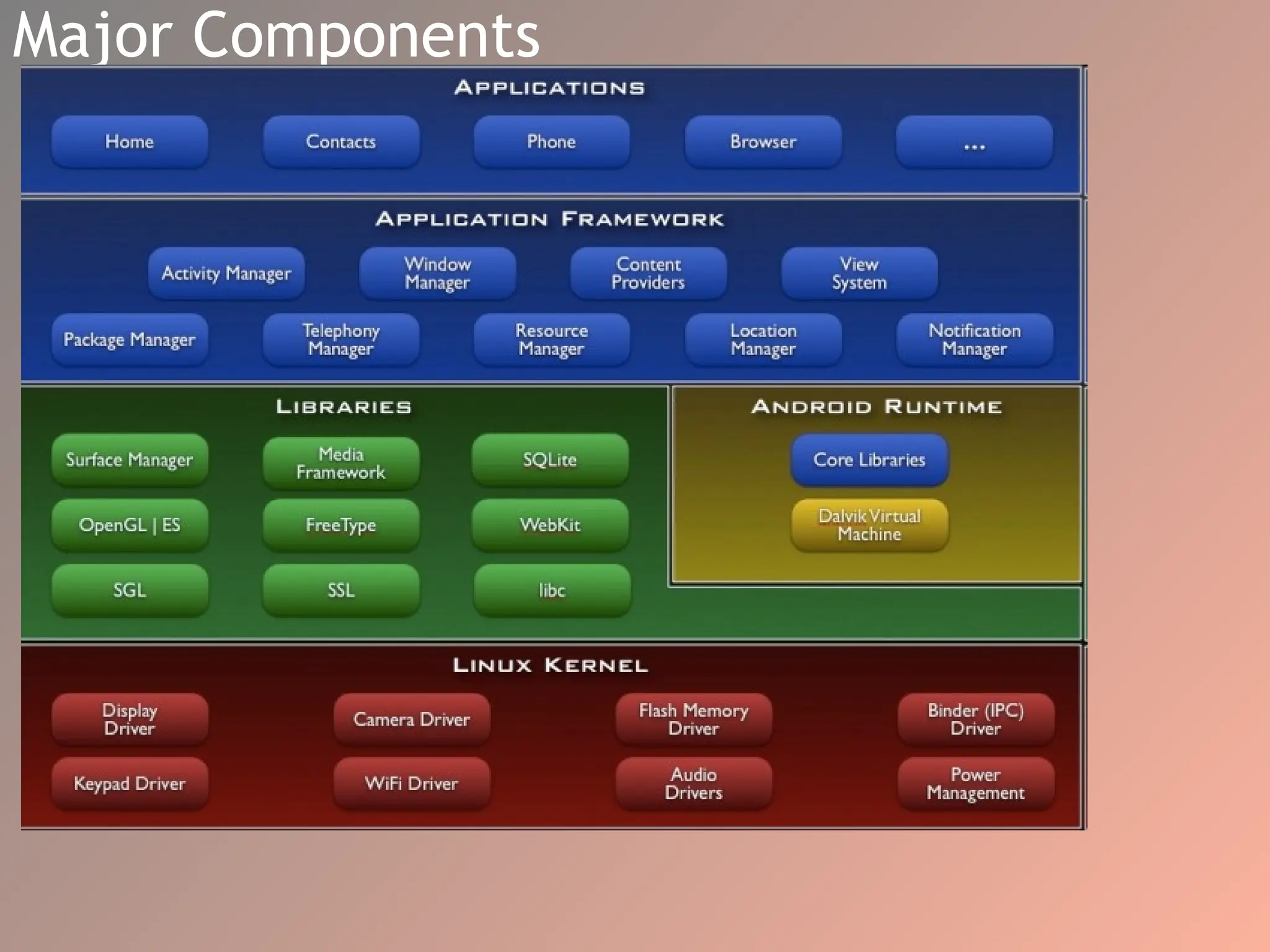
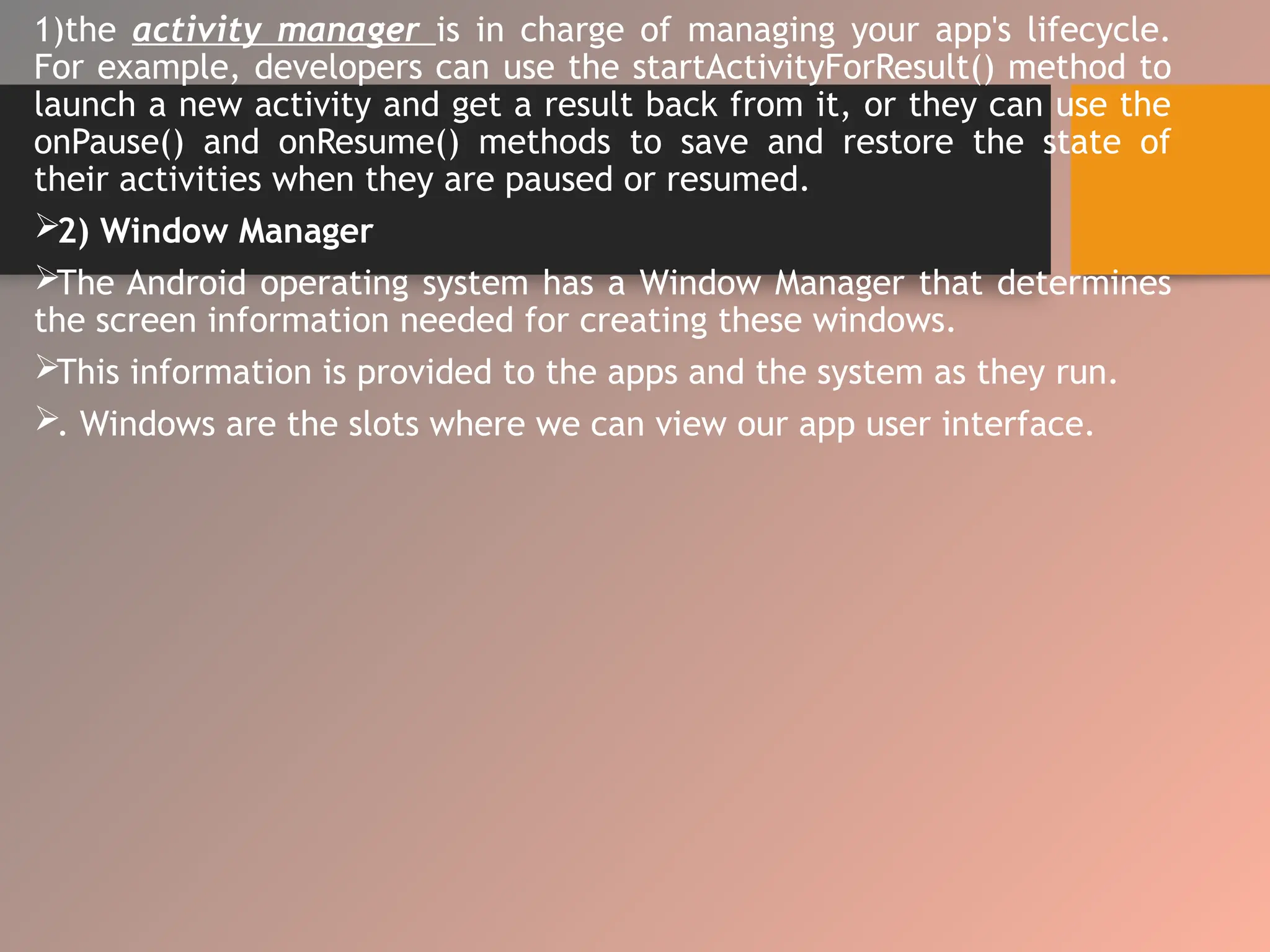
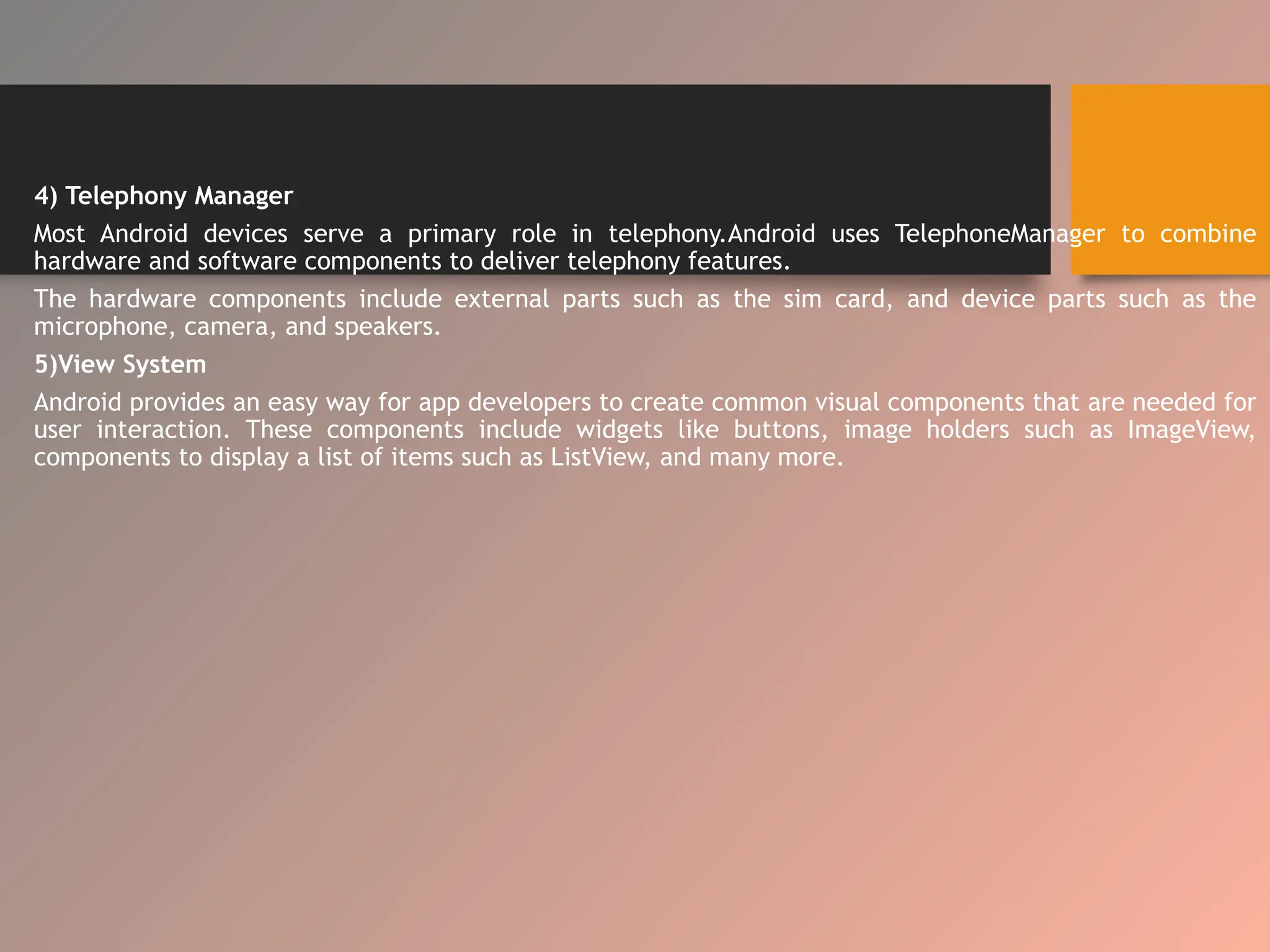
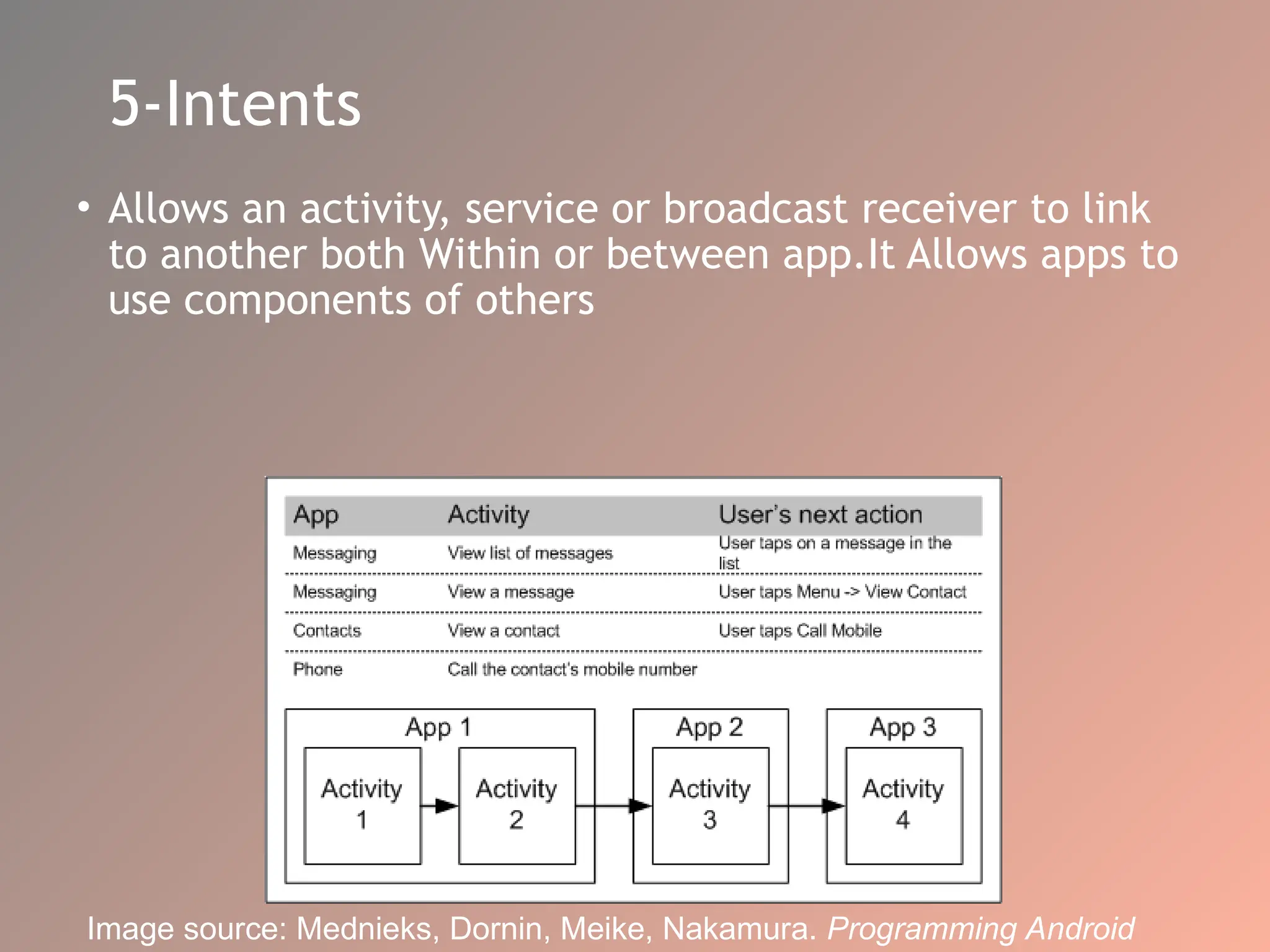
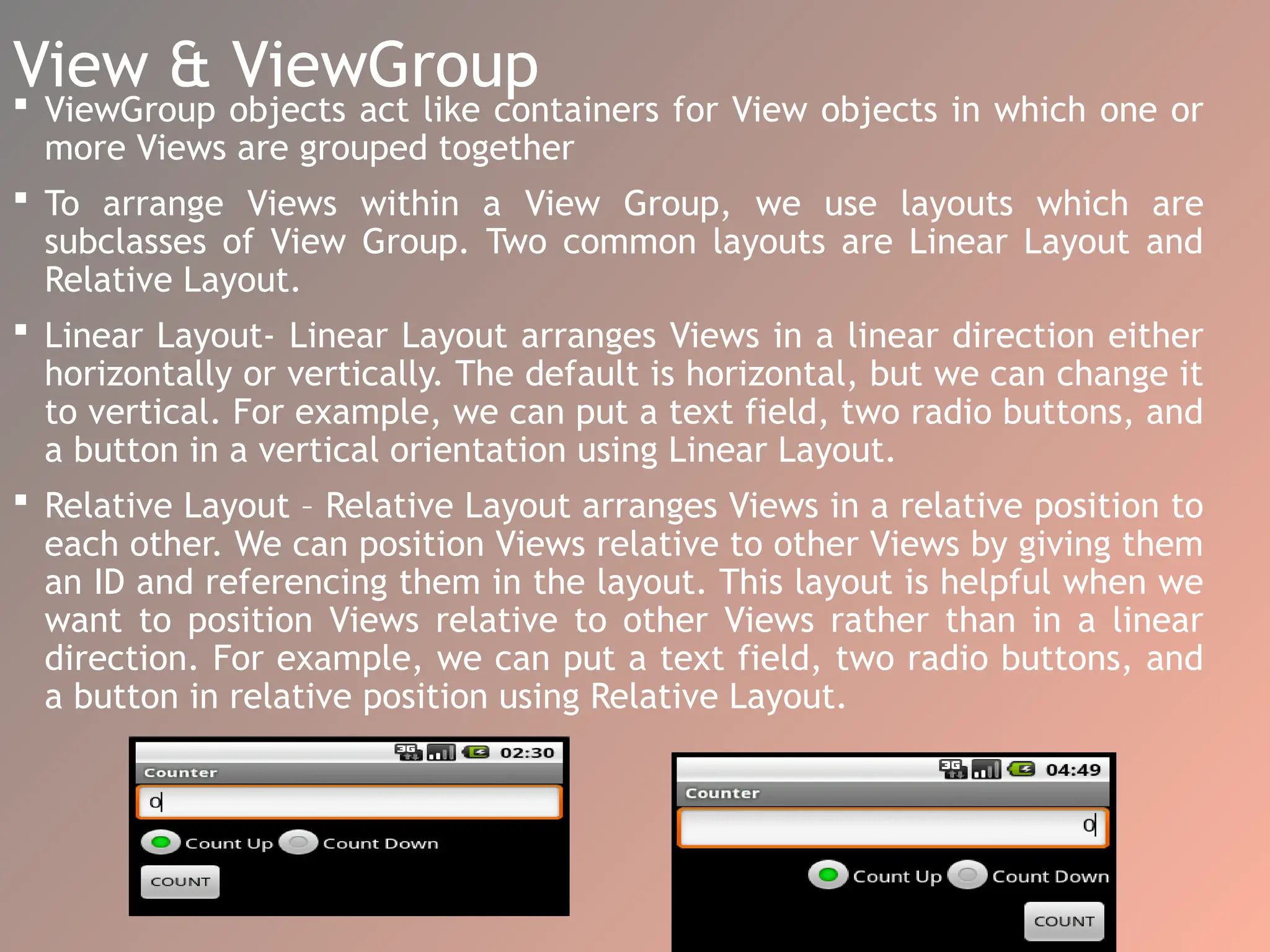
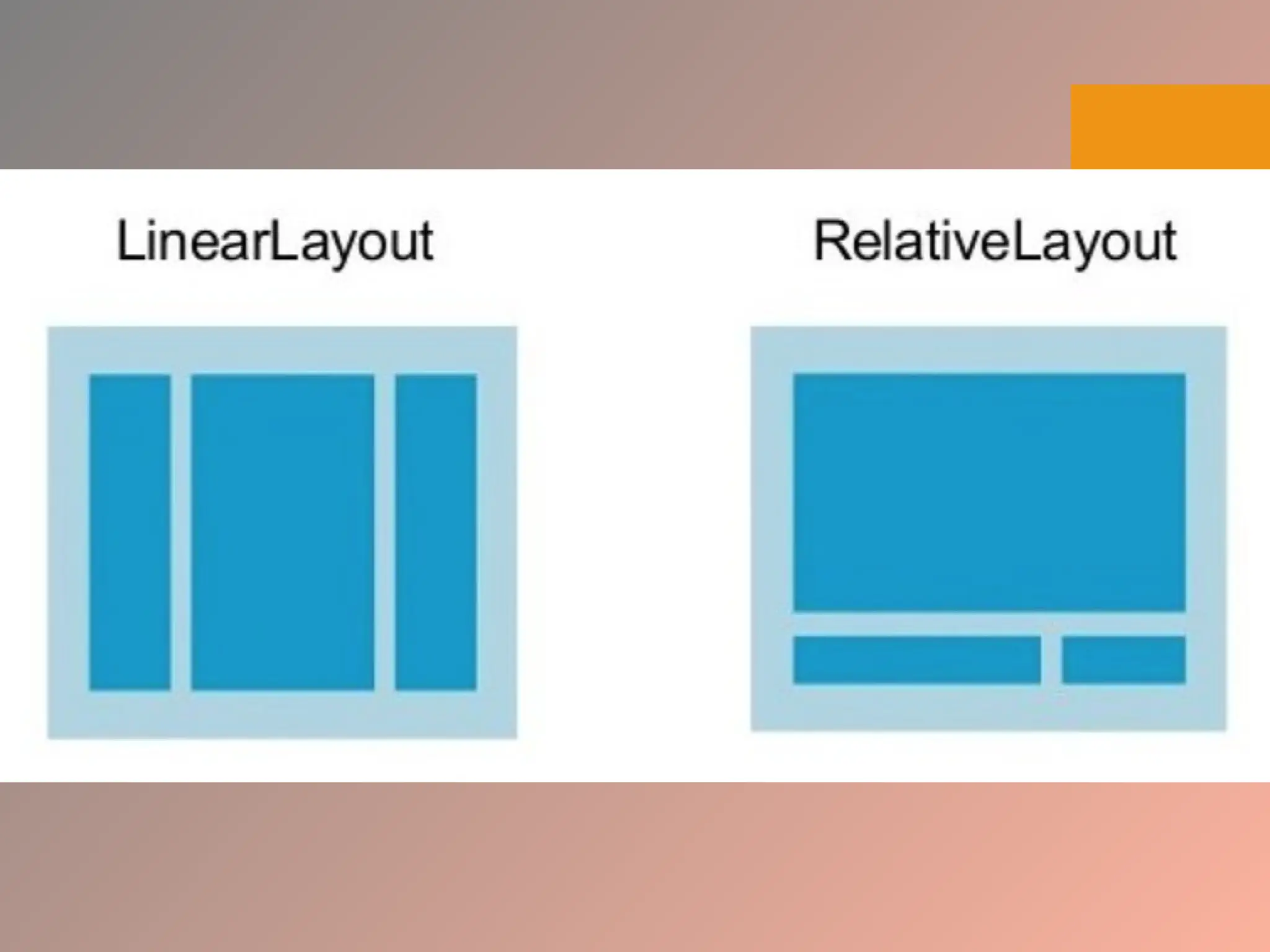
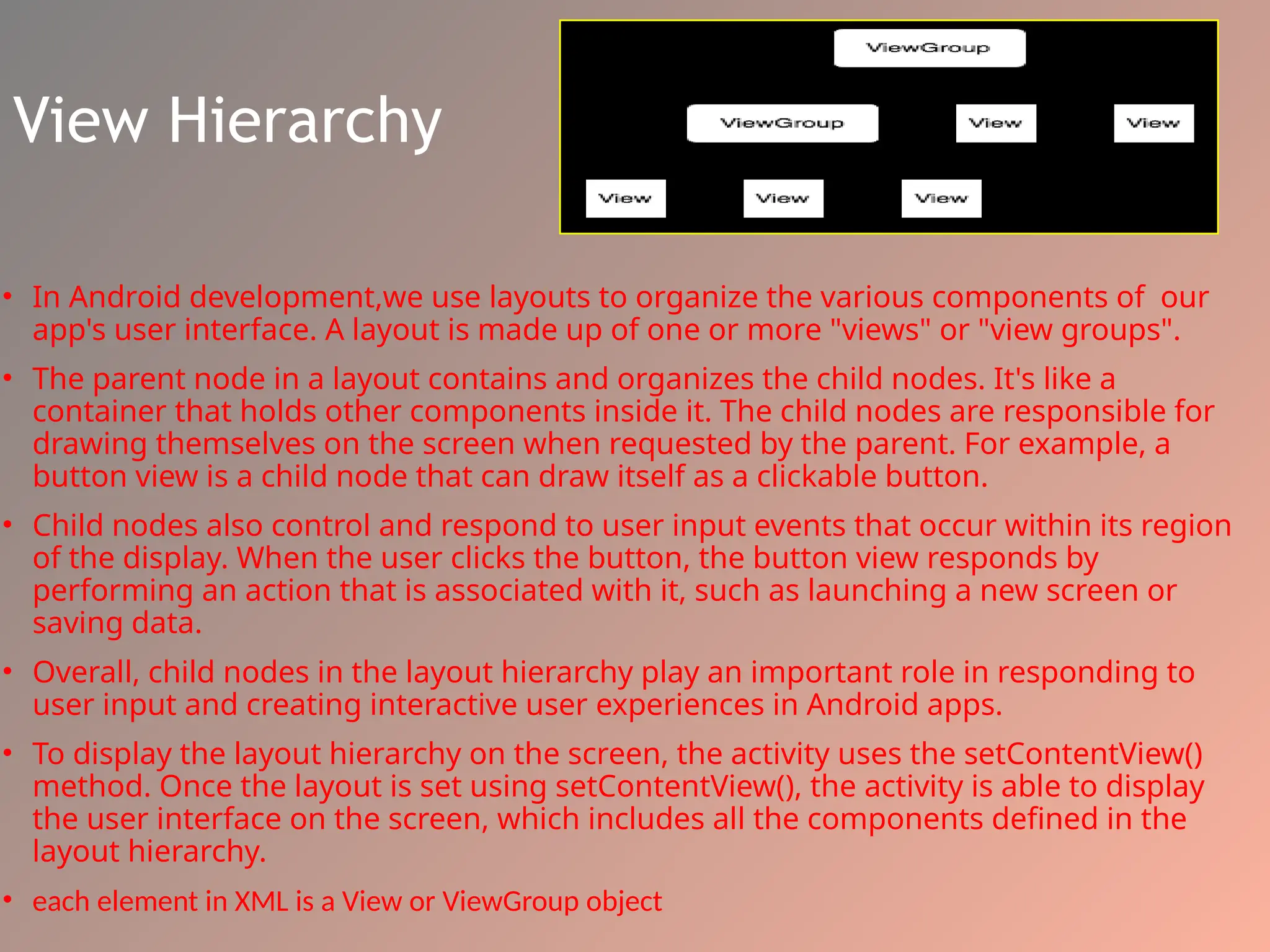
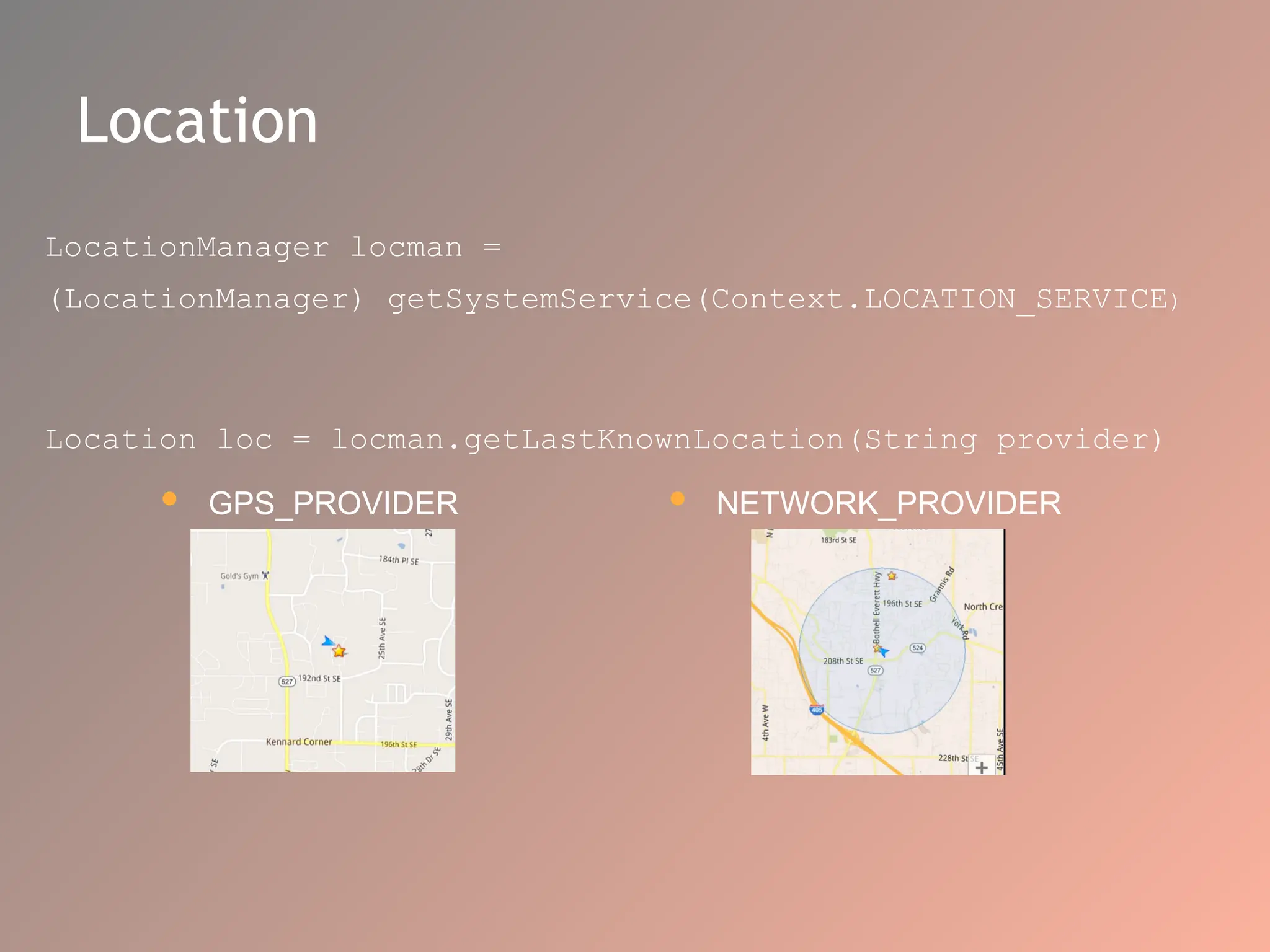
The document provides an overview of the Android operating system, detailing its software stack which includes the Android Runtime (ART), Linux kernel, and various libraries. It describes key components for app development such as activities, services, content providers, and broadcast receivers, alongside essential APIs for accessing device features. Additionally, the document outlines user interface construction using views and view groups, event handling, application menus, and Bluetooth functionalities.