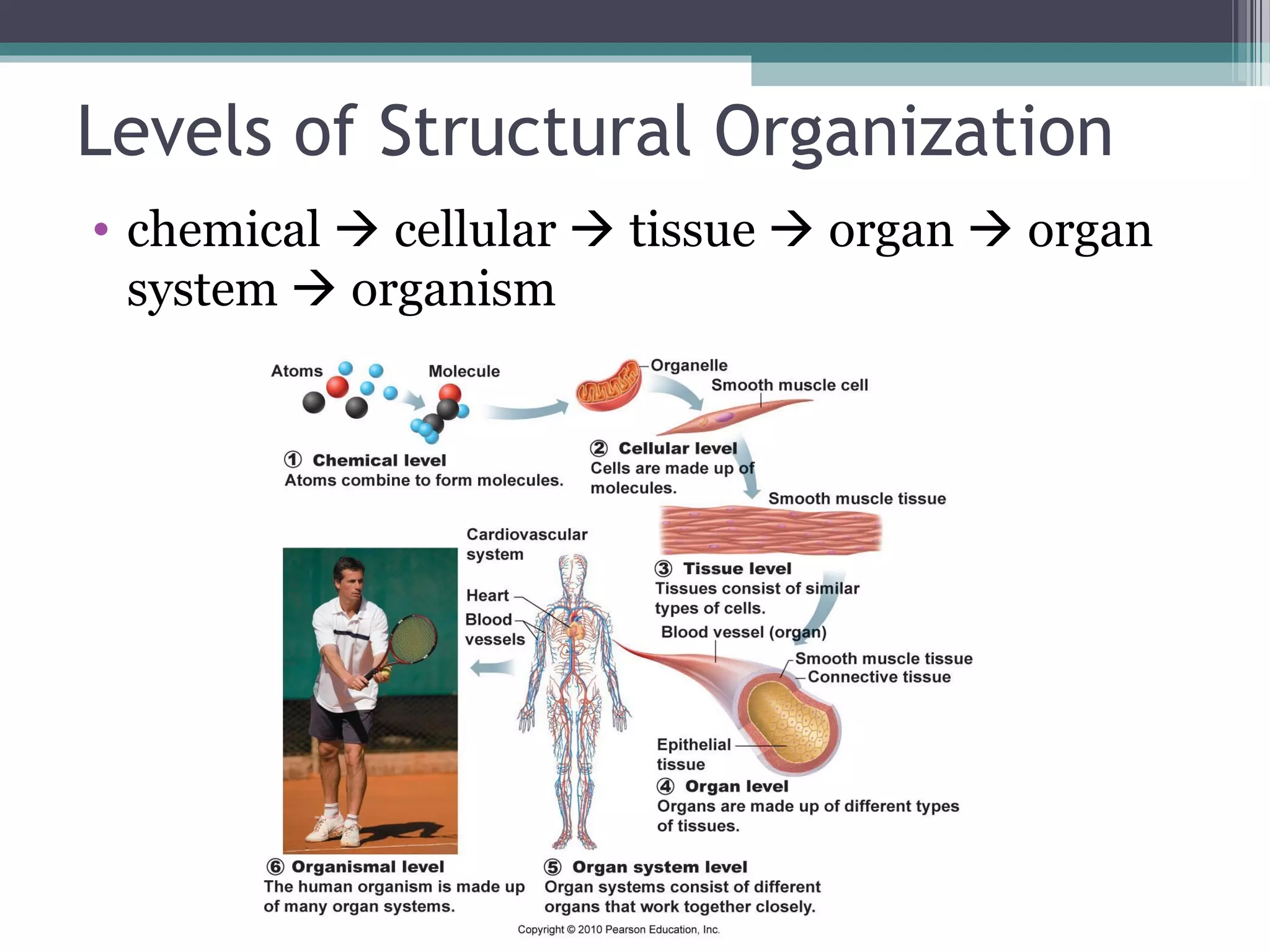
