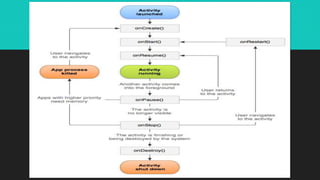
The document outlines the basics of the Android application lifecycle and how applications are defined through the Android manifest file. It explains that each application consists of activities, with specific attributes and methods for managing their lifecycle. The Android system automatically manages processes and provides callbacks for activities to handle various states like creation, start, resume, pause, and destruction.