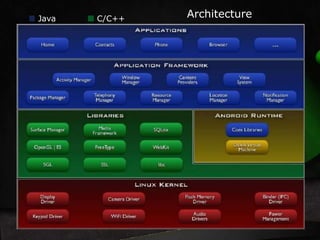
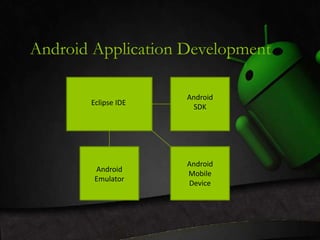
The document presents information on Android architecture. It discusses that Android is a mobile operating system based on the Linux kernel that is developed using Java and C/C++ programming languages. It then describes some key components of the Android architecture, including the Linux kernel, Dalvik virtual machine, activities manager, package manager, content providers, and views system. It also mentions using Eclipse IDE, Android SDK, and emulators for application development.