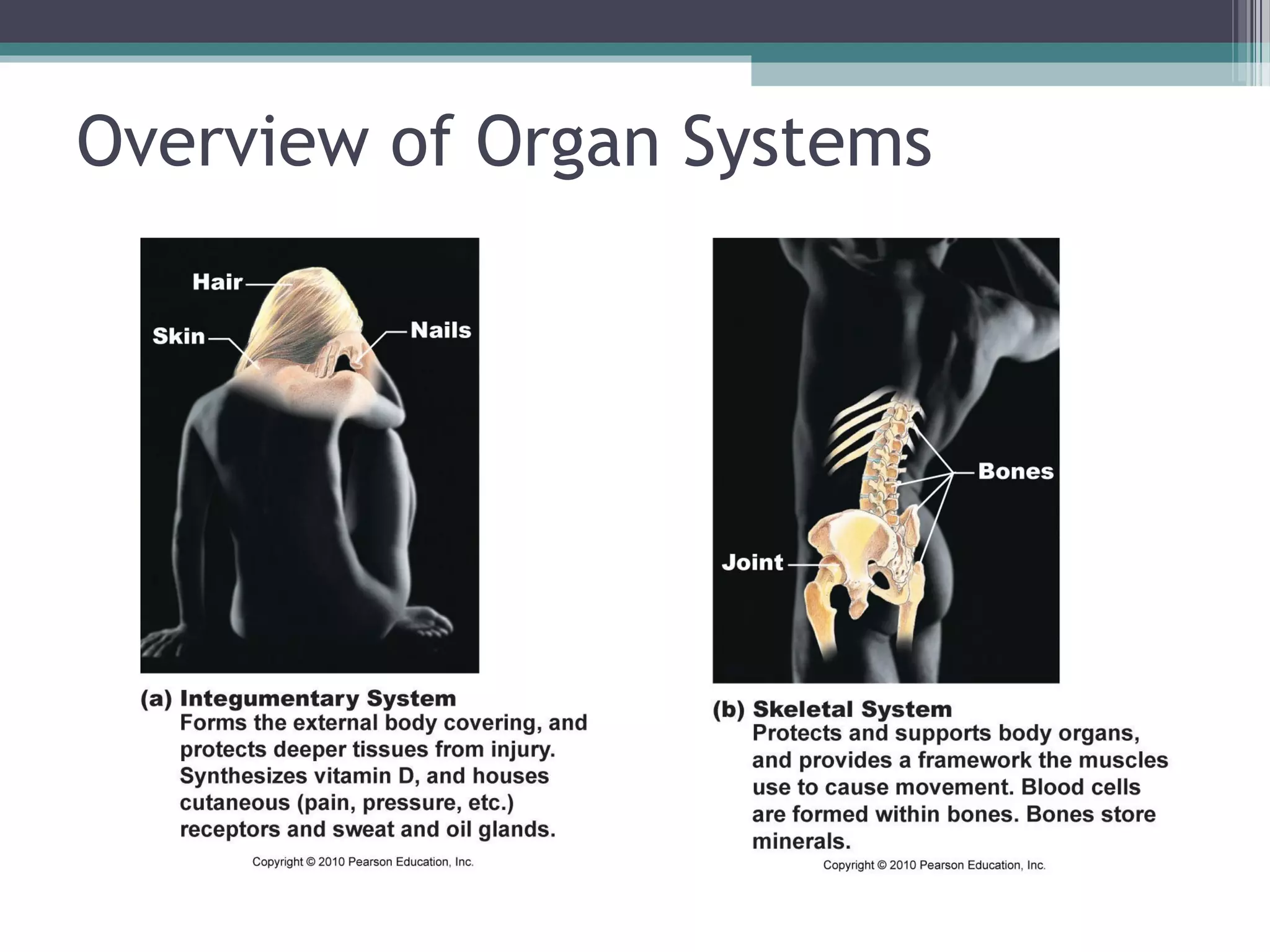
