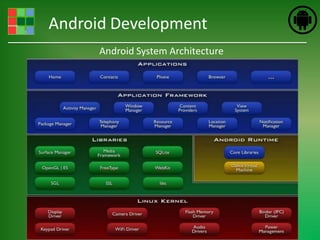
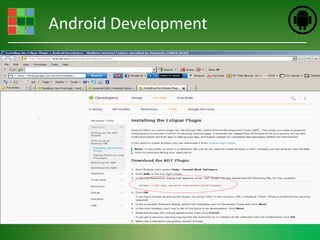
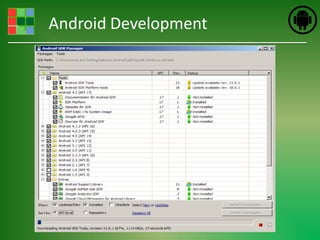
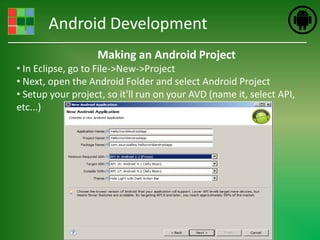
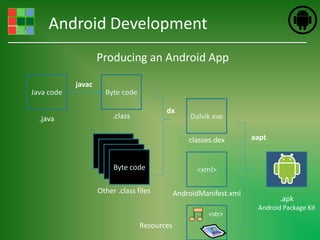
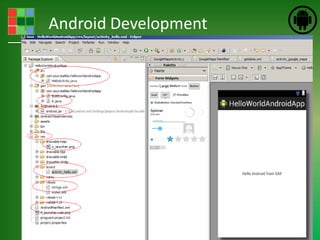
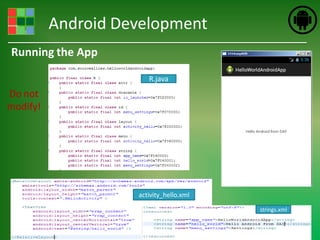
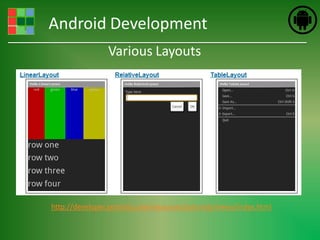
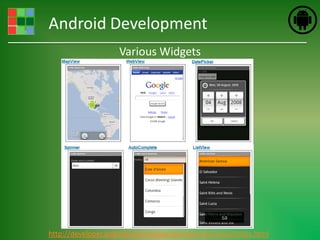
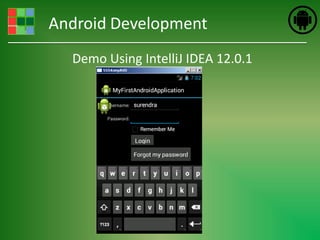
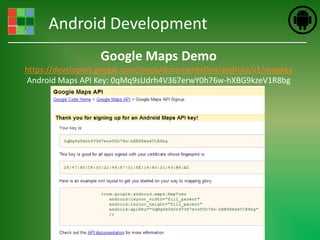
This document provides an introduction and overview of Android application development. It discusses what Android is, how to install the necessary development tools like Eclipse and the Android SDK, and covers Android application fundamentals such as the different application components and the Android manifest file. It also demonstrates how to create a simple "Hello World" Android application in Eclipse by setting up an Android virtual device, creating an Android project, writing the code, and running the app on the emulator.