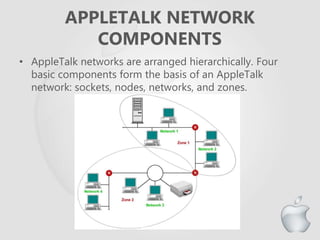
AppleTalk is a network operating system designed to connect Apple computers using their built-in networking capabilities. It uses CSMA/CA and can be implemented using twisted pair or fiber optic cabling in a bus or tree topology. AppleTalk networks are arranged hierarchically with sockets, nodes, networks, and zones. Common protocols used include AARP for address resolution, DDP as the network layer protocol, and AFP/SMB for file sharing. While once popular for small Apple networks, it has limitations for large networks and bandwidth intensive uses.