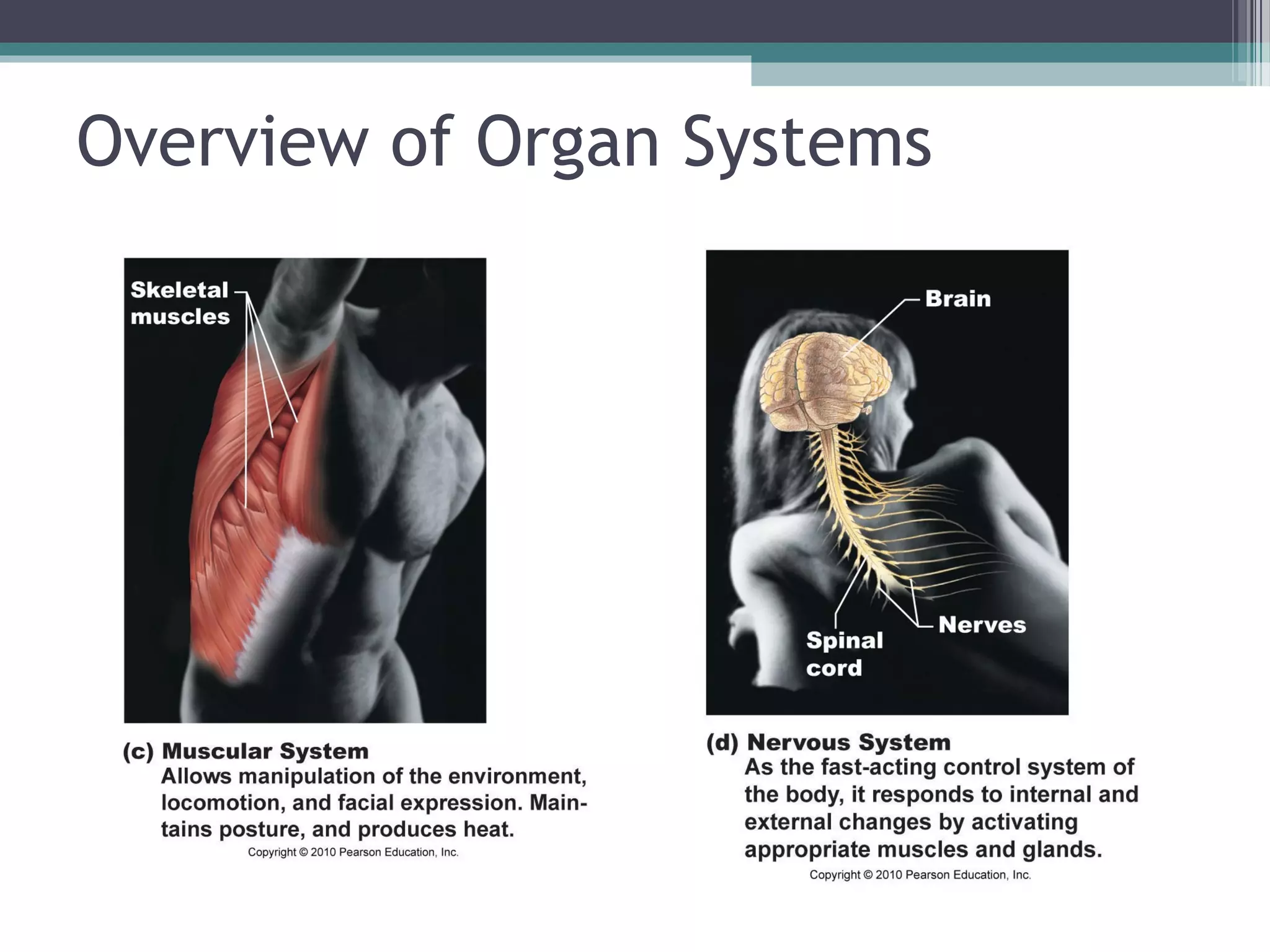
