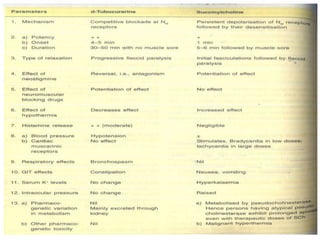
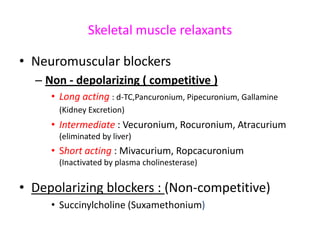
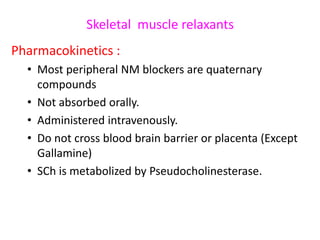
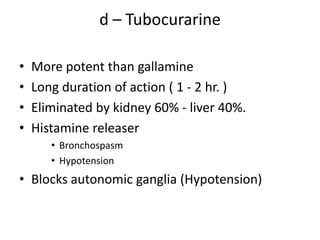
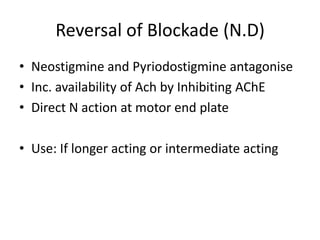
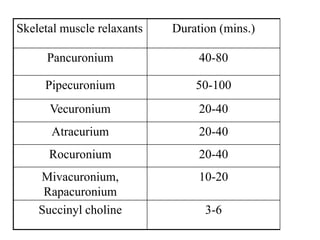
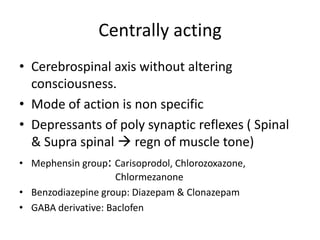
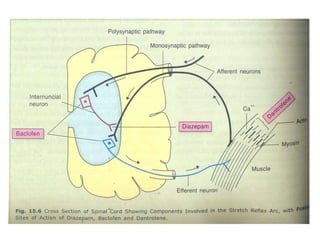
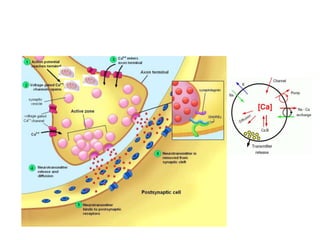
This document discusses neuromuscular blockers (muscle relaxants) including their physiology, classification, and role in surgery. It describes how muscle relaxants work by blocking acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction, classifying them as depolarizing or non-depolarizing. Specific muscle relaxants are outlined, their mechanisms of action, durations, and side effect profiles. The document also briefly discusses centrally-acting muscle relaxants and direct acting drugs like dantrolene. Choice of muscle relaxant depends on factors like required duration, excretion route, and side effect risks.