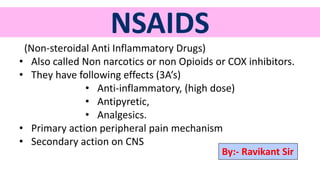
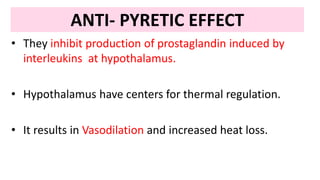
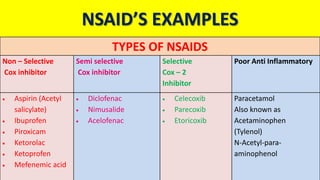
NSAIDs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that work by inhibiting the COX enzyme and subsequent production of prostaglandins. They have analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory effects. COX enzymes come in three types, with COX-1 found in normal tissues and COX-2 induced during inflammation. NSAIDs work by blocking COX receptors, preventing prostaglandin formation and thereby reducing pain, fever, and swelling. Common NSAID types include non-selective COX inhibitors like aspirin and ibuprofen, and selective COX-2 inhibitors like celecoxib. Side effects can include gastric irritation and ulceration.