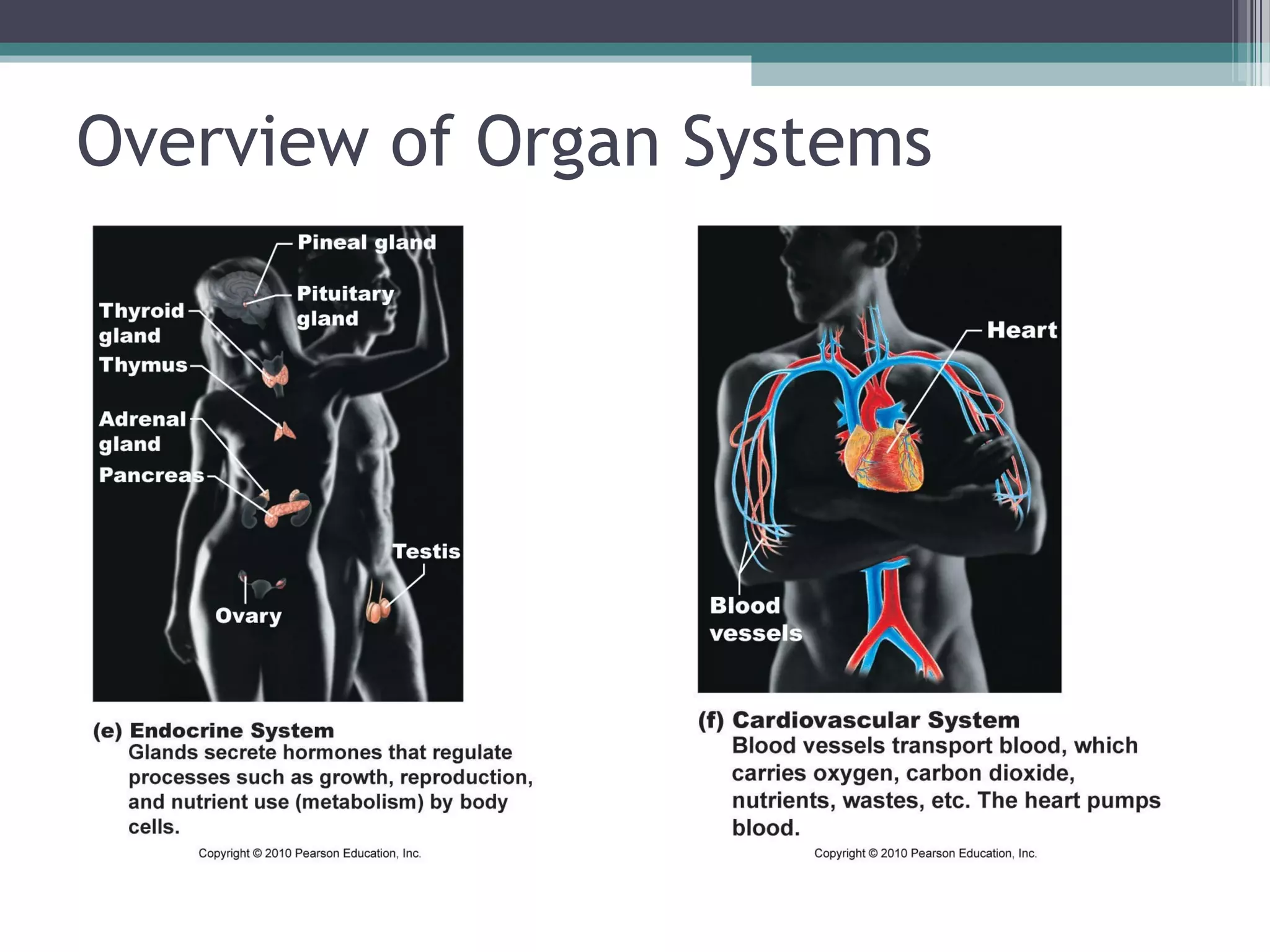
