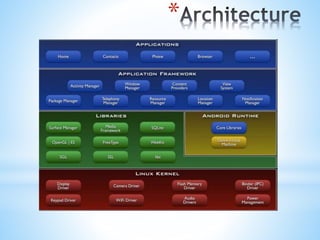
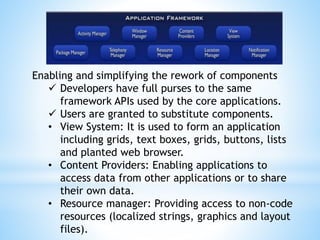
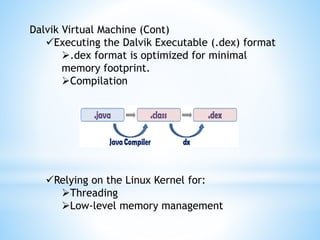
The document provides an overview of Android app development, detailing its origin as a Linux-based operating system developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance. It outlines the software stack comprising four layers, core applications, and various managers that facilitate functionality within applications. Additionally, it discusses the Dalvik virtual machine, which optimizes application performance and memory usage within the Android environment.