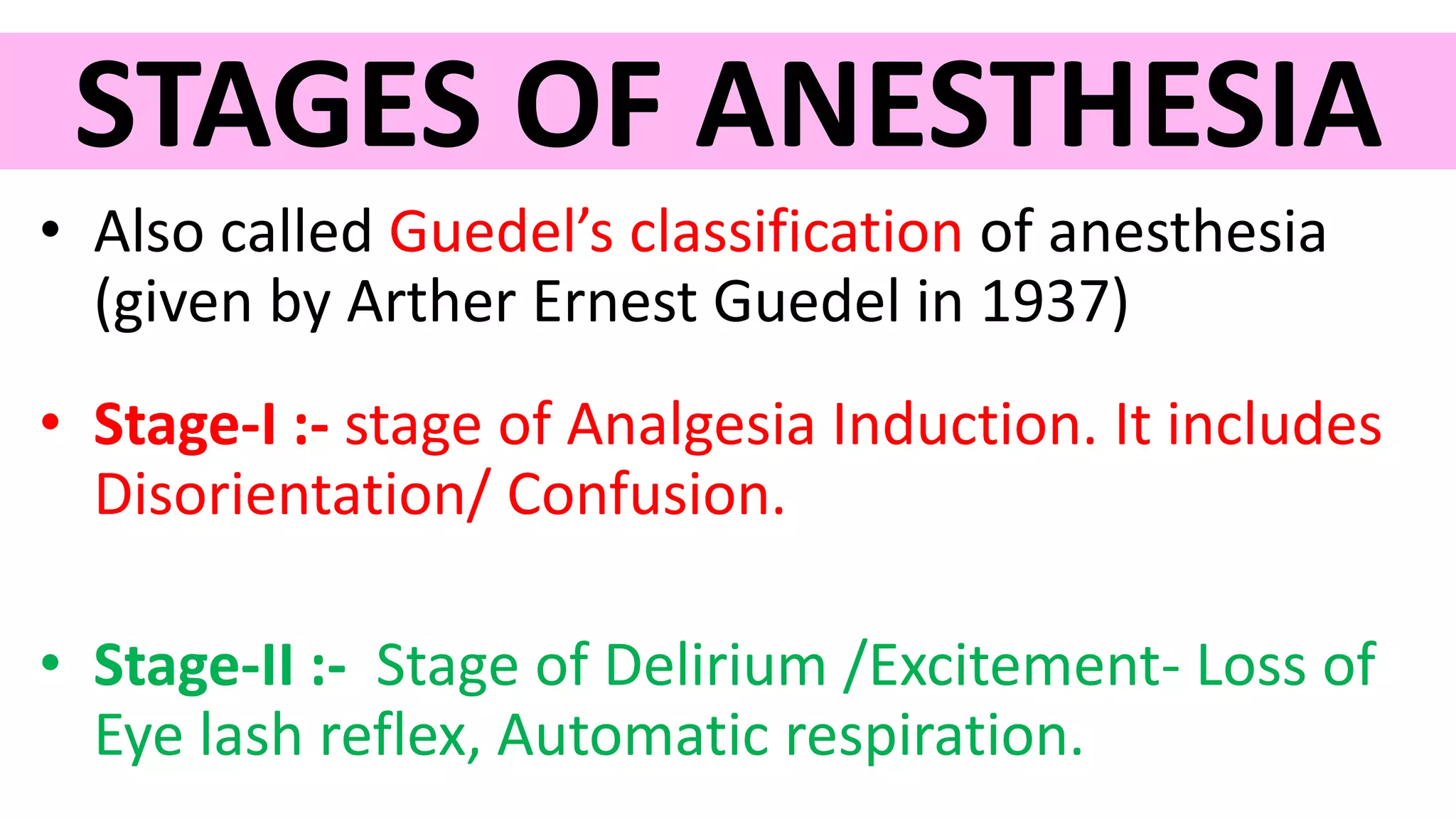
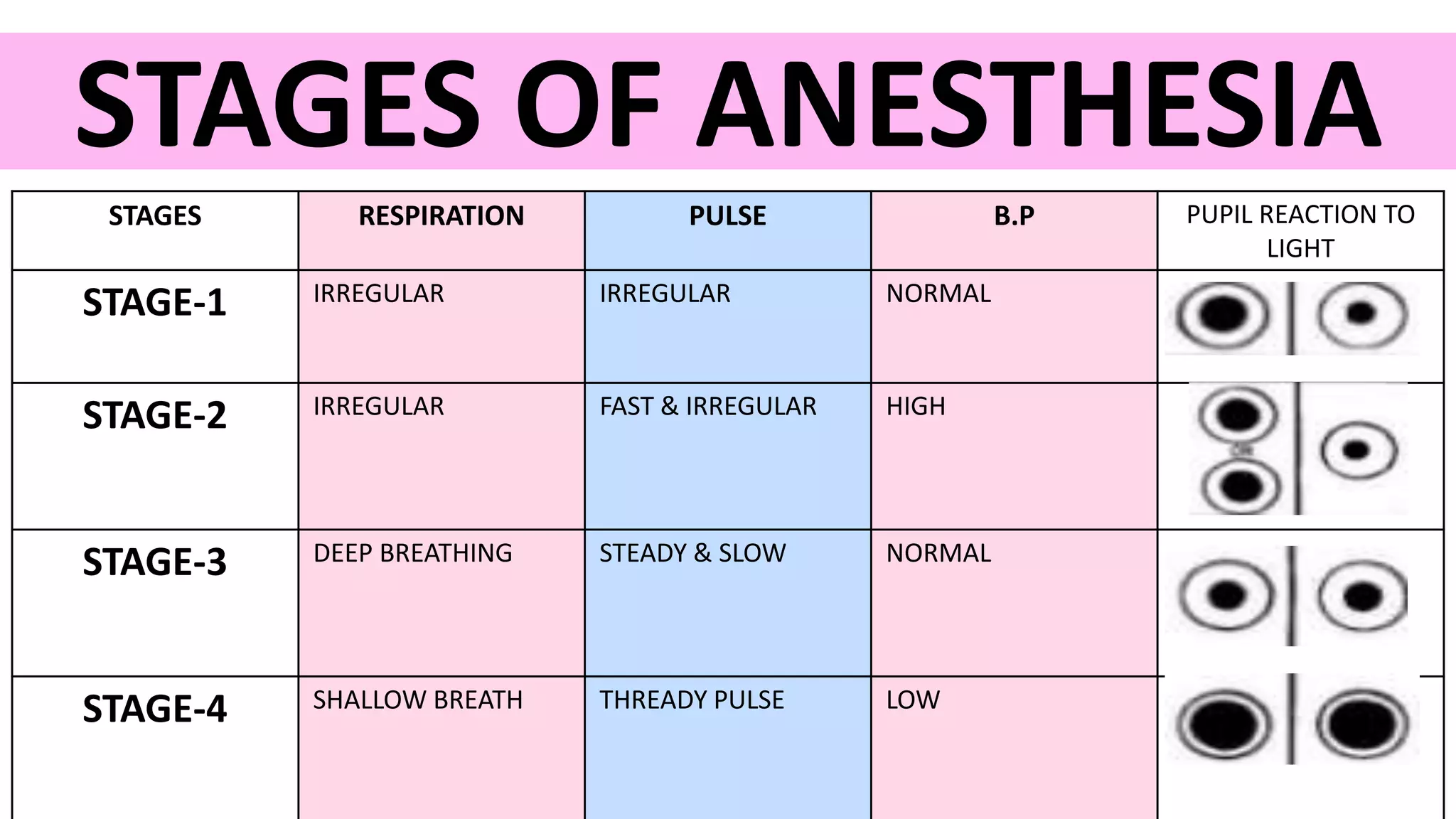
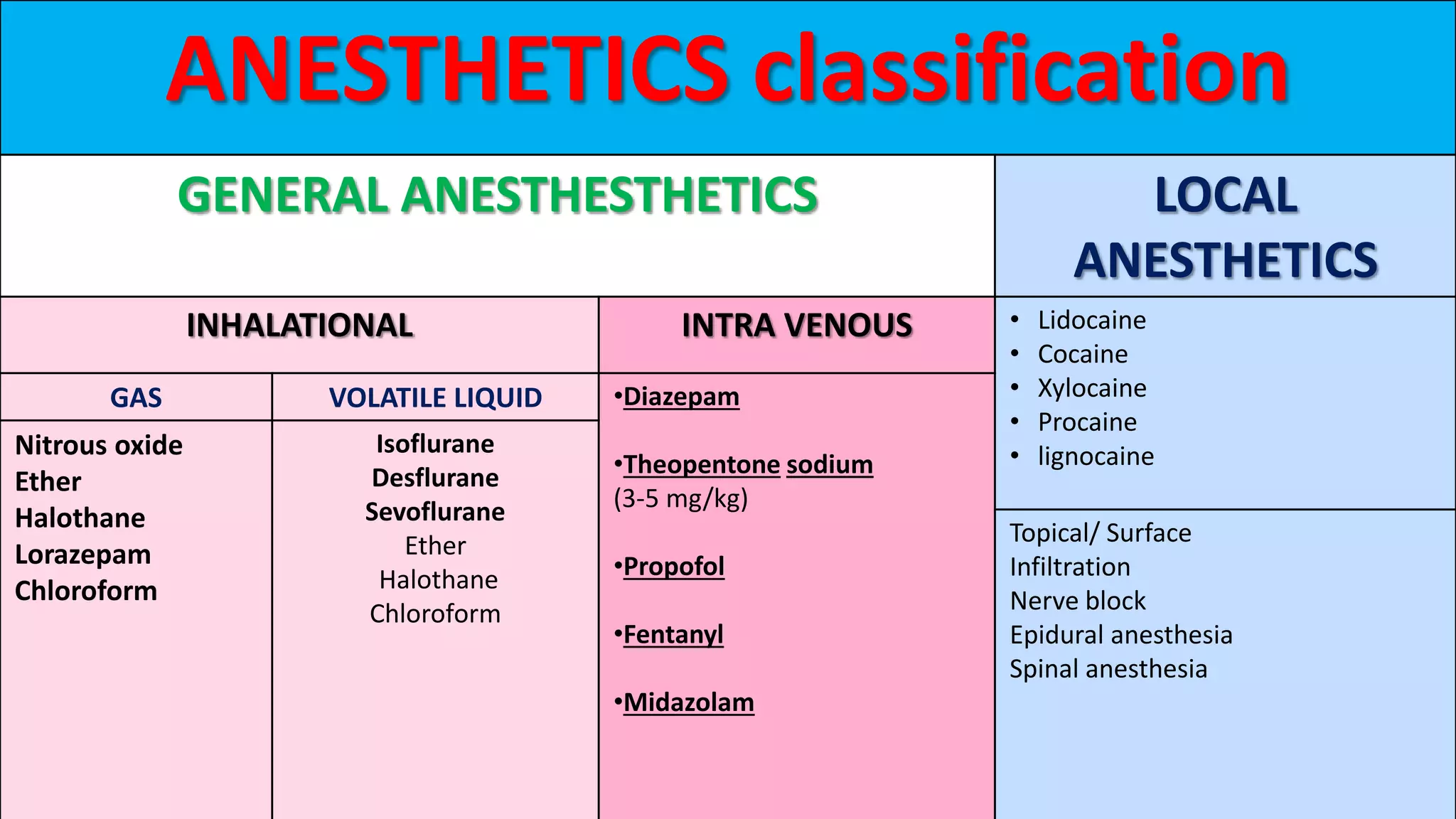
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness induced for therapeutic purposes. It may involve analgesia, paralysis, amnesia, or unconsciousness. There are different stages of anesthesia from initial induction to recovery. General anesthesia uses inhaled gases or intravenous drugs to cause unconsciousness, while local anesthesia uses topical or injected drugs to block sensory nerves and relieve pain in a specific area without unconsciousness. Careful monitoring is needed during anesthesia and recovery due to risks like nausea, vomiting, hypotension, and hypothermia.