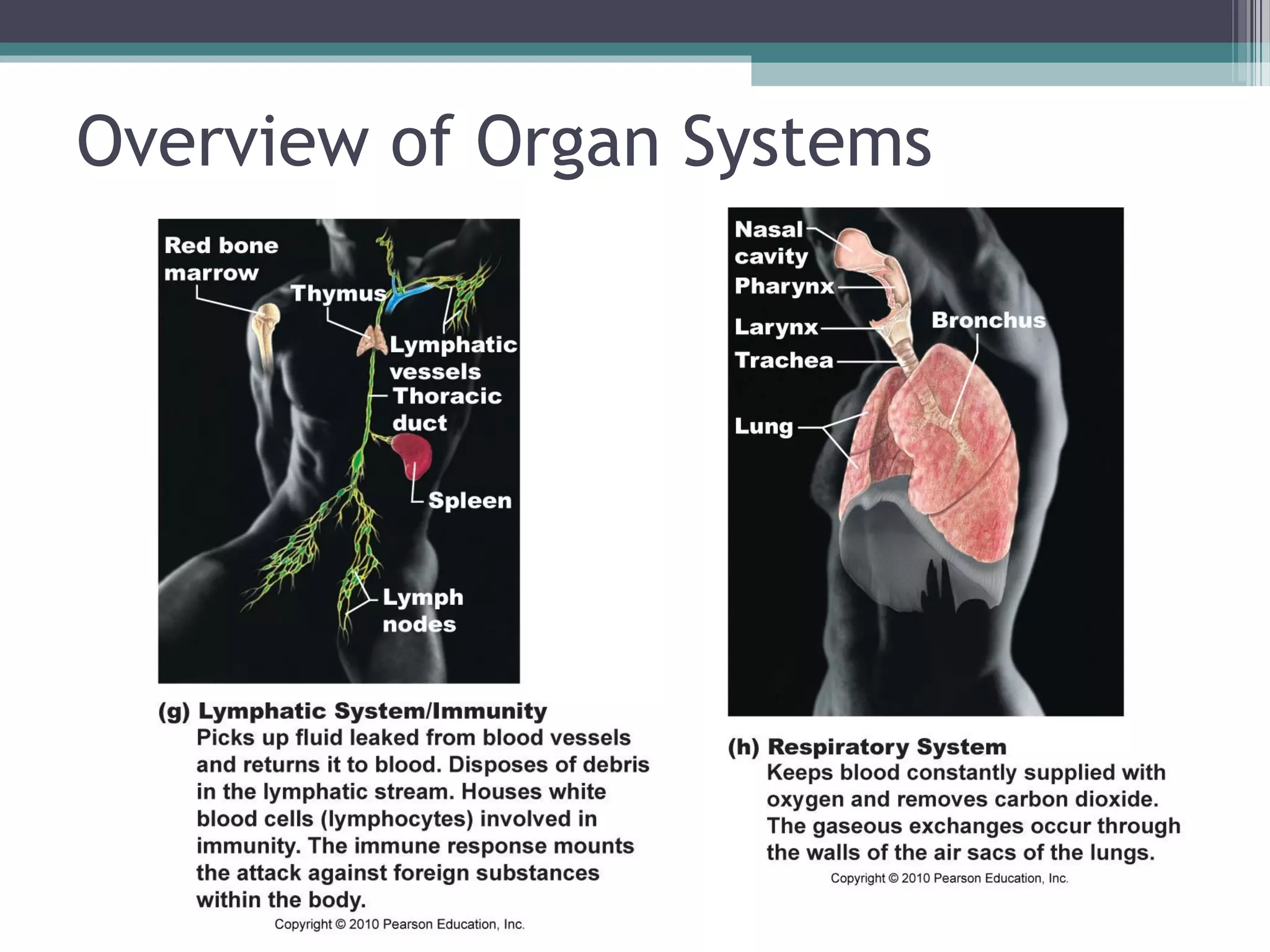
