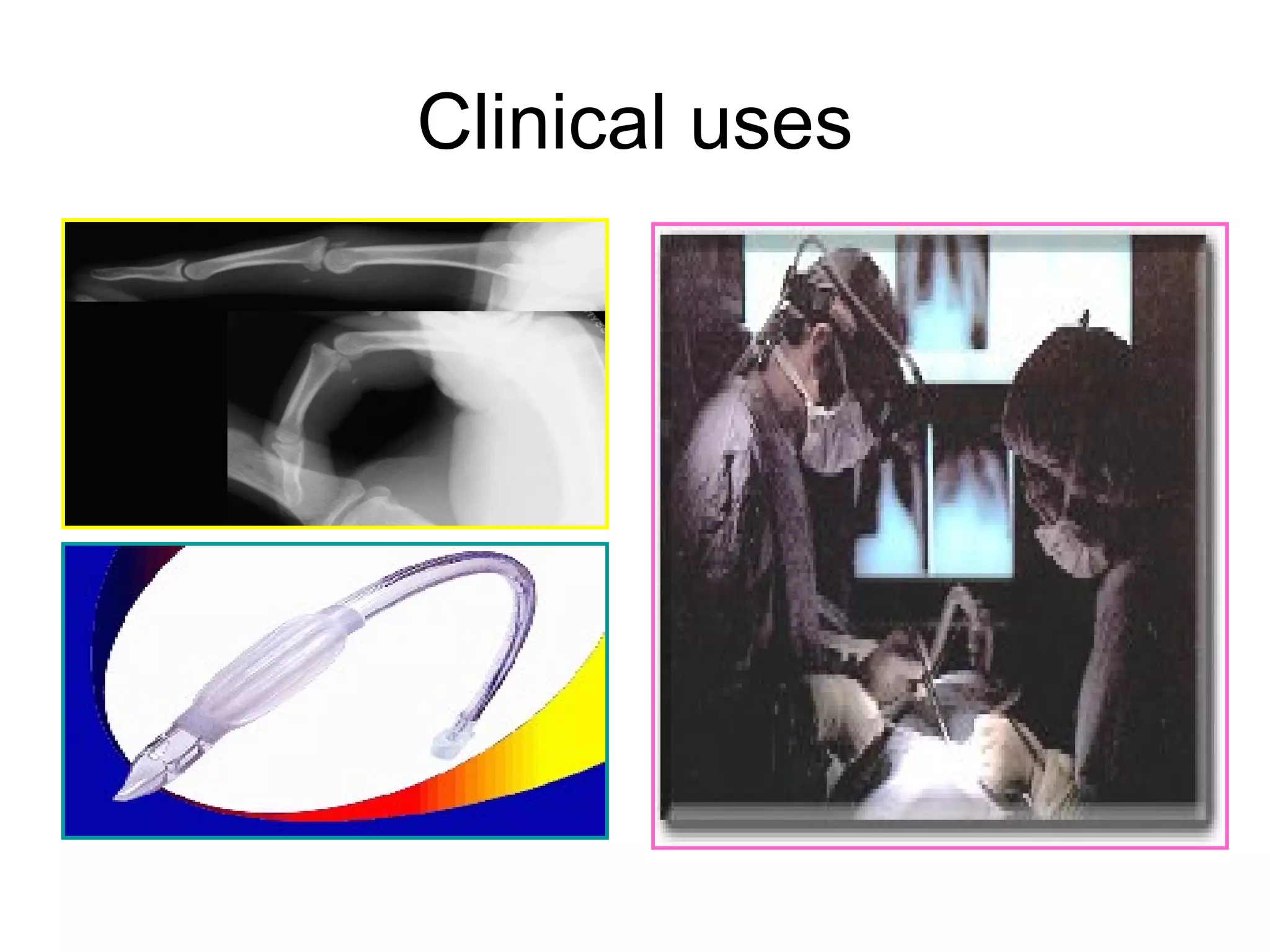
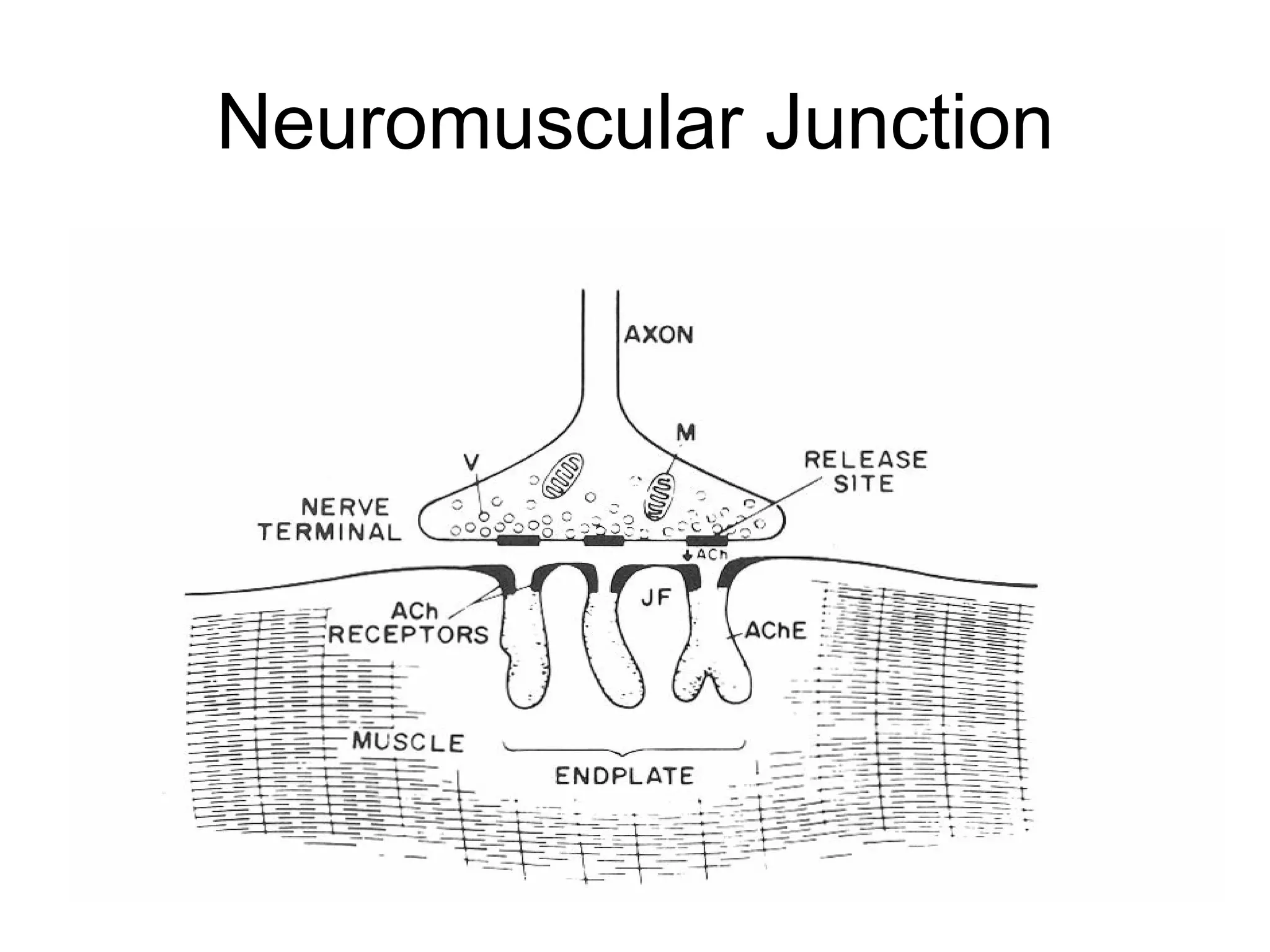
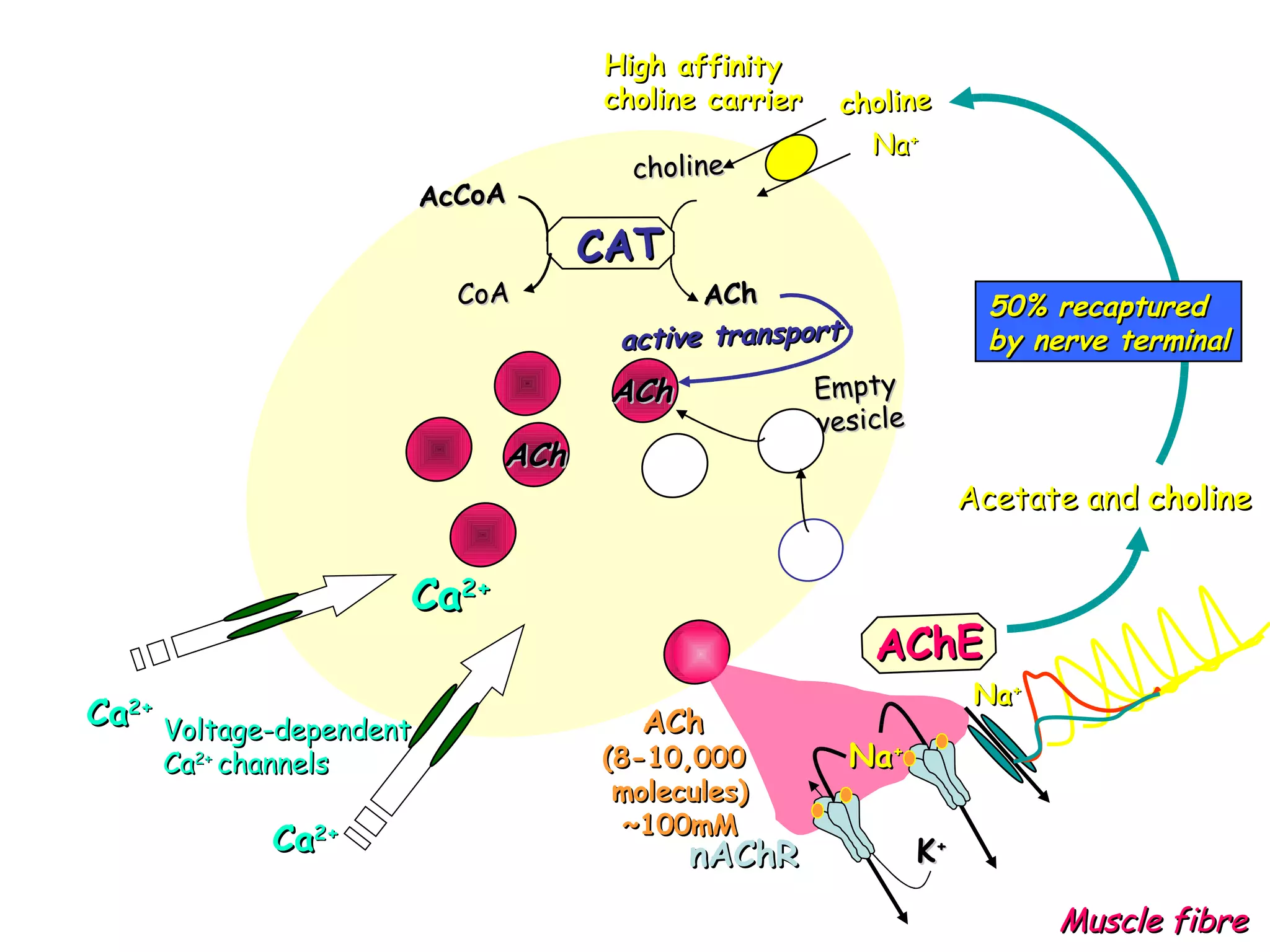
