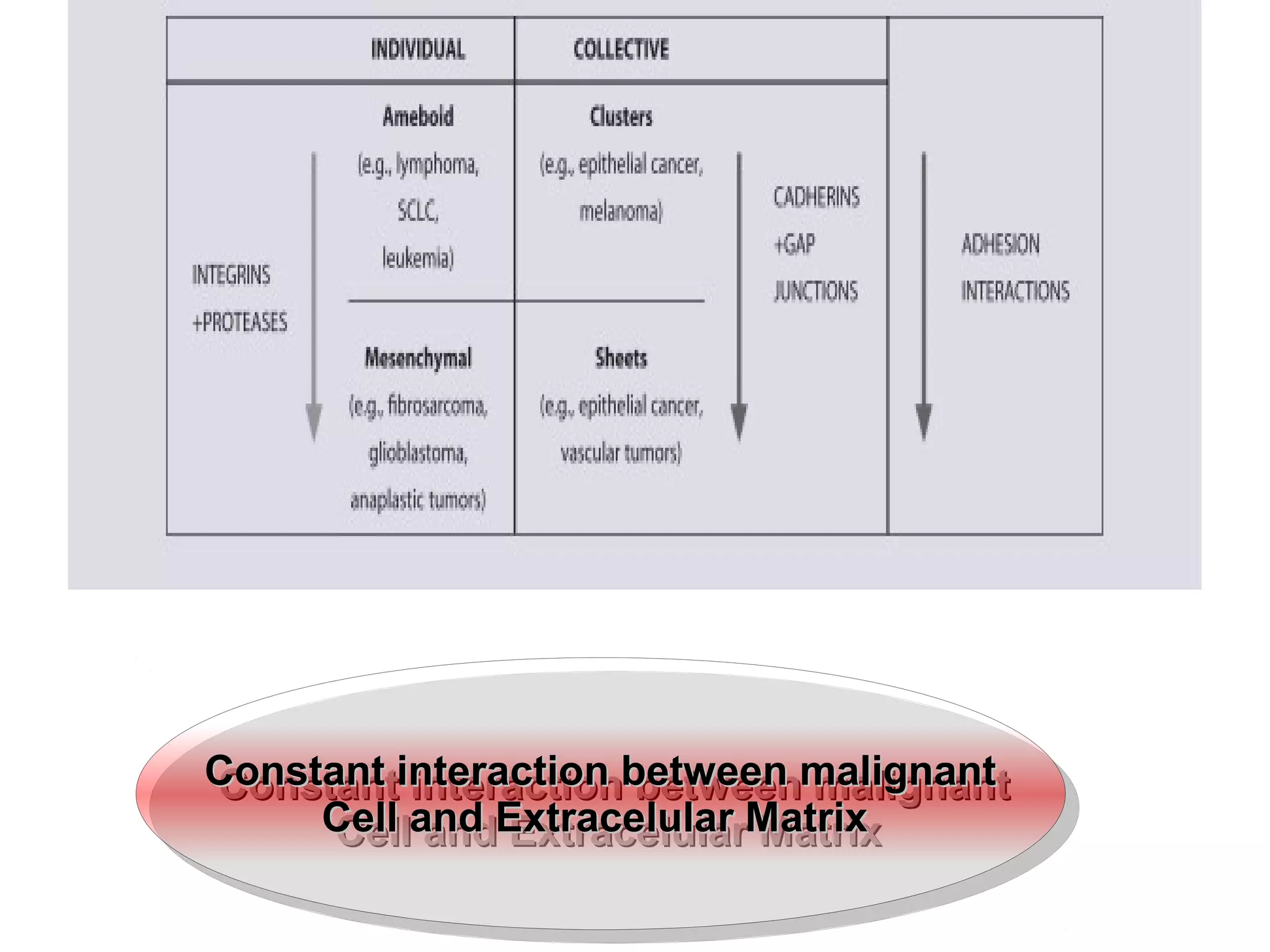
1) Tumors exist within a complex microenvironment consisting of various cell types that influence tumor growth, progression, and metastasis.