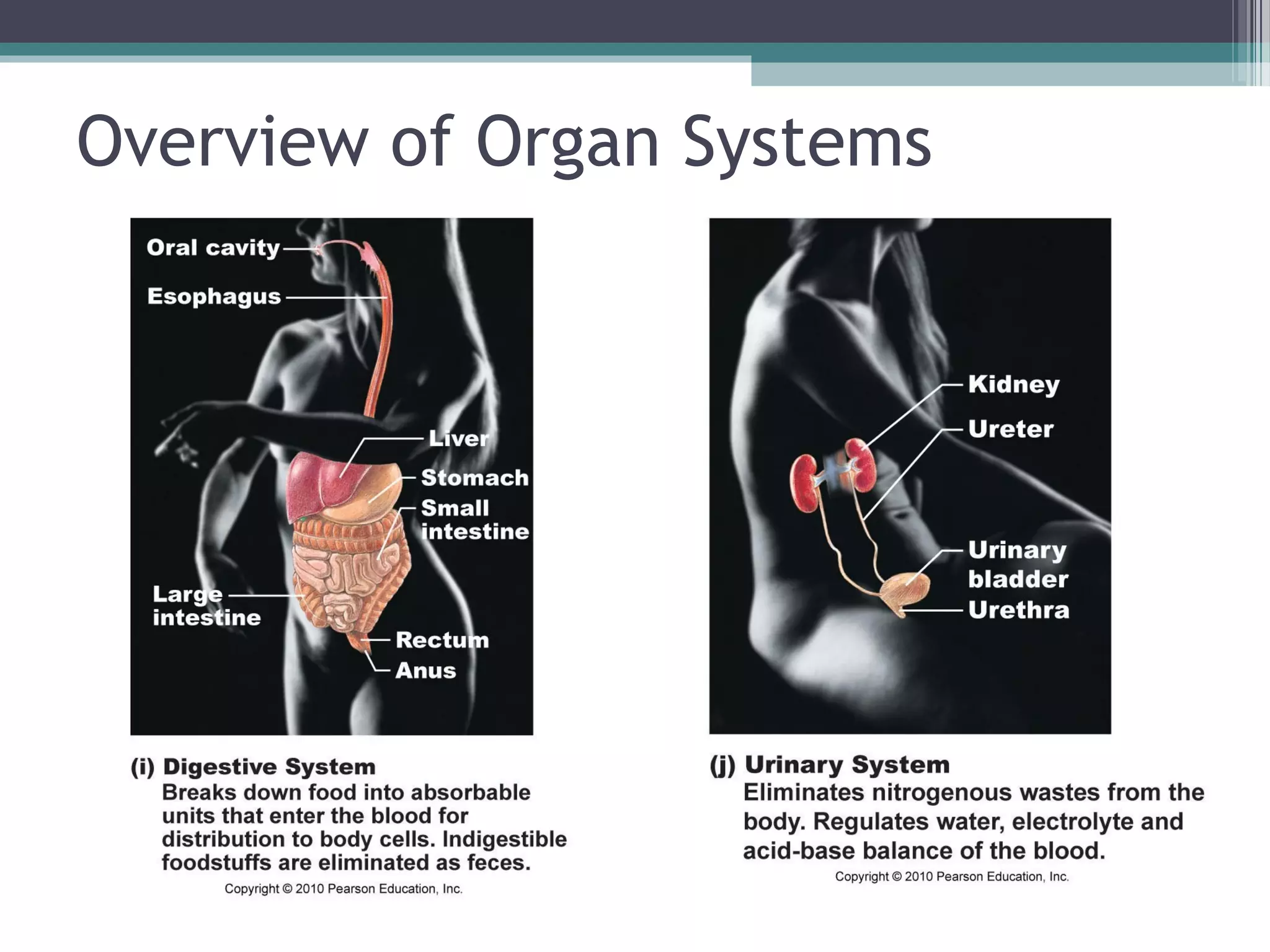
