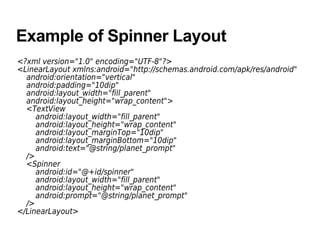
Android UI adapters allow AdapterViews like ListView and Spinner to display data. AdapterViews rely on Adapters to provide Views for each data item. Adapters implement interfaces like ListAdapter and bind data to Views. ListActivity makes it easy to display a list using a ListAdapter like ArrayAdapter. Spinner displays a single child and uses a SpinnerAdapter to provide its dropdown options.












![Example of ListActivity Class
public class HelloListView extends ListActivity {
static final String[] COUNTRIES = new String[] {
"Yemen", "Yugoslavia", "Zambia", "Zimbabwe"
};
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Create an adapter
ArrayAdapter<String> arrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(
this, // Application context
R.layout.list_item, // layout description for each list item
COUNTRIES); // String array of countries defined
// Notice that this does not load a layout file for the Activity (which you
// usually do with setContentView(int)). Instead, setListAdapter(ListAdapter)
// automatically adds a ListView to fill the entire screen of the ListActivity.
setListAdapter(arrayAdapter);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androiduiadapter-101126073314-phpapp01/85/Android-ui-adapter-13-320.jpg)