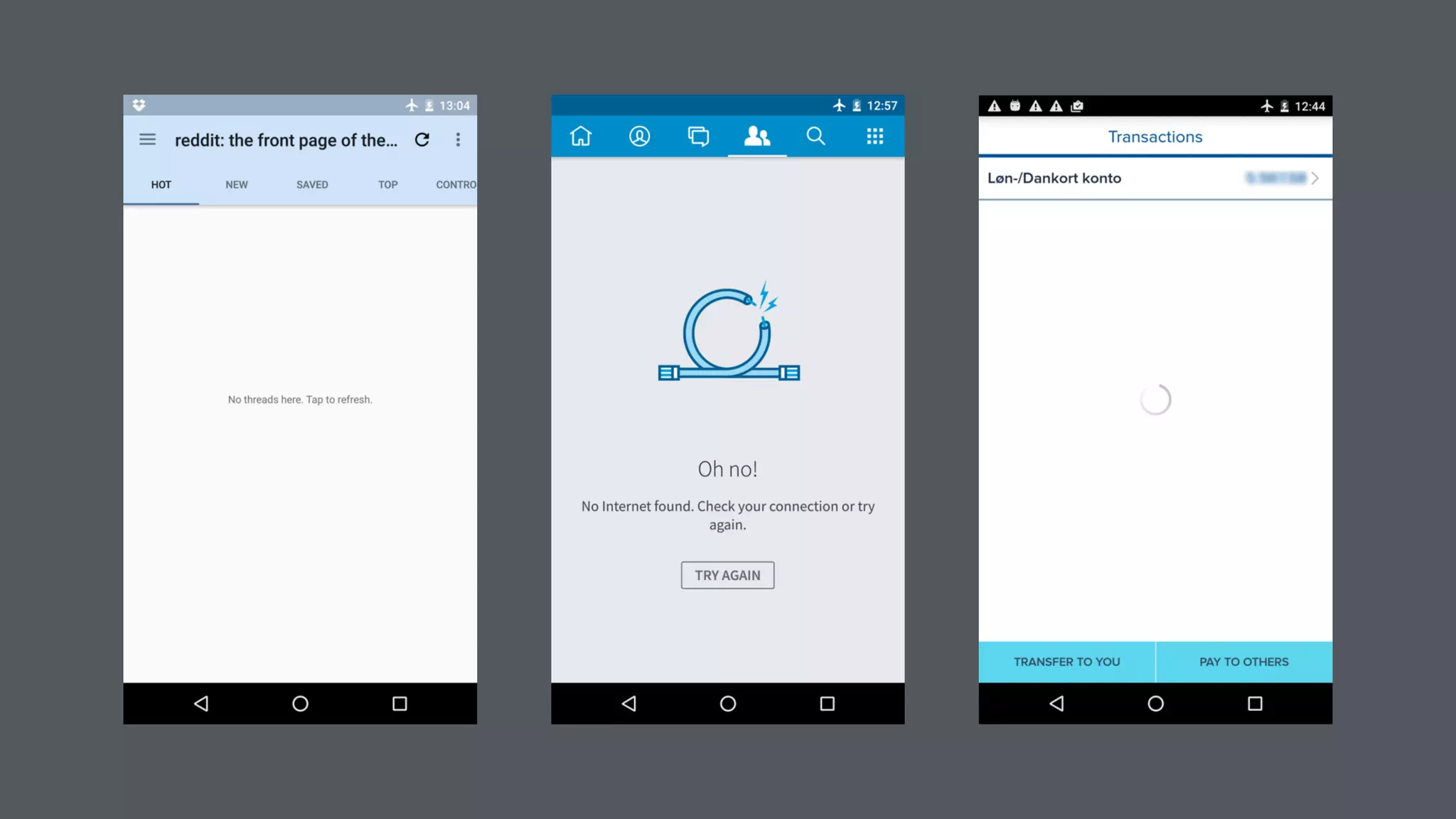
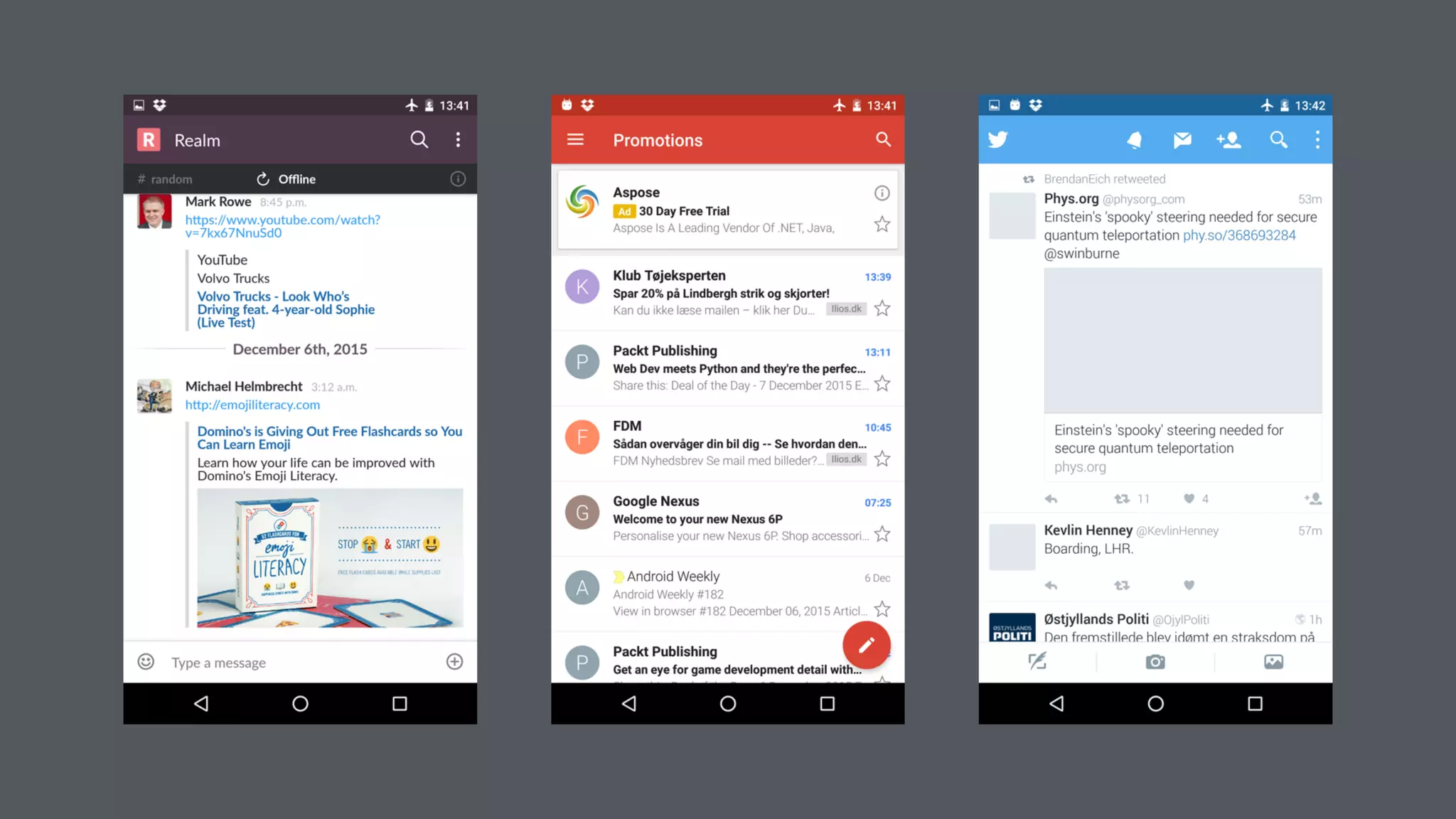
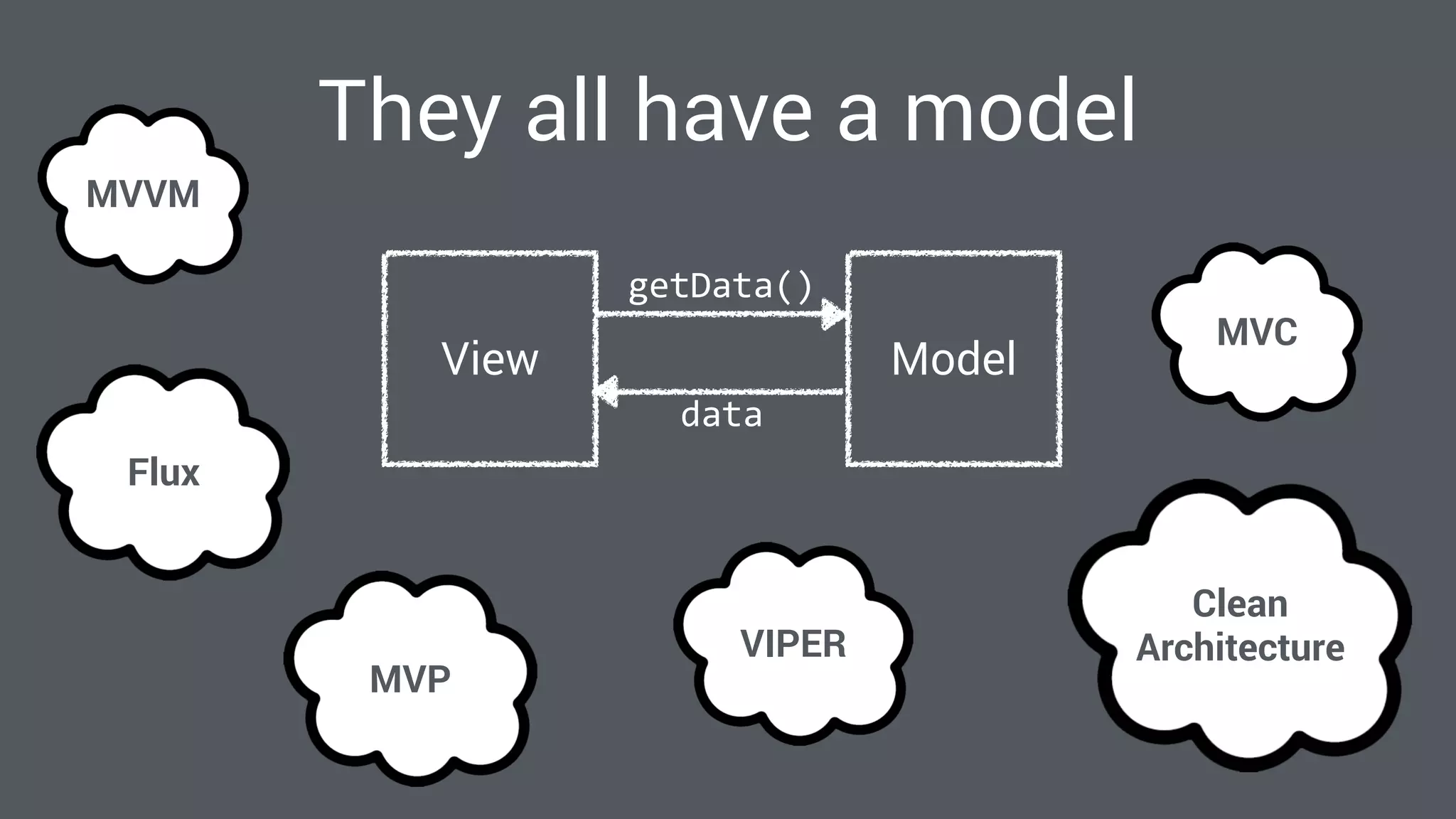