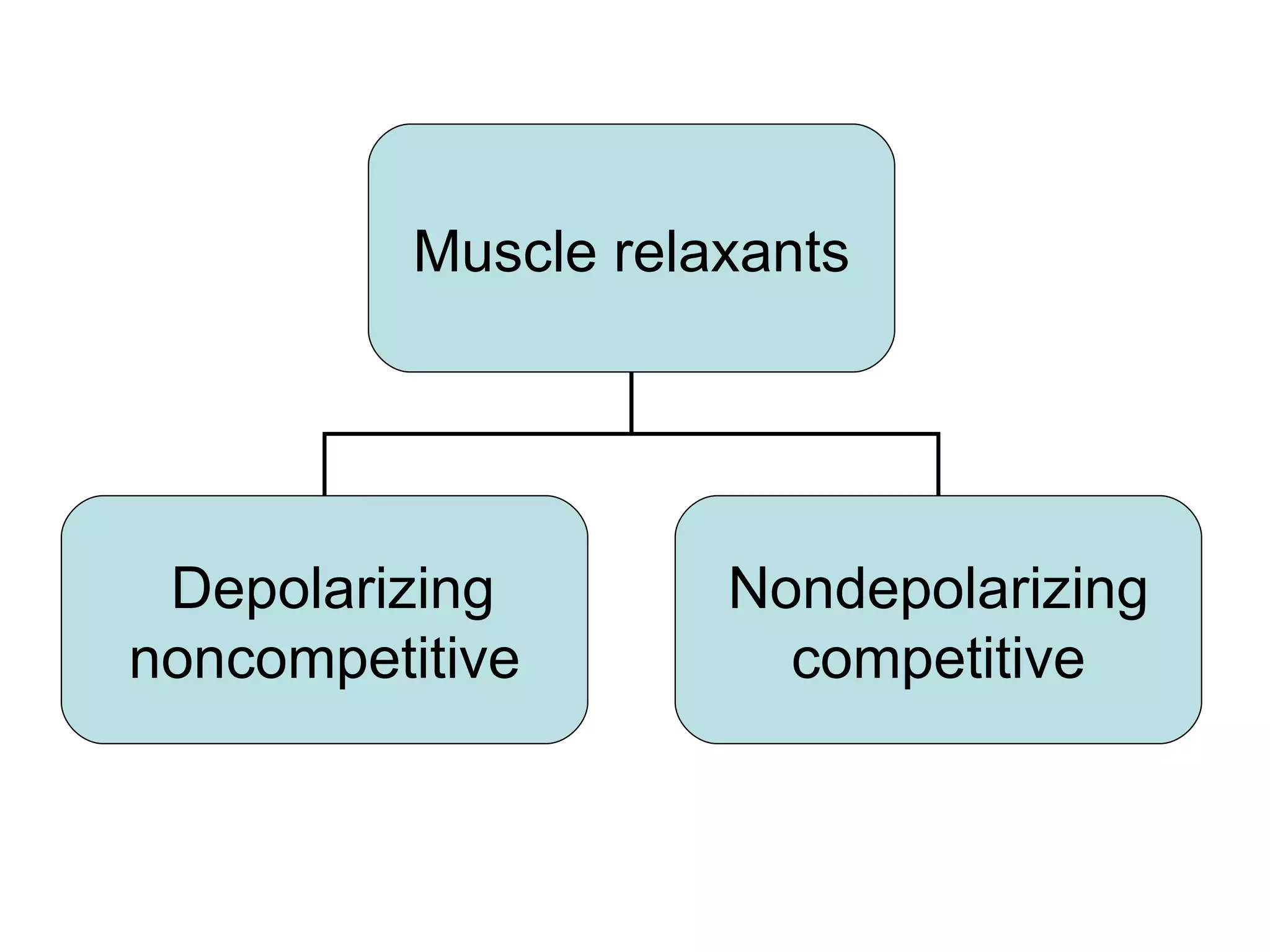
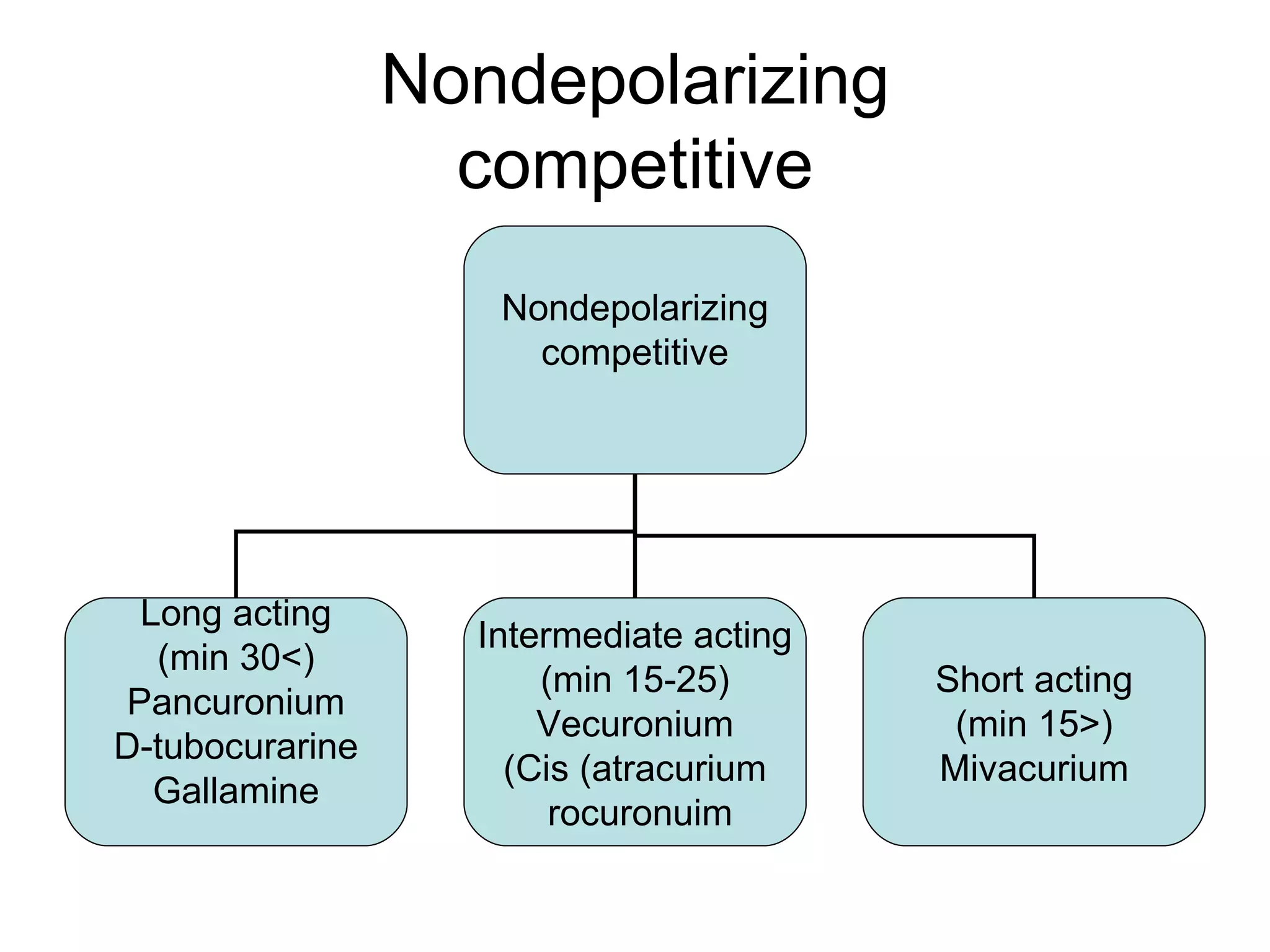
