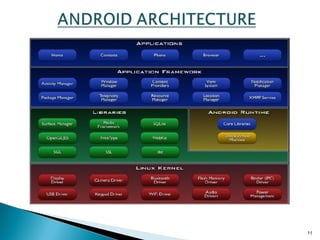
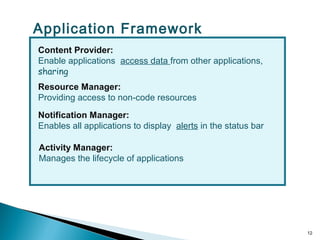
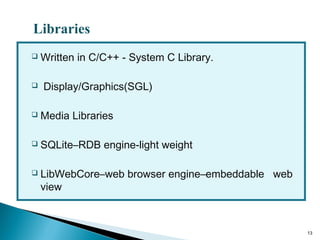
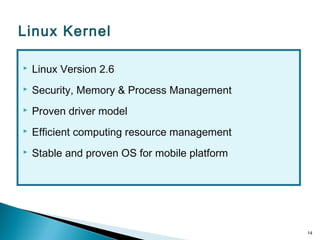
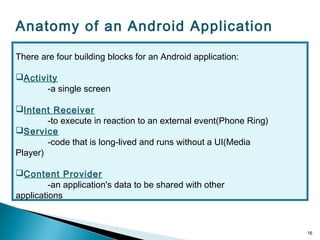
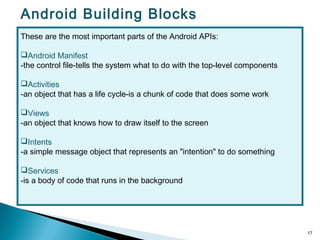
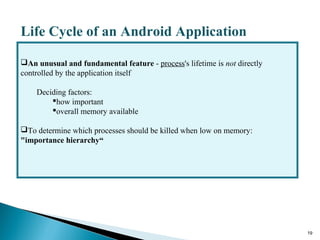
Secure-Net Technologies is a training institute in Chandigarh, recognized for its partnerships with major brands like Microsoft and Oracle. The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Android platform, detailing its architecture, features, development tools, and application lifecycle. It emphasizes the open-source nature of Android and its community support, making it a significant player in mobile software development.