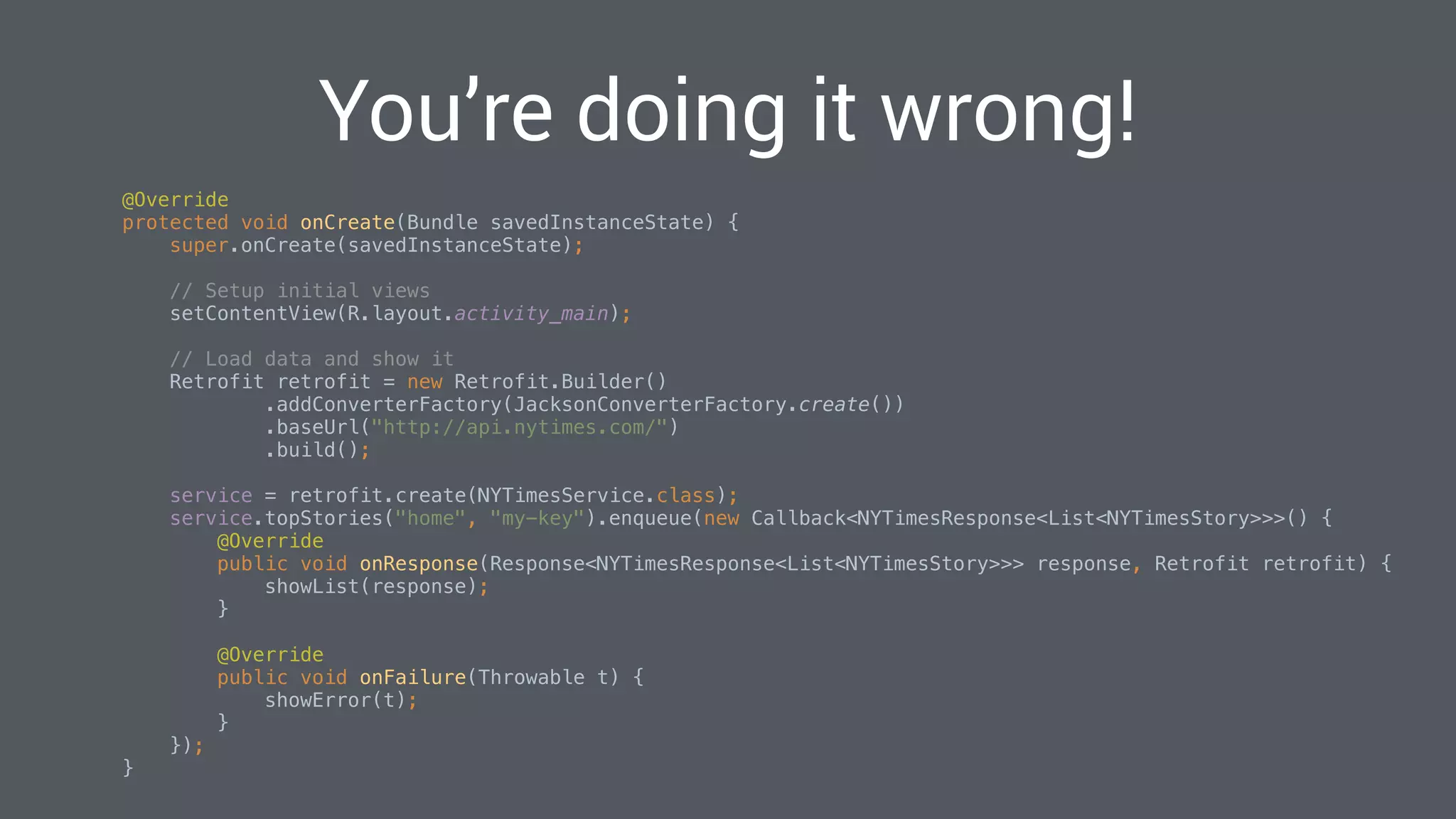
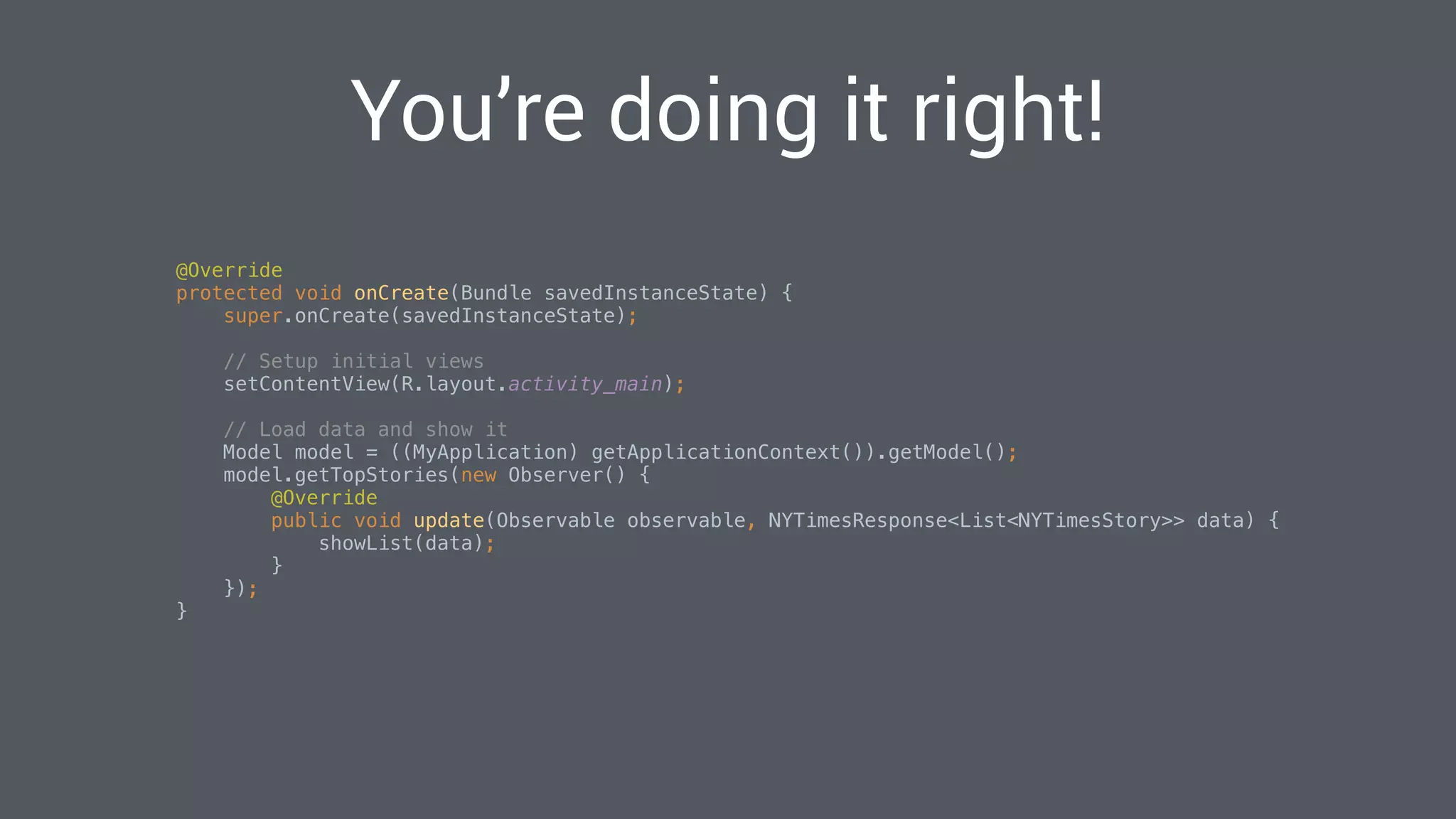
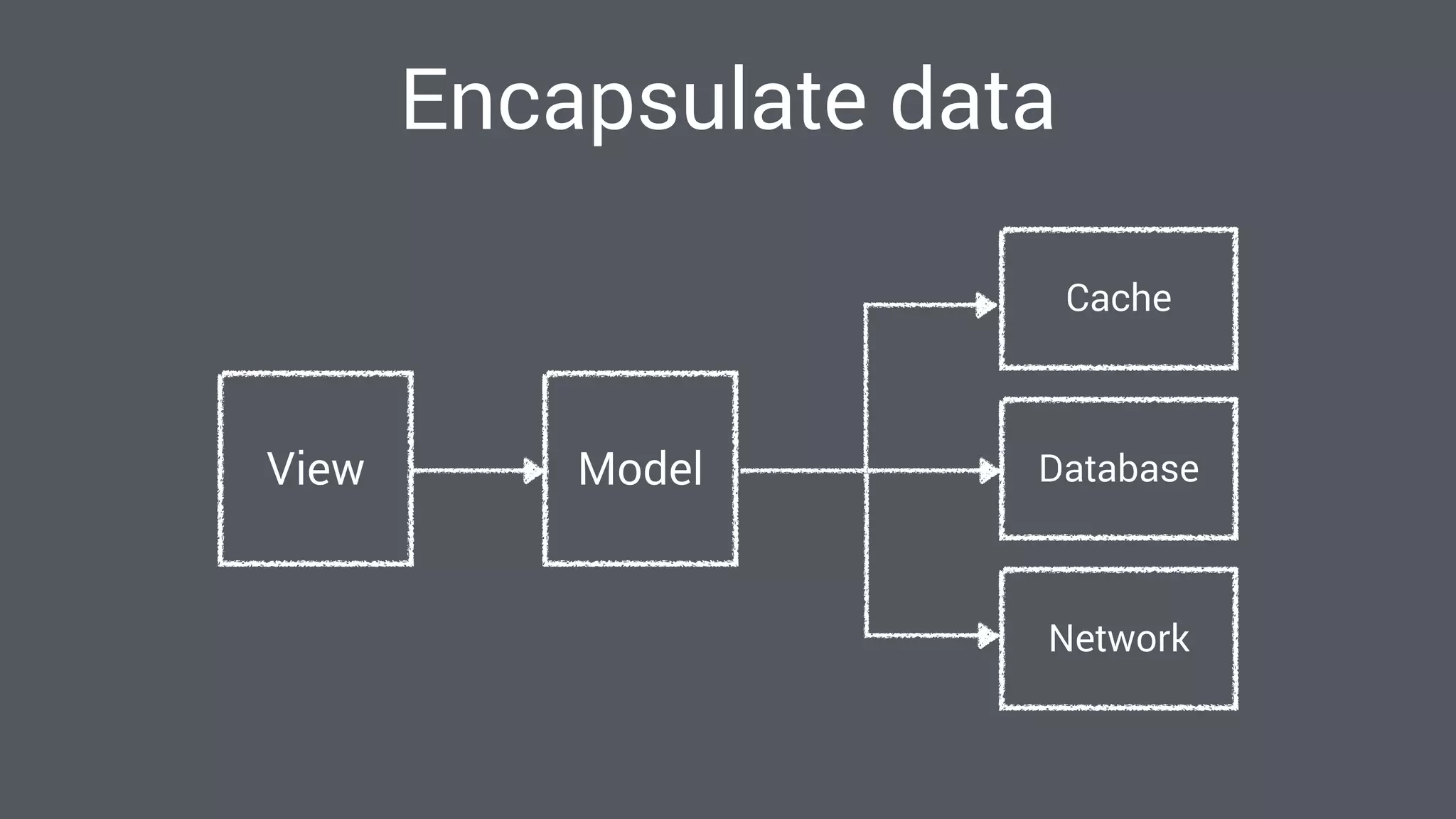
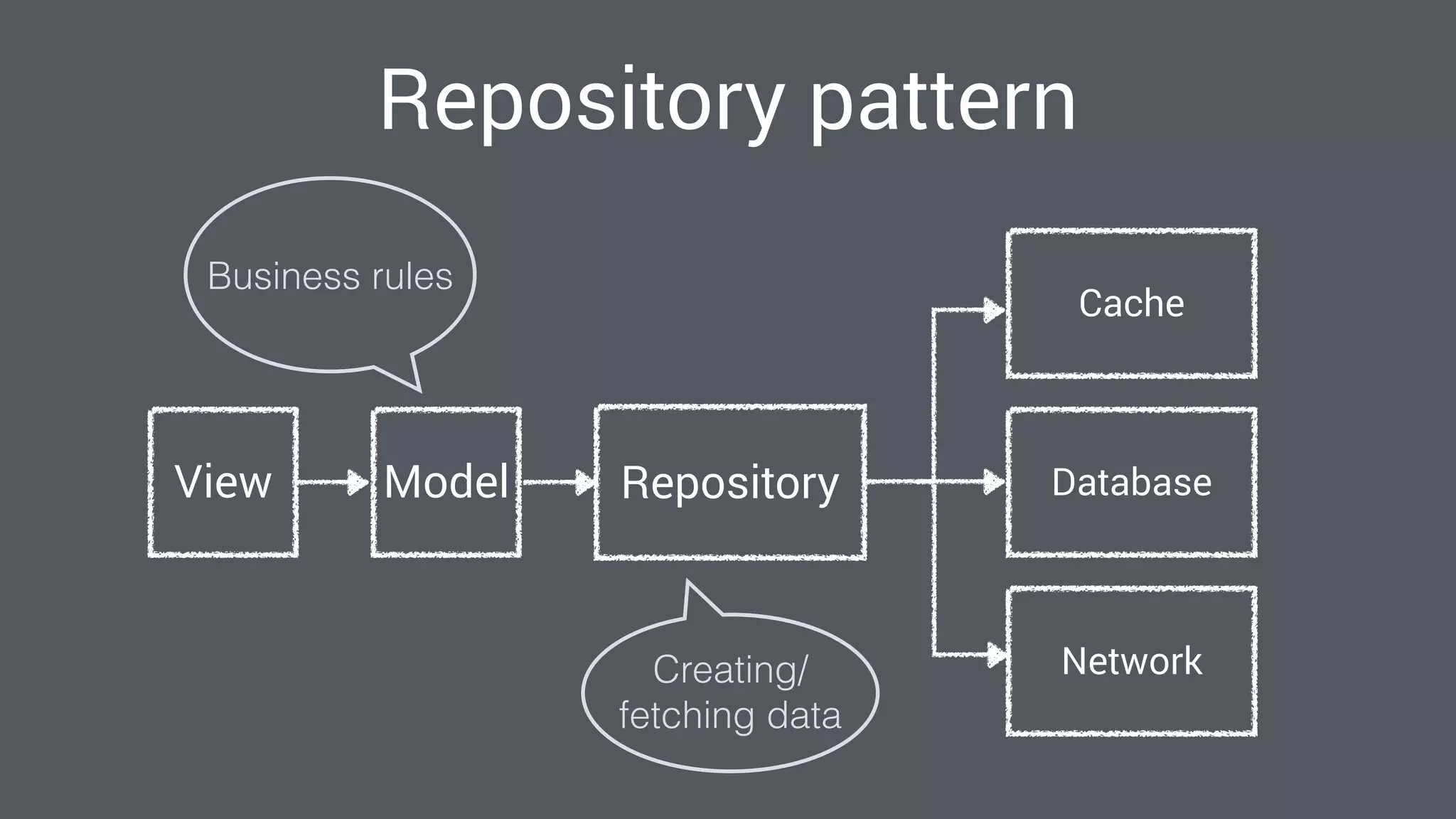
