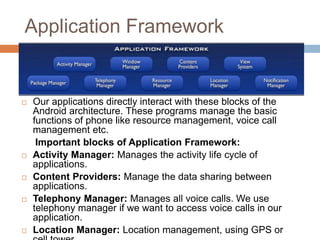
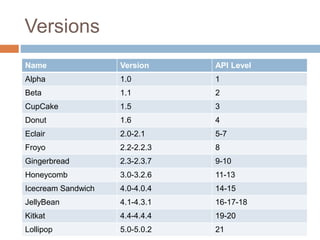
Android is an open-source operating system used for smartphones and tablets. It was developed by Android Inc., which was acquired by Google in 2005. The Android architecture includes the Linux kernel, native libraries, Android runtime including Dalvik virtual machine and core Java libraries, application framework, and applications. Key components of the application framework include activities, services, broadcast receivers, and content providers. Android features include a beautiful UI, connectivity, storage, media support, messaging, web browsing, multi-touch, multi-tasking, and resizable widgets. Major Android versions include Cupcake, Donut, Eclair, Froyo, Gingerbread, Honeycomb, Ice Cream Sandwich, Jelly Bean, KitKat, and