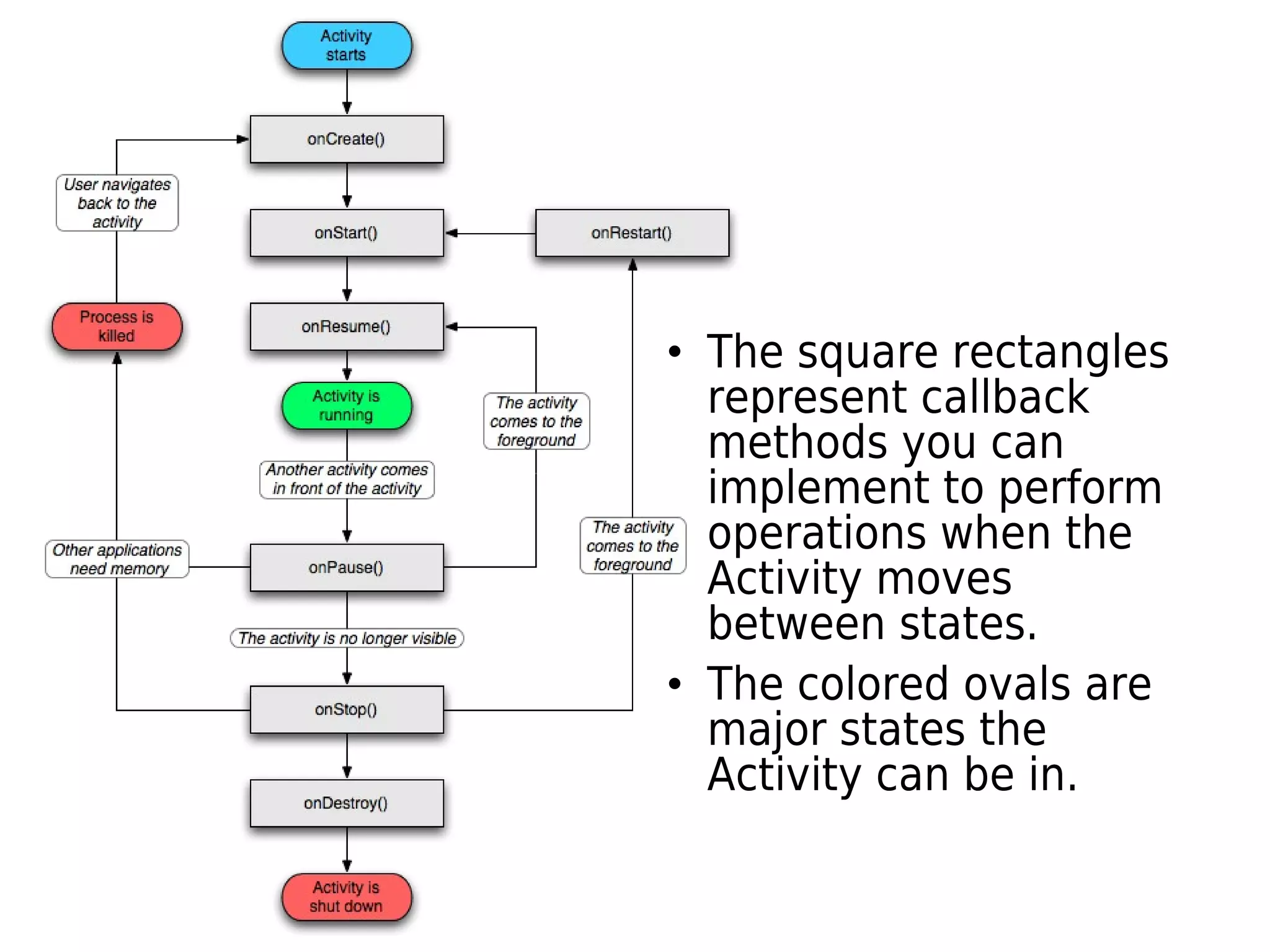
An Android activity presents a visual user interface for a focused task. It contains a hierarchy of views that provide the visual content and user interaction. Each activity has a default window and a content view hierarchy set with setContentView(). An application can contain multiple activities, with one specified as the initial activity in the manifest. Activities transition between running, paused, and stopped states, notifying the activity of changes through callback methods like onCreate(), onStart(), onResume(), etc. Activities are managed in a stack, with new activities placed on top and previous activities remaining below until the top activity exits.