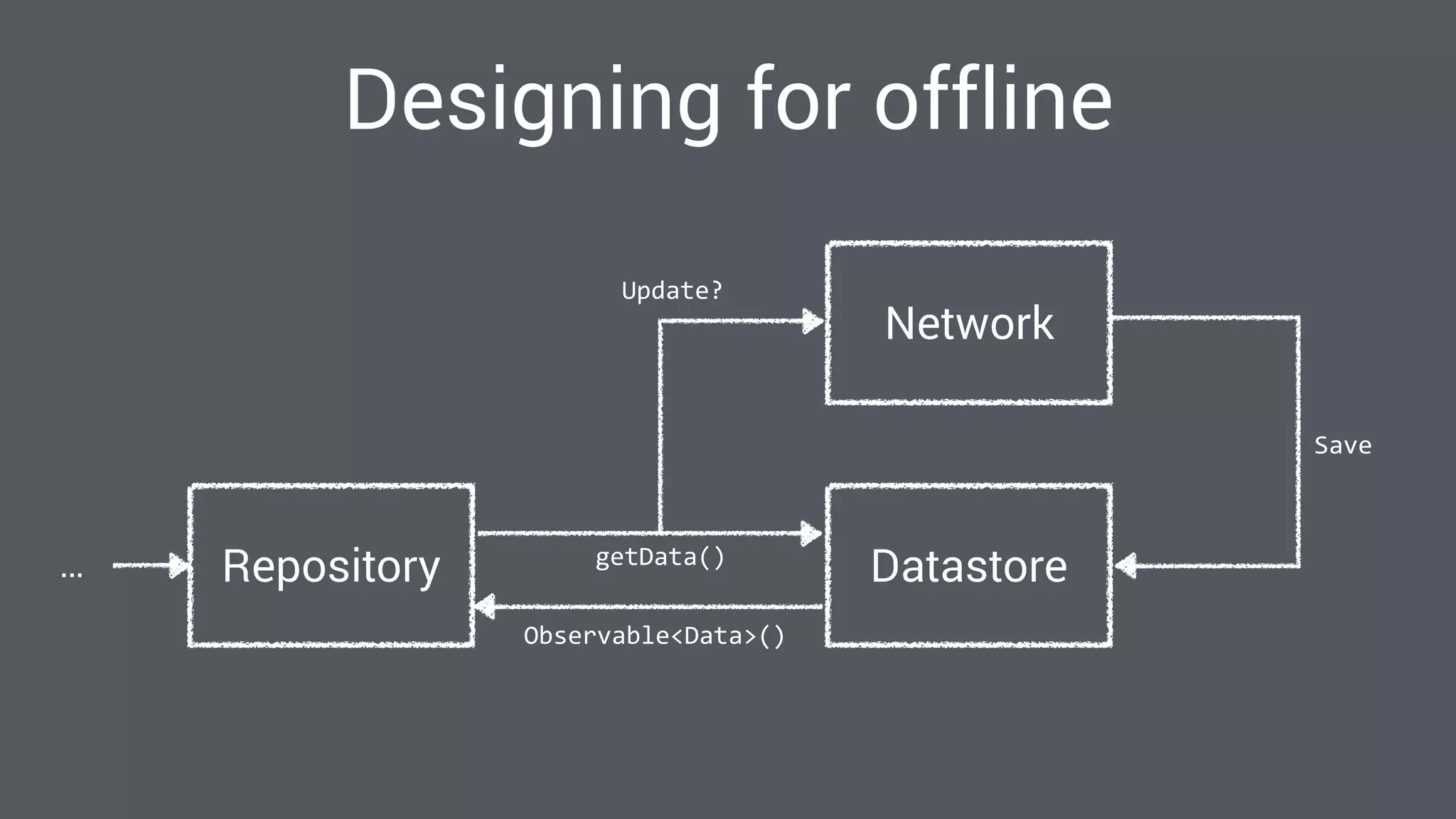
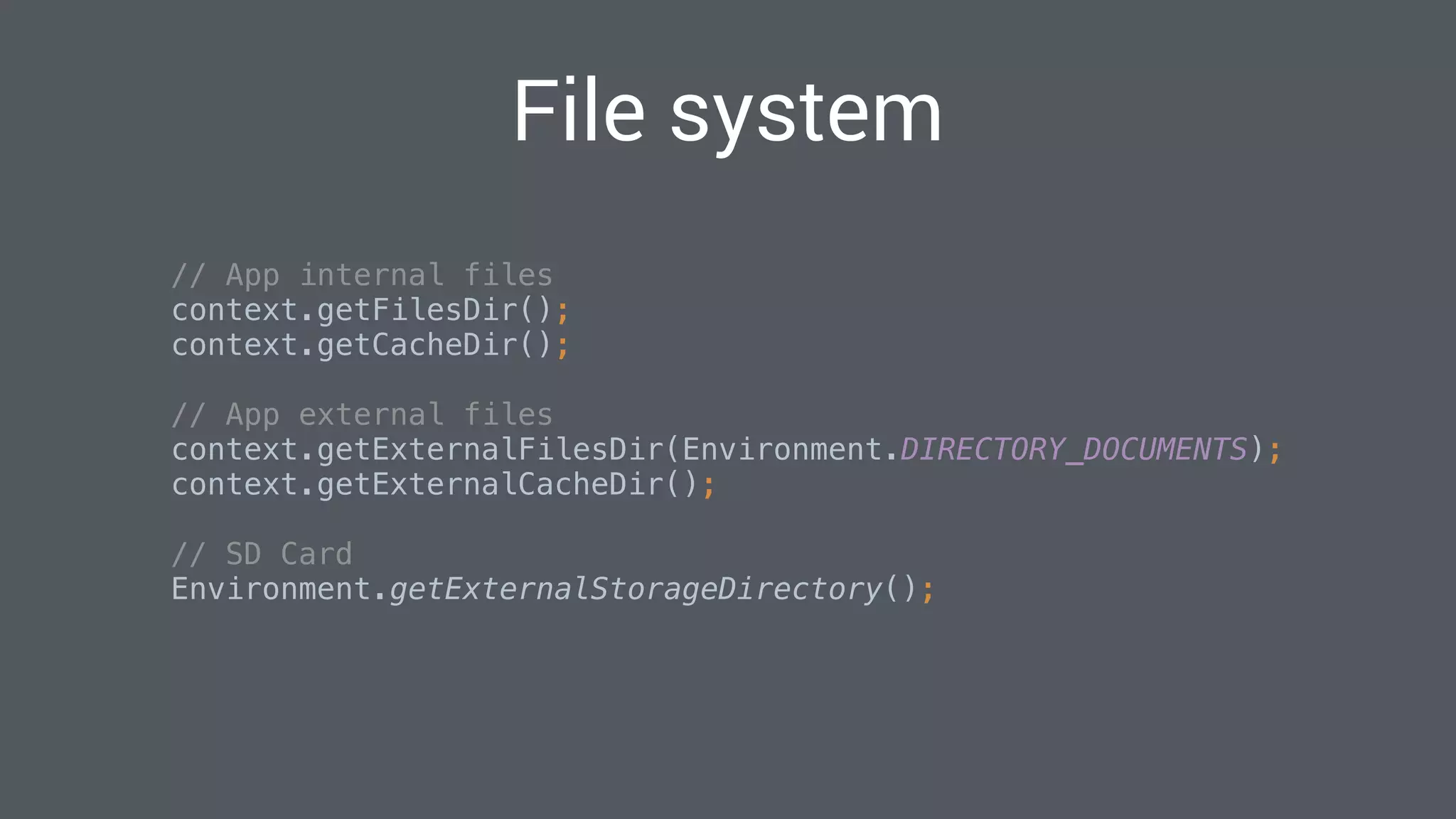
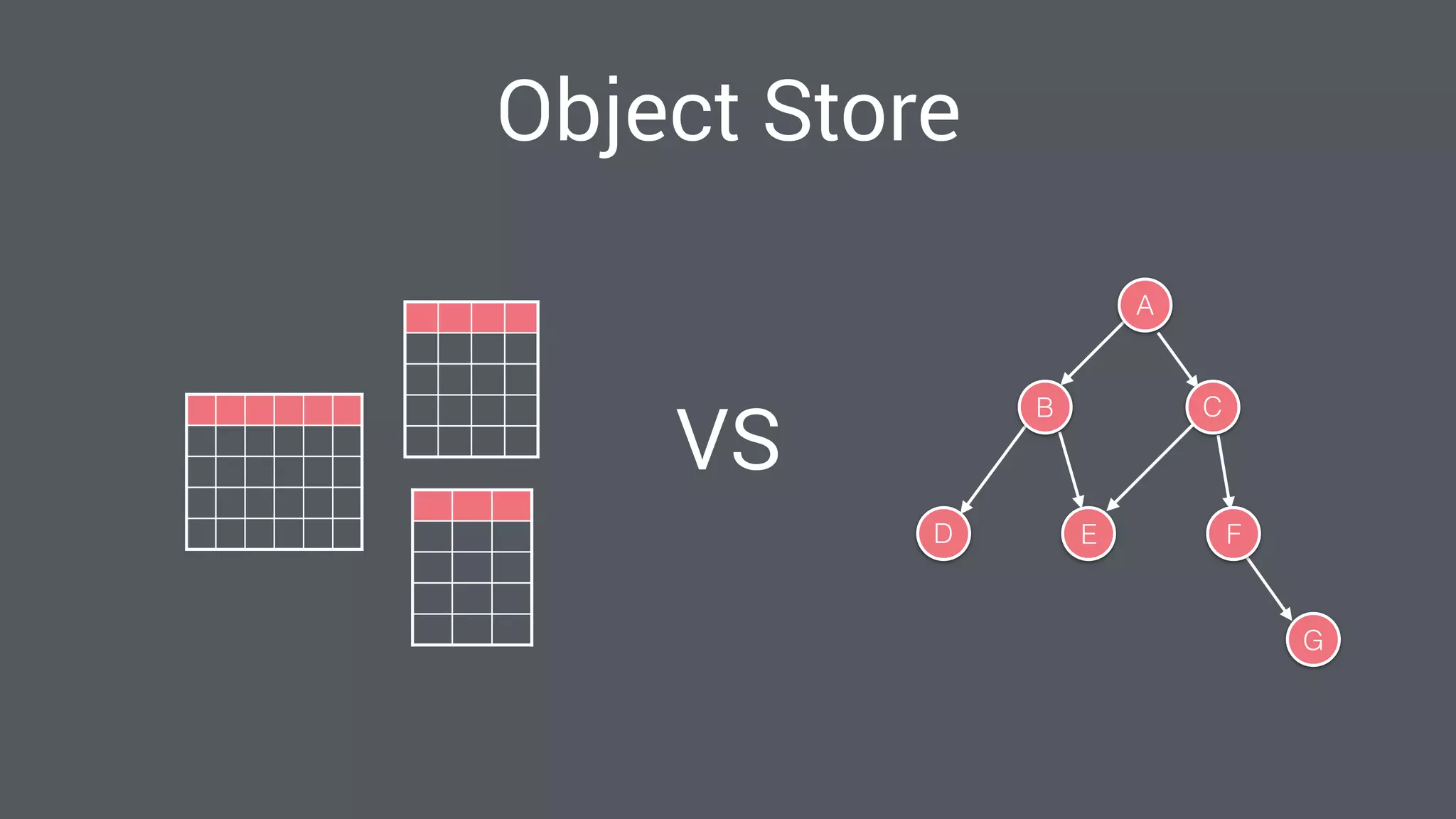