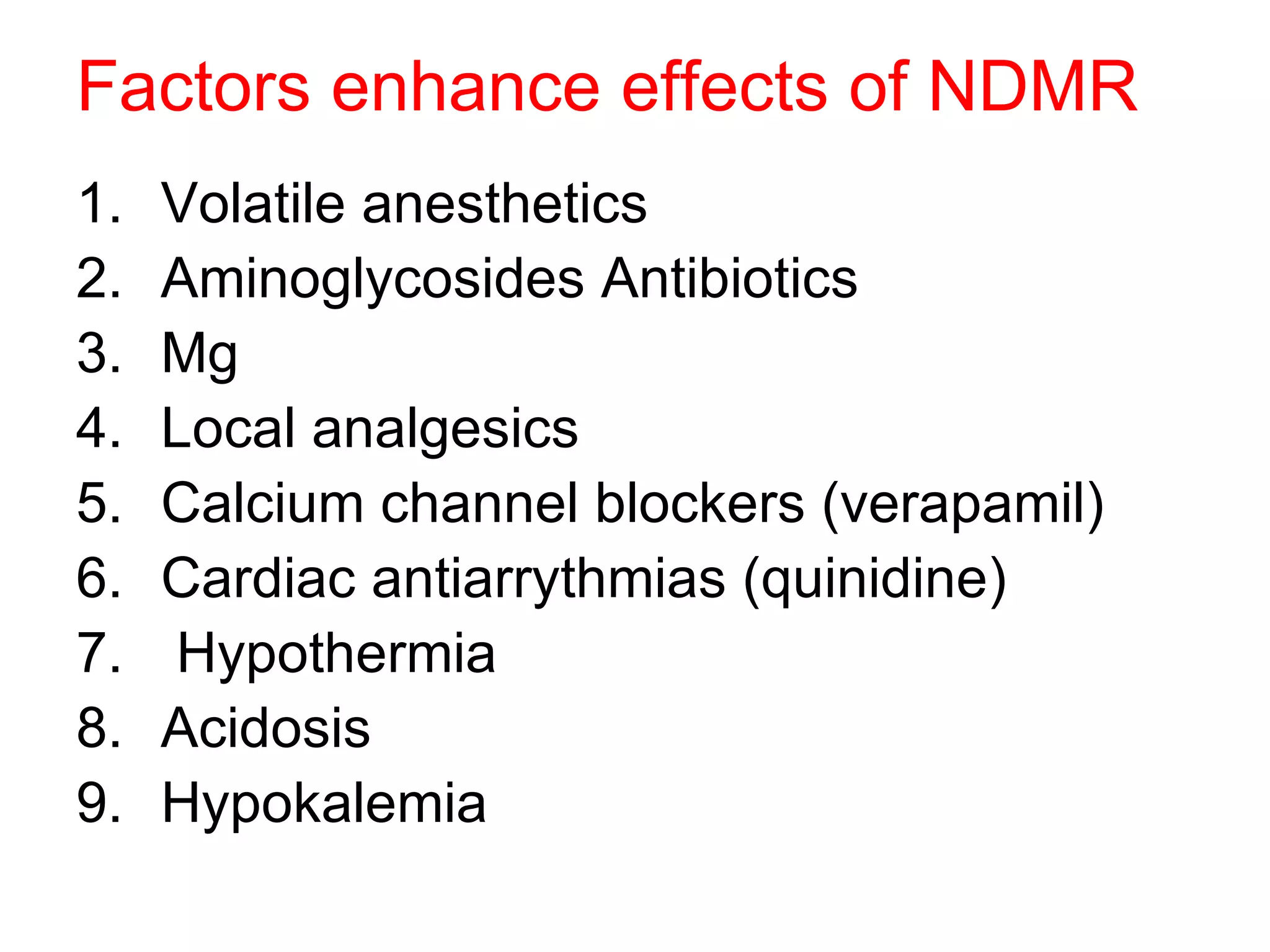
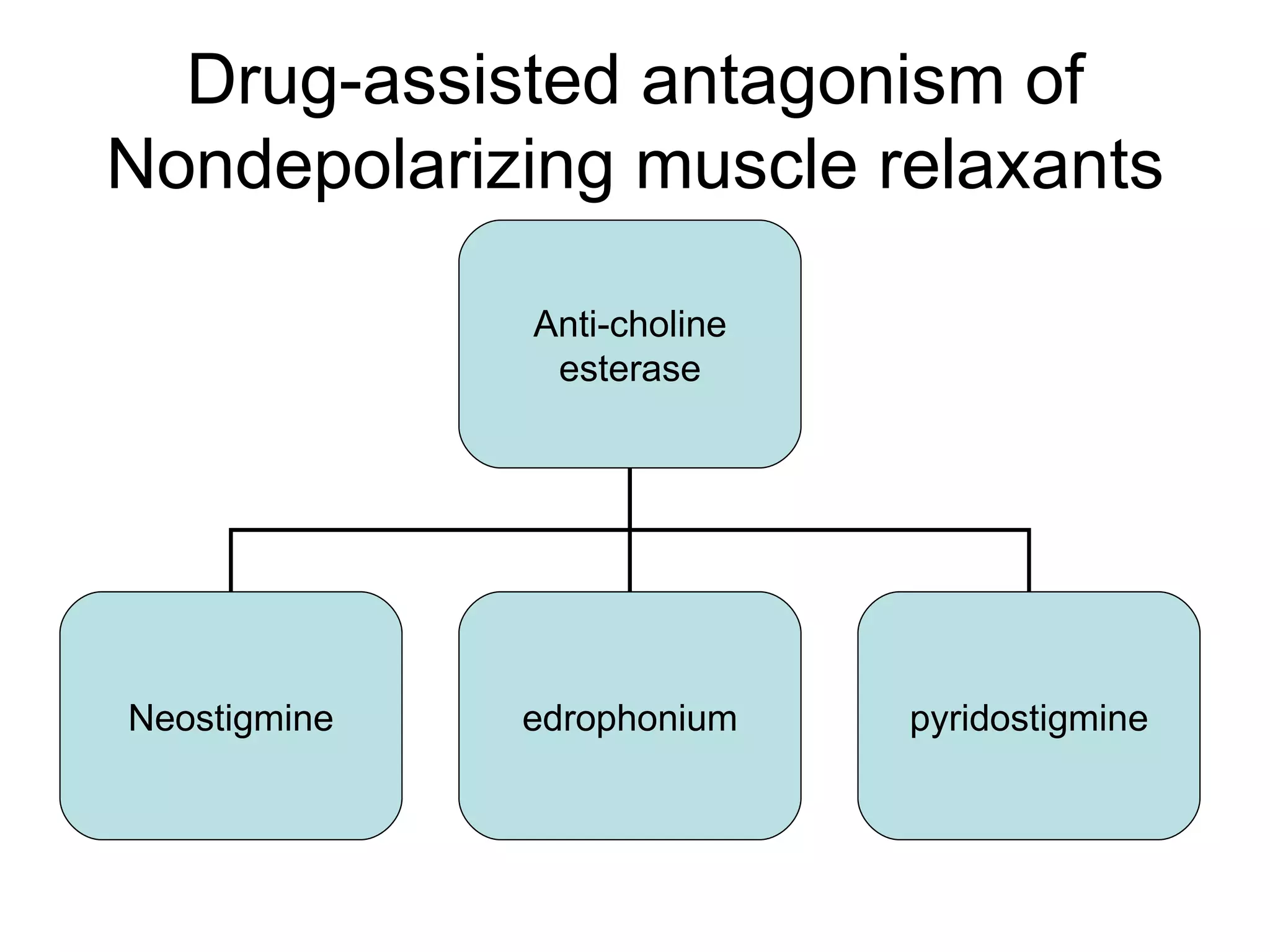
Muscle relaxants are drugs that interrupt neural impulses at the neuromuscular junction. They provide skeletal muscle relaxation for procedures like intubation and surgery. The choice of muscle relaxant depends on its onset, duration, route of elimination, and side effects. They work by blocking nicotinic cholinergic receptors at the neuromuscular junction. Anticholinesterases can reverse the effects of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase and increasing acetylcholine levels.