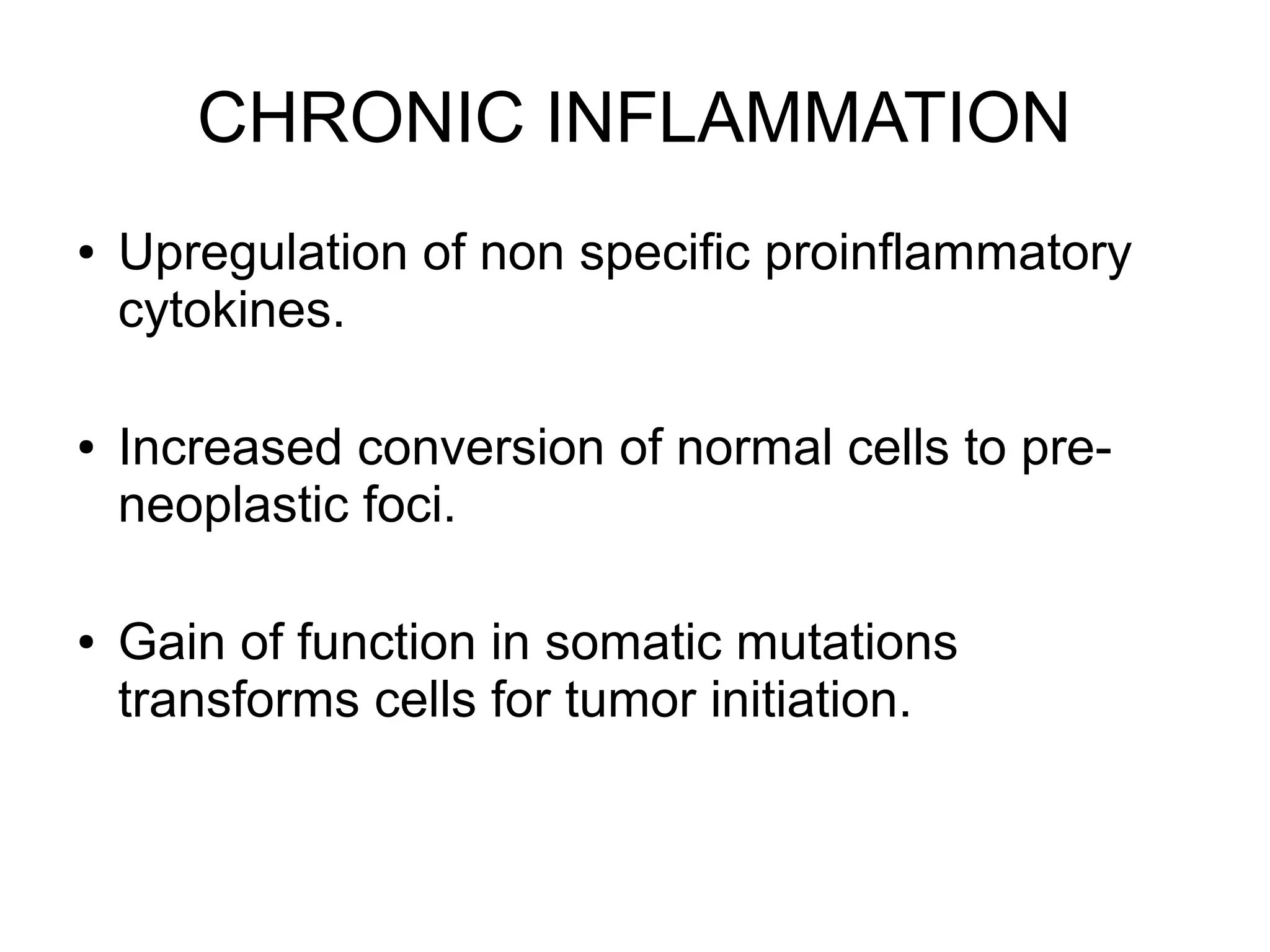
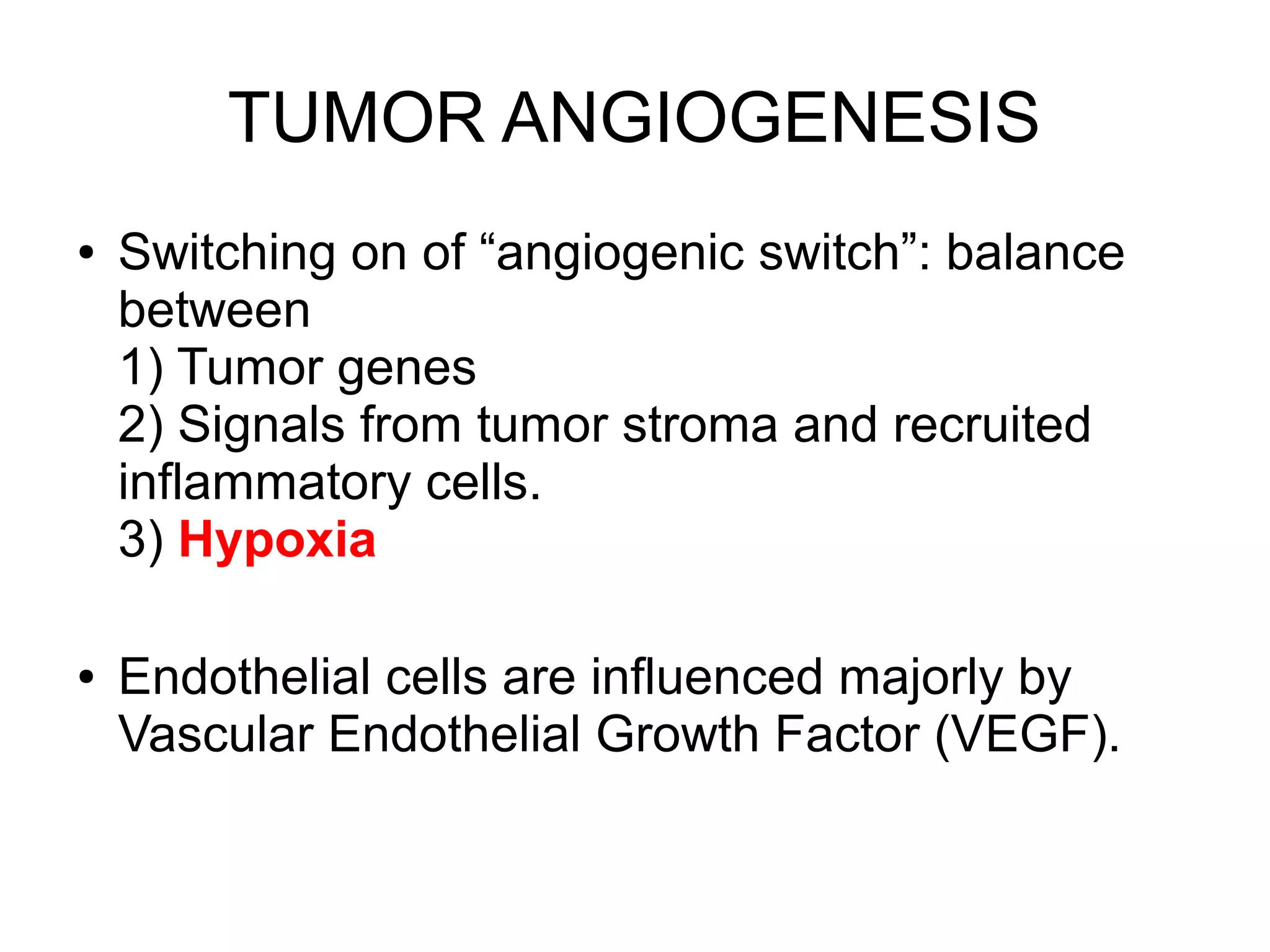
2) Chronic inflammation can promote tumor development by increasing genetic mutations while also stimulating angiogenesis and tumor cell proliferation.