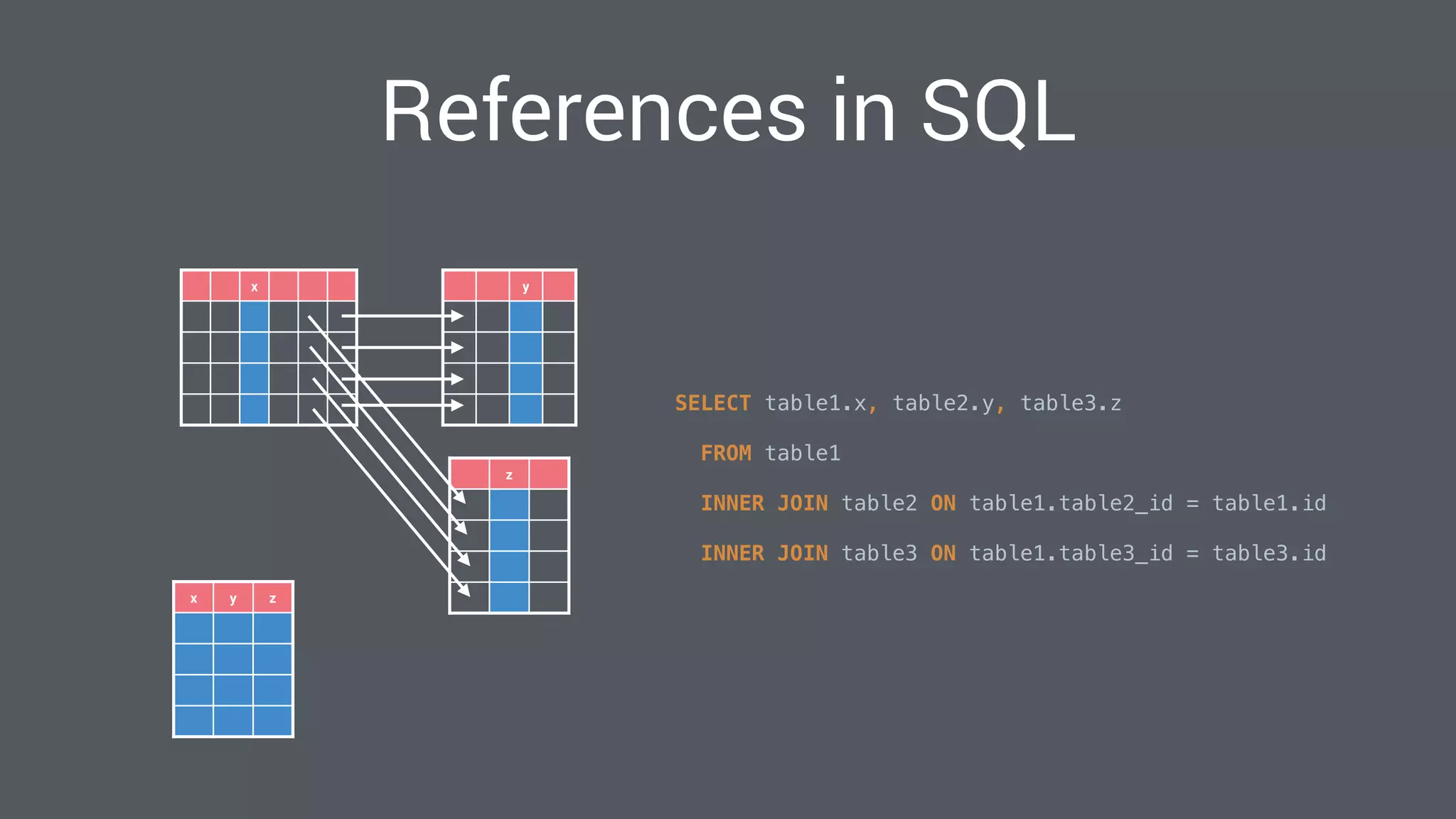
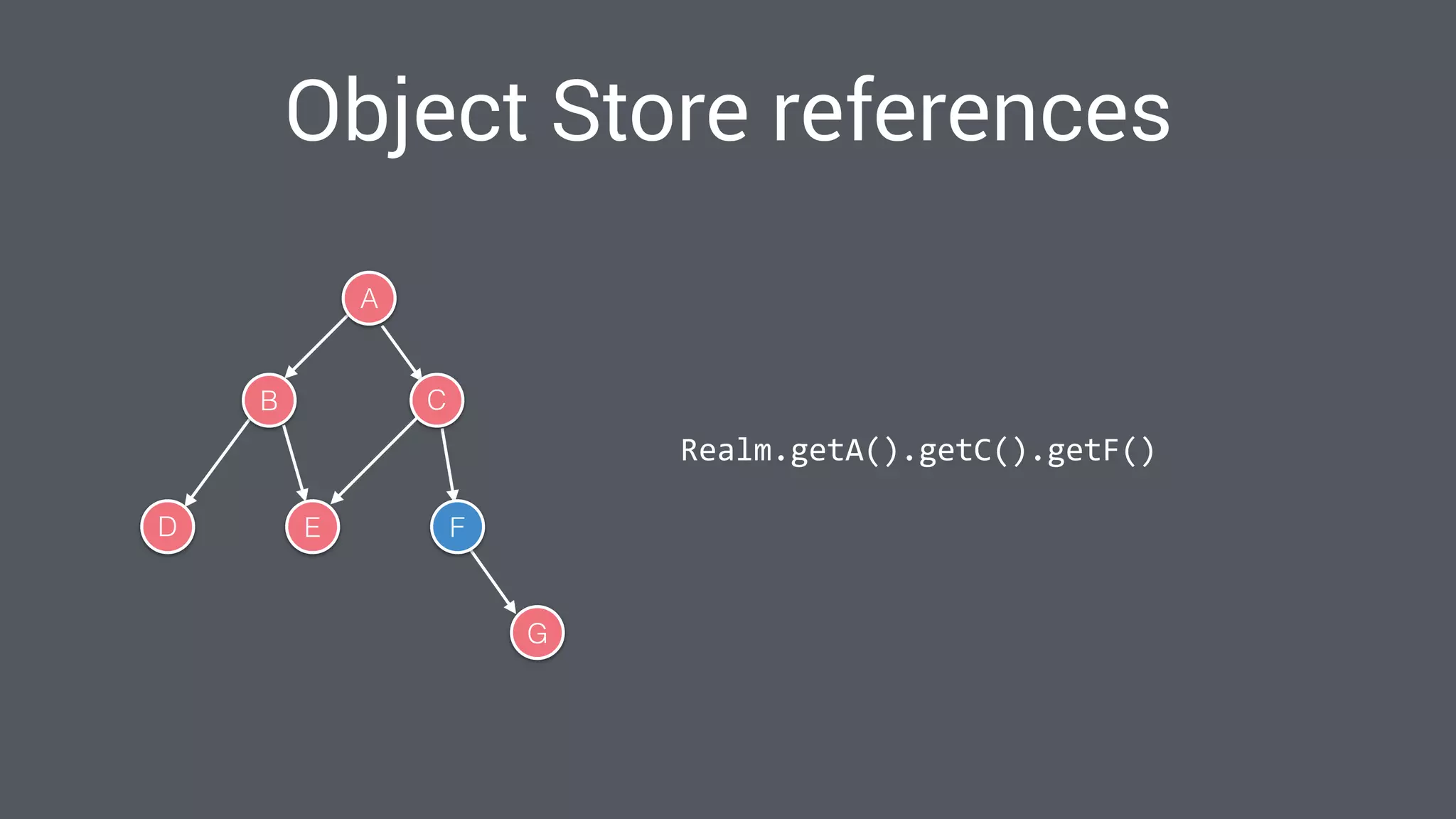
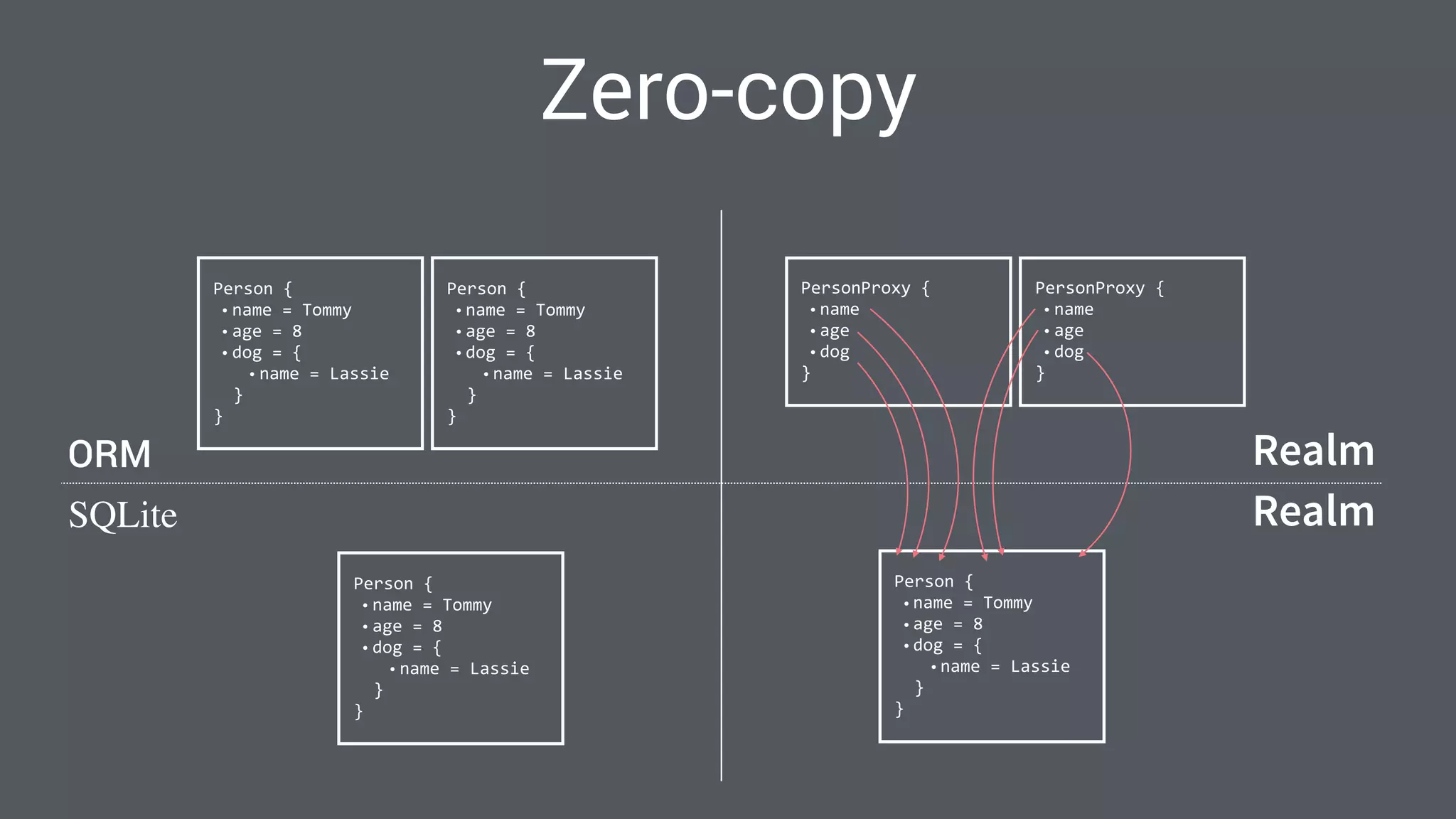
