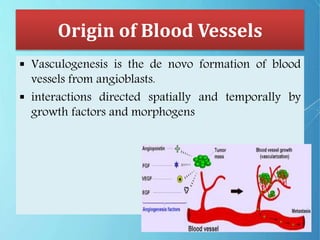
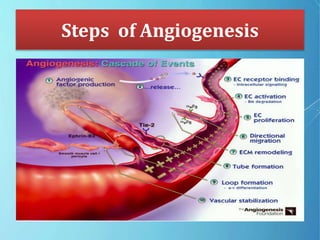
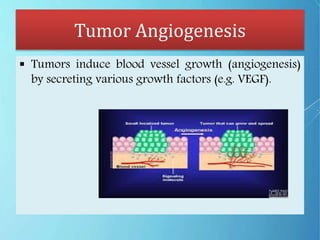
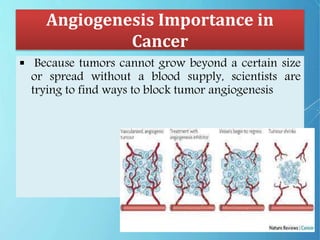
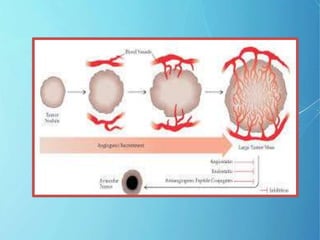
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels from pre-existing vessels. The modern study of angiogenesis began with Judah Folkman's work in the 1970s showing that tumor growth depends on angiogenesis. There are two main types of angiogenesis: sprouting, which occurs in hypoxic tissues, and intussusceptive, which involves the splitting of existing blood vessels. Angiogenesis involves multiple steps and is important in cancer, as tumors secrete growth factors to induce blood vessel formation for their supply and metastasis. Ongoing research focuses on angiogenesis inhibitors that block steps in this process as a potential cancer treatment.