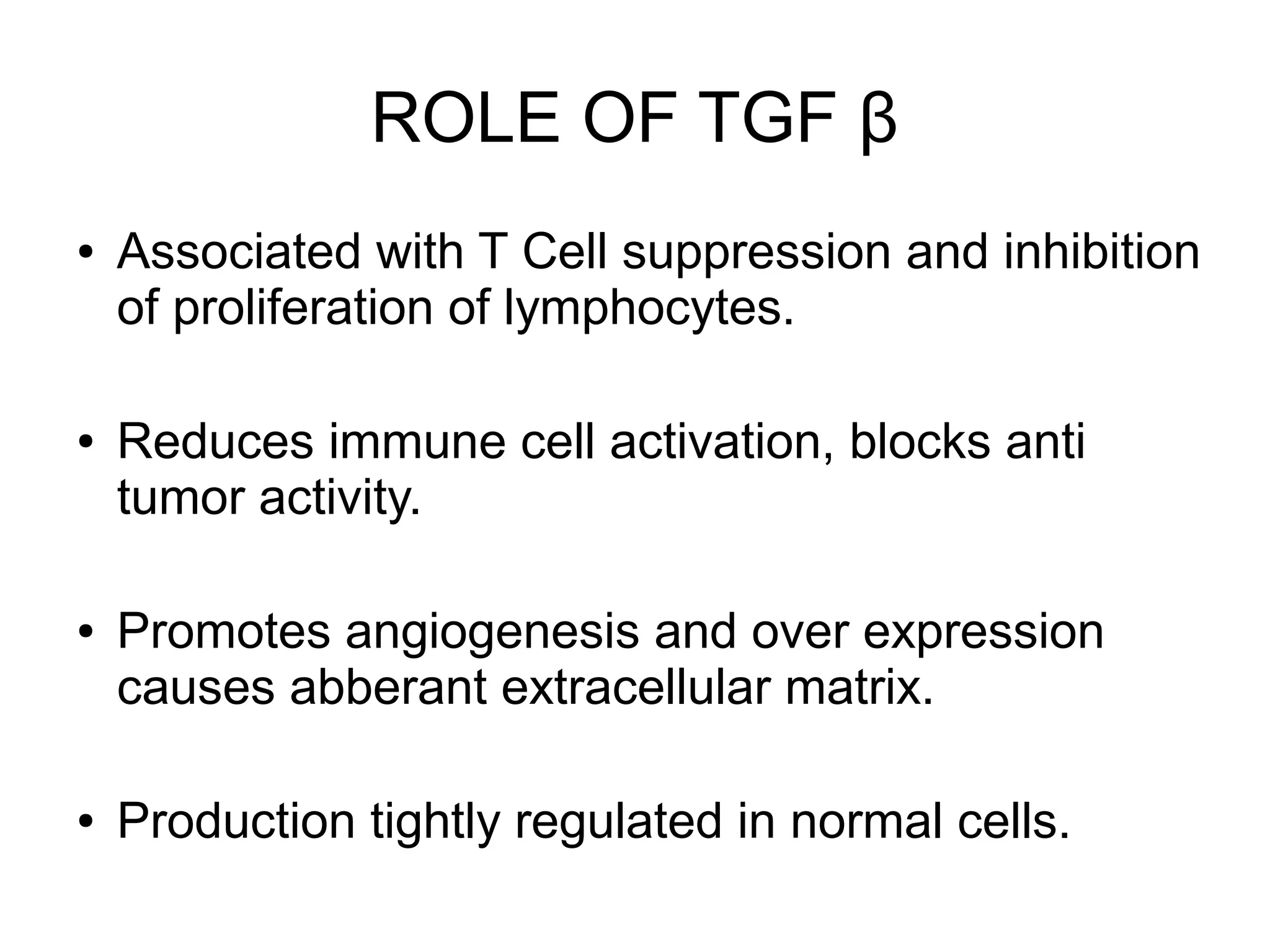
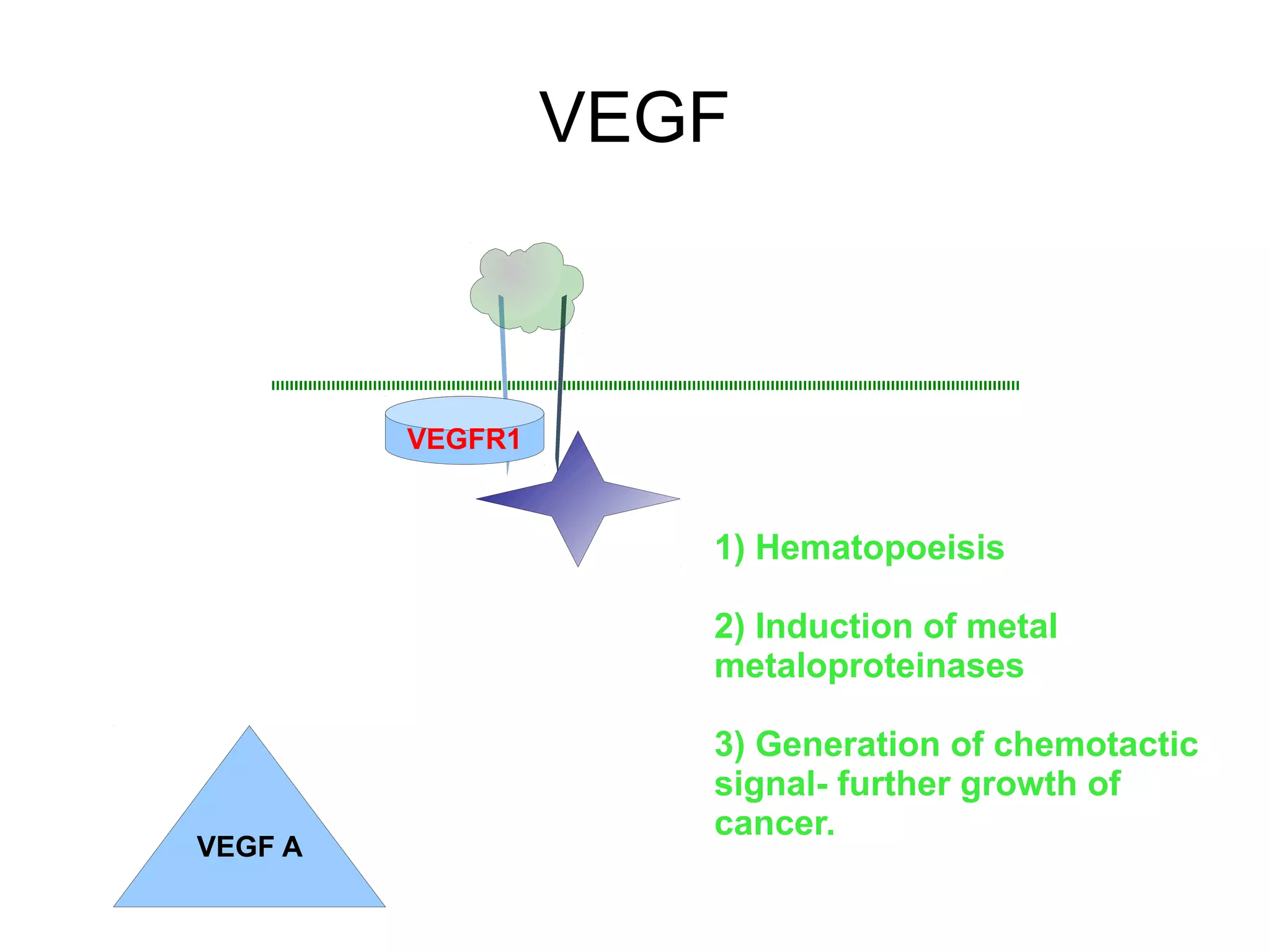
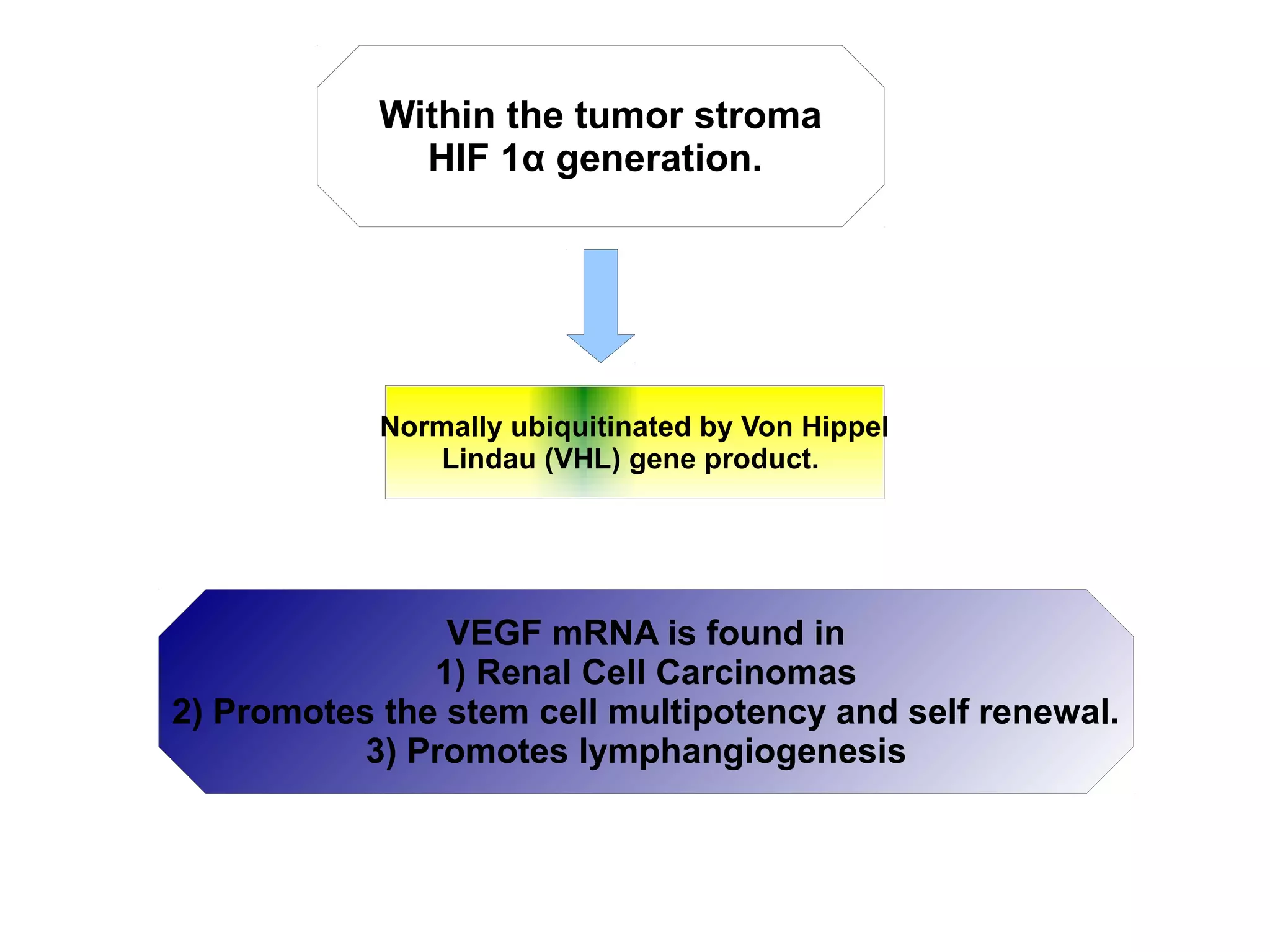