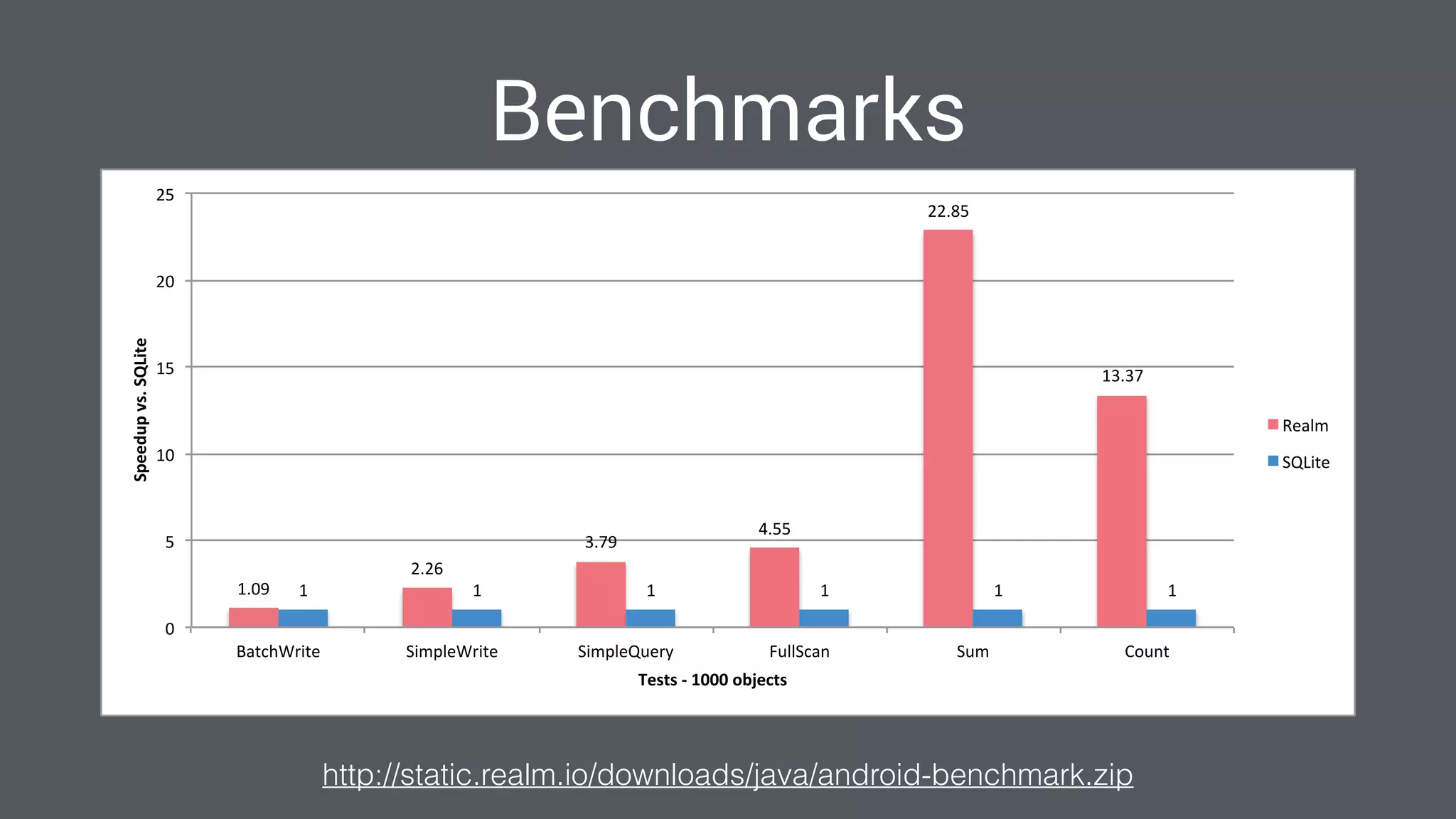
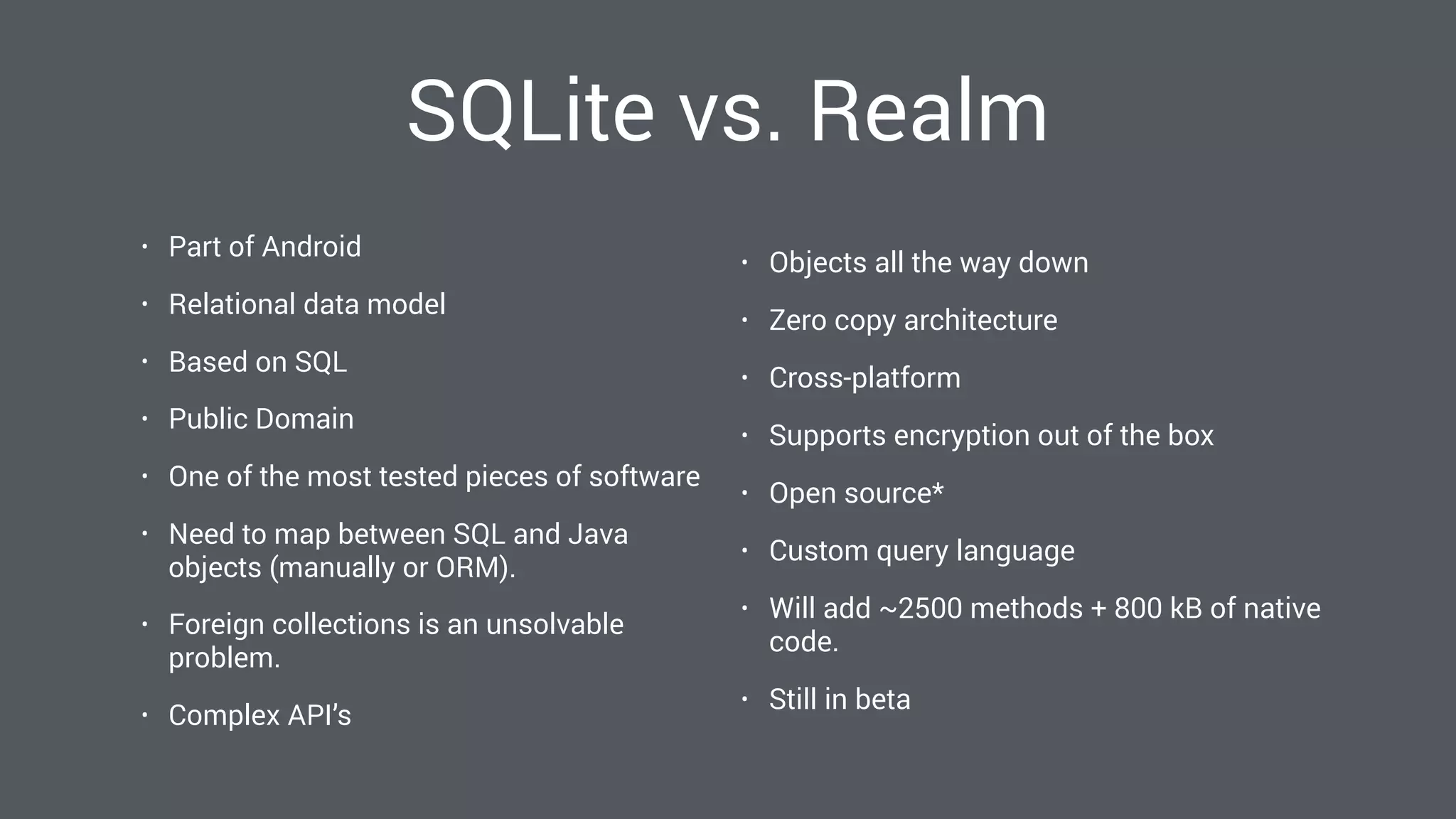
The document discusses best practices for designing Android applications that support offline functionality, highlighting the benefits such as improved user experience and reduced network usage. It covers various architectural patterns, data storage options, and the use of tools like Retrofit and Realm for data management. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of encapsulating data access and ensuring applications remain functional without a constant internet connection.