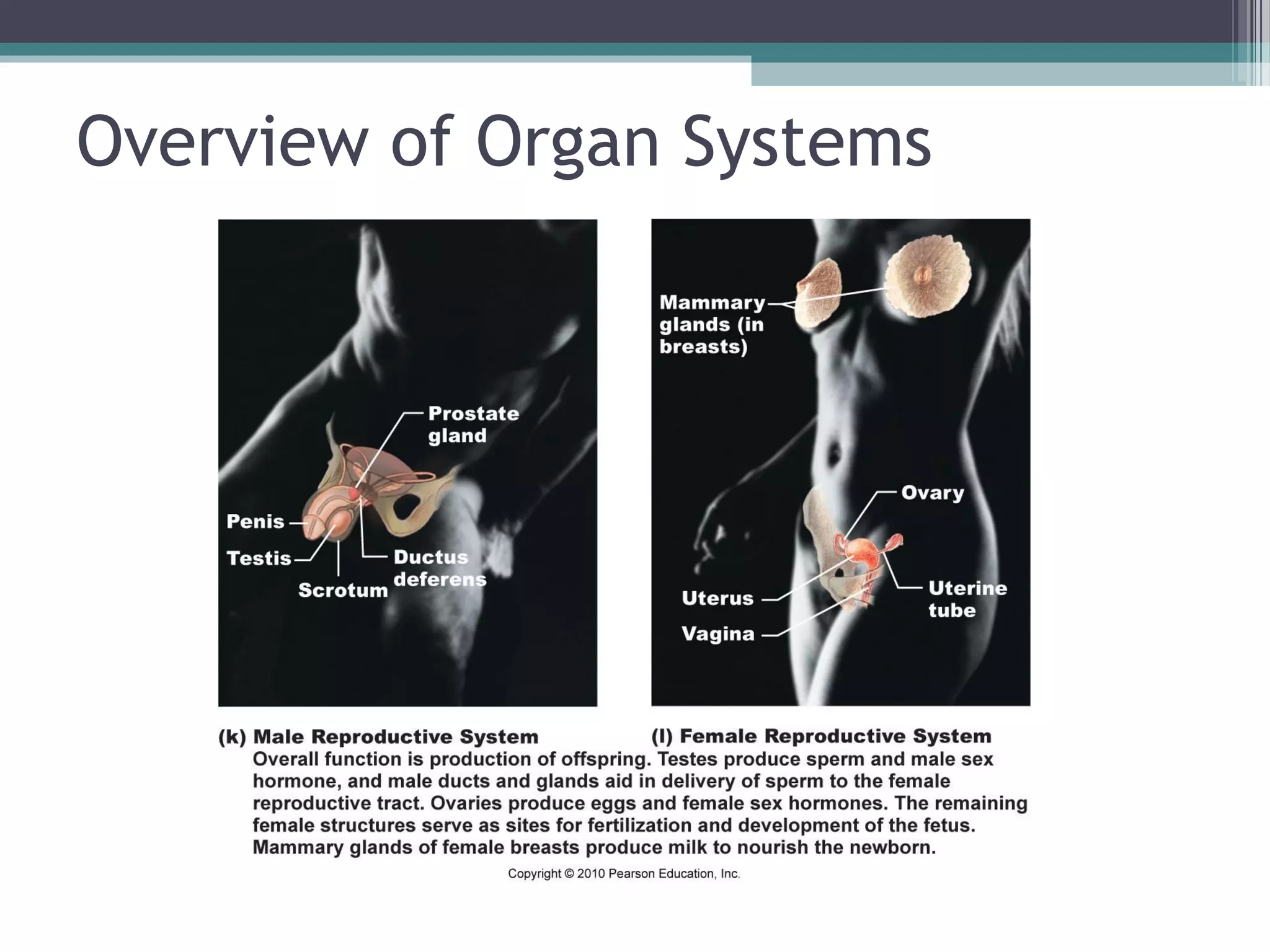
