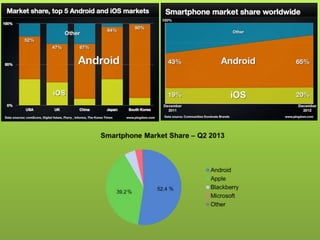
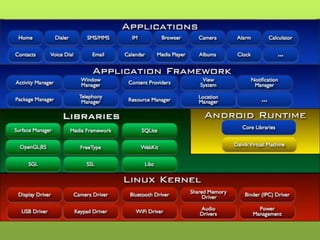
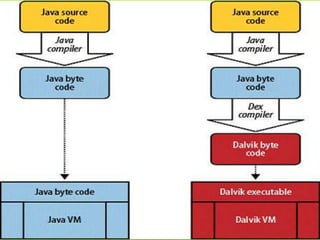
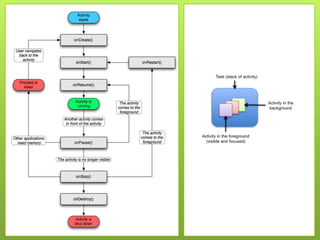
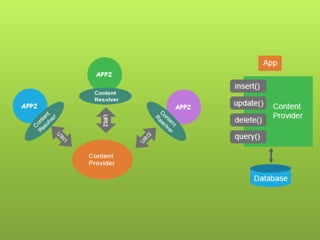
This document provides an overview of Android including its history, architecture, and key components. It began as a startup called Android Inc. in 2005 and was later acquired by Google in 2007. The latest version is Android 4.4 KitKat. The architecture includes the Linux kernel, libraries like Webkit and SQLite, the Dalvik virtual machine, core apps framework, and applications. It discusses the main roles of the activity manager, window manager, content providers, and other framework components.