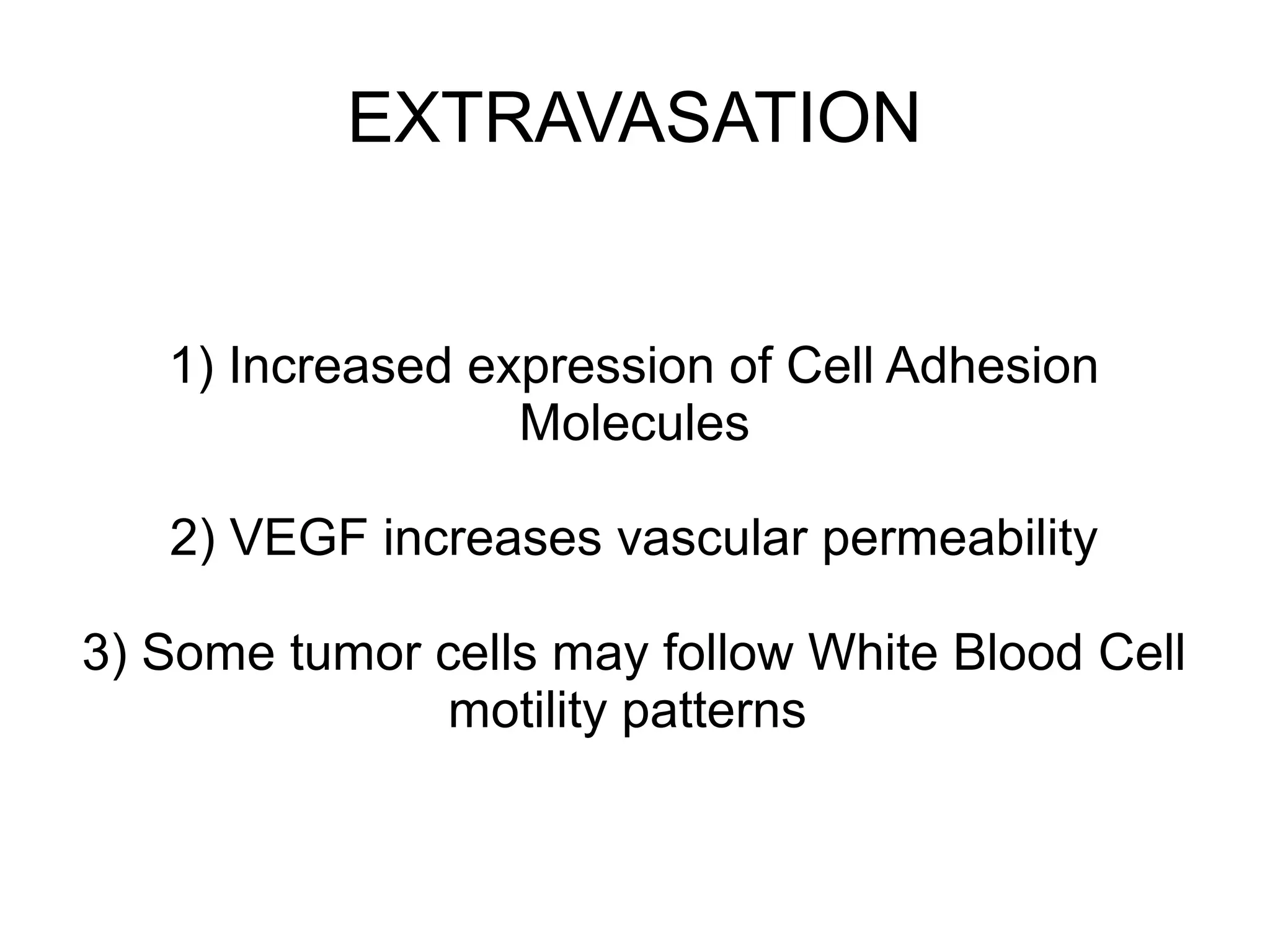
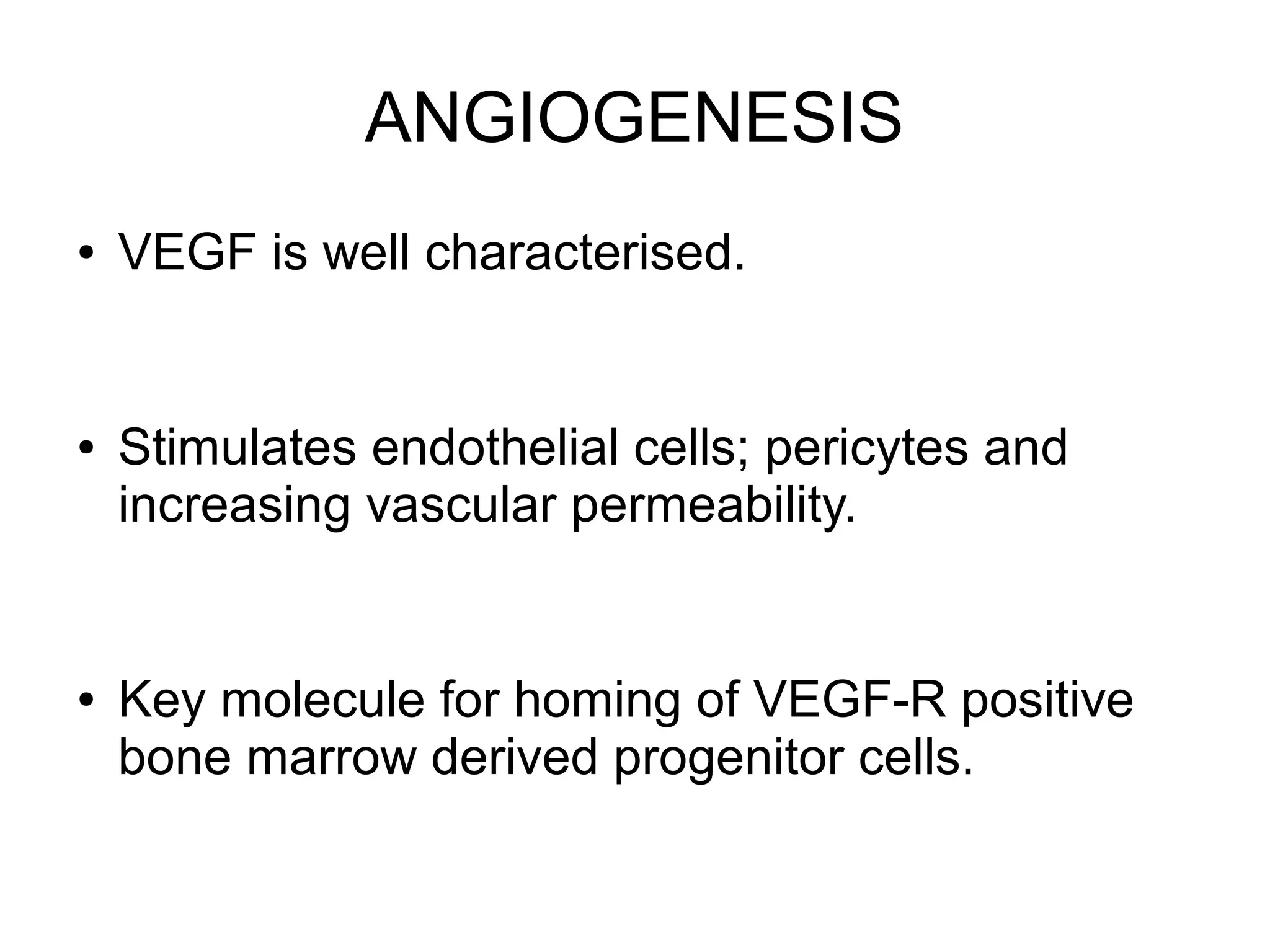
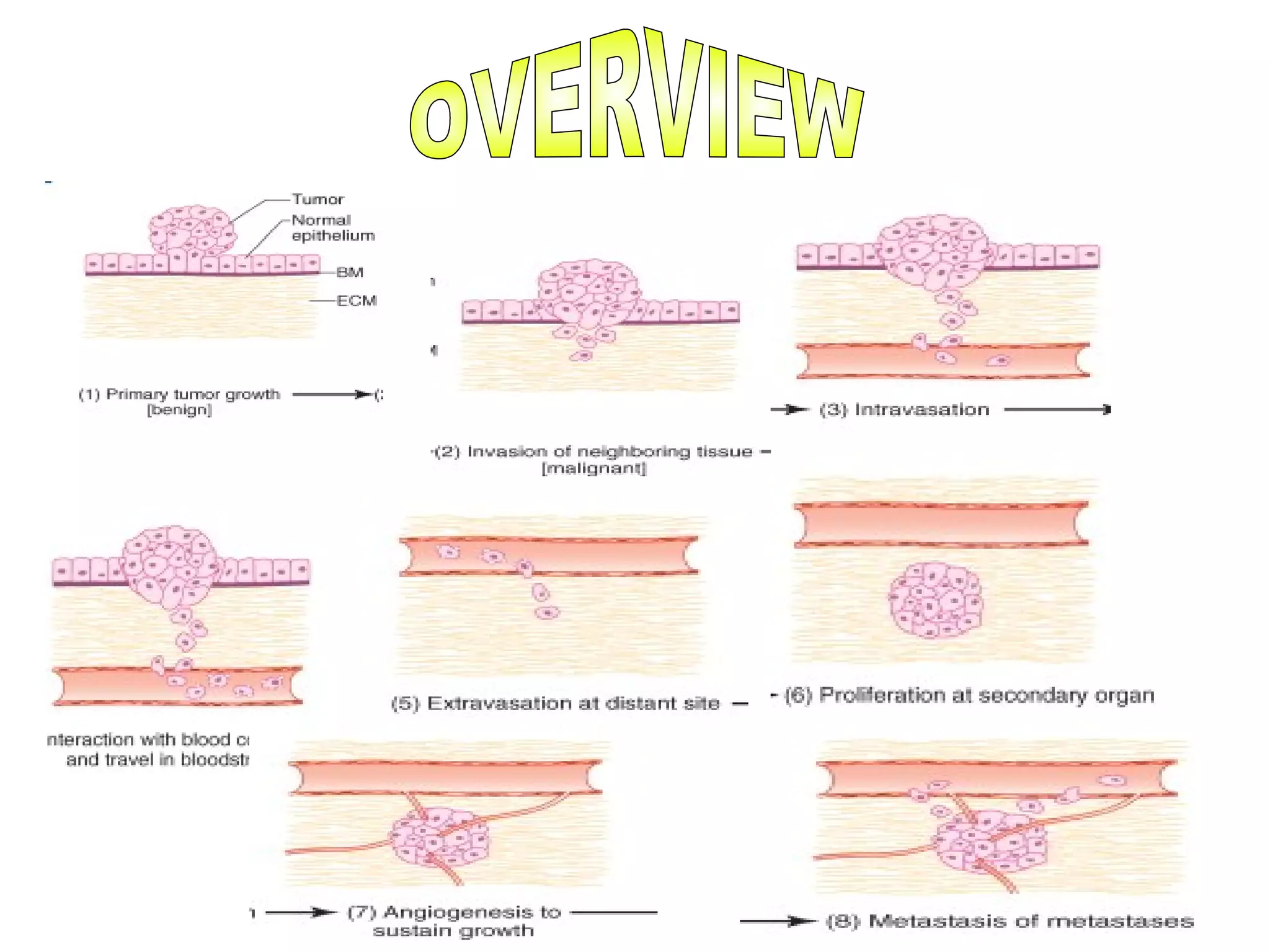
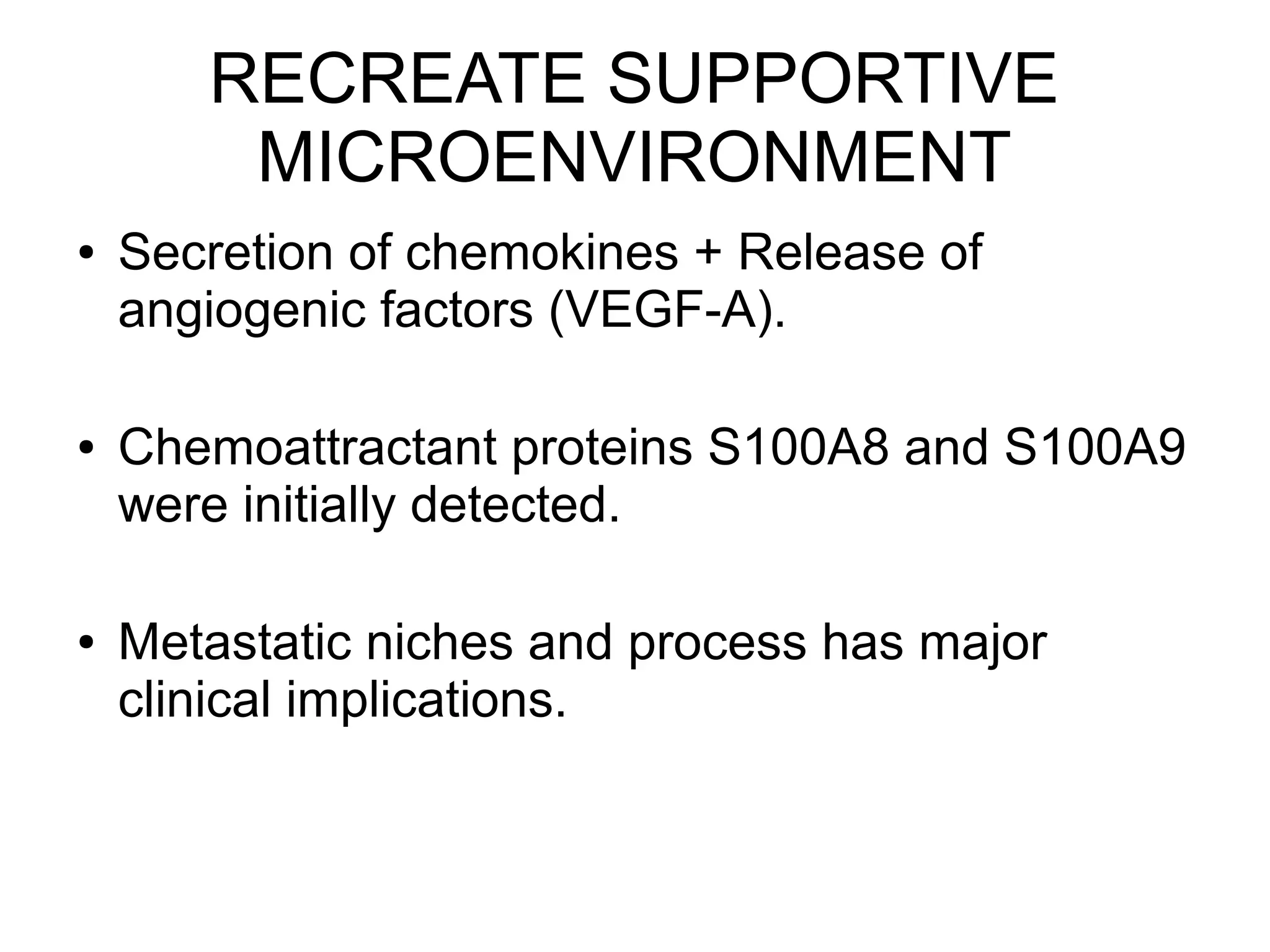
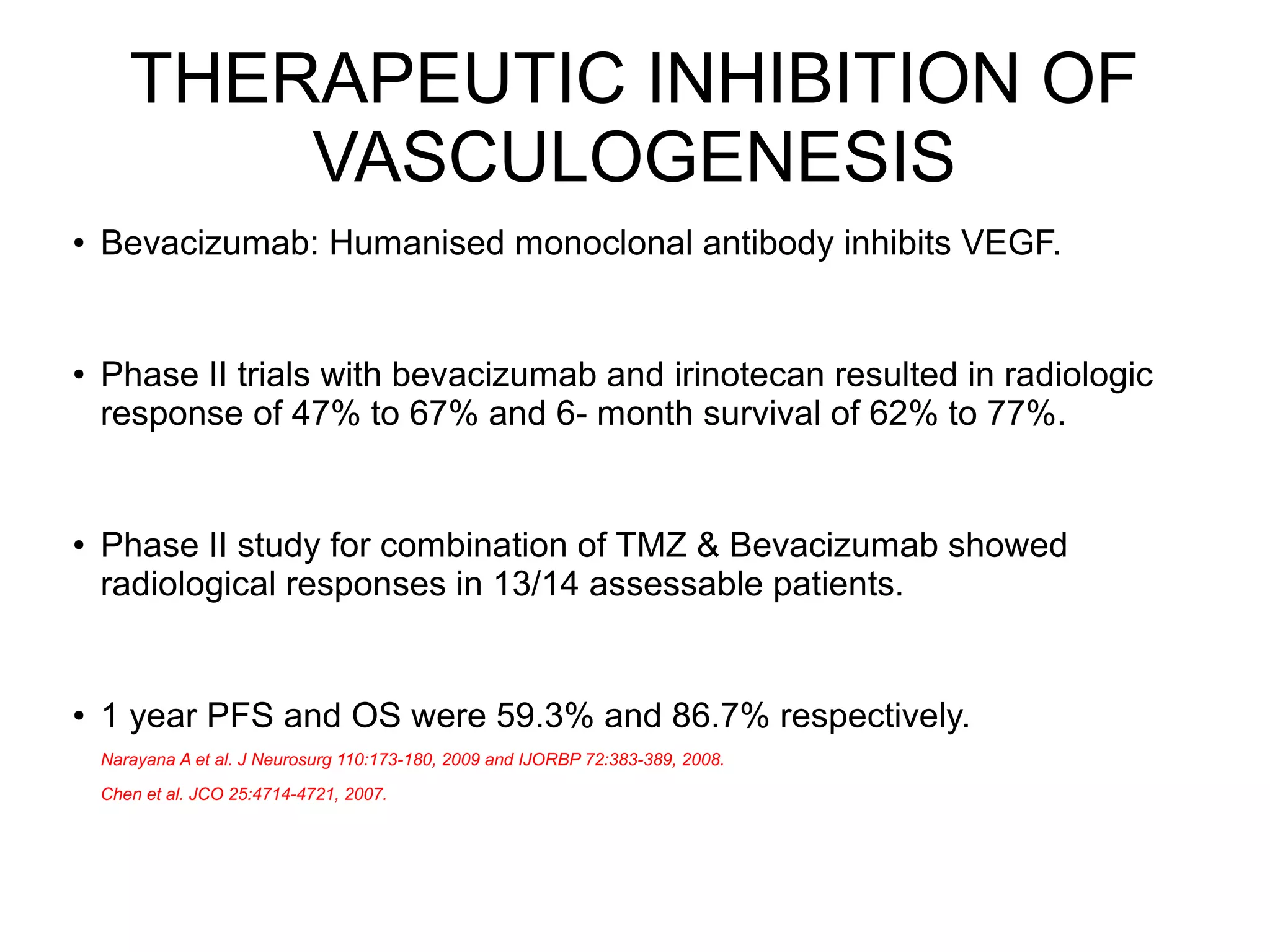
3) The tumor microenvironment interacts bidirectionally with cancer cells to encourage processes like angiogenesis, immune suppression, invasion, and metastasis through factors such as TGF-β, VEGF, and cytokines.
4) Therapies targeting the tumor microenvironment can impact its composition and make cancer cells more invasive, highlighting the need for combination treatments.