This document provides an overview of Android technology, including:
- What Android is and its history as an open source operating system developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance.
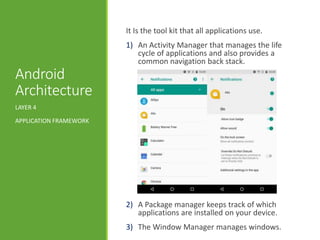
- The key components of the Android architecture including the Linux kernel, native libraries, runtime libraries, application framework, and applications.
- How to develop an Android app using Java and Kotlin, and some popular Android apps like Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp that have been downloaded billions of times.
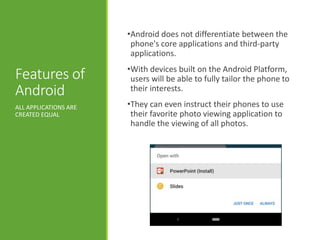
- Android versions, features like being open, customizable and breaking down barriers for developers, and benefits like reusability and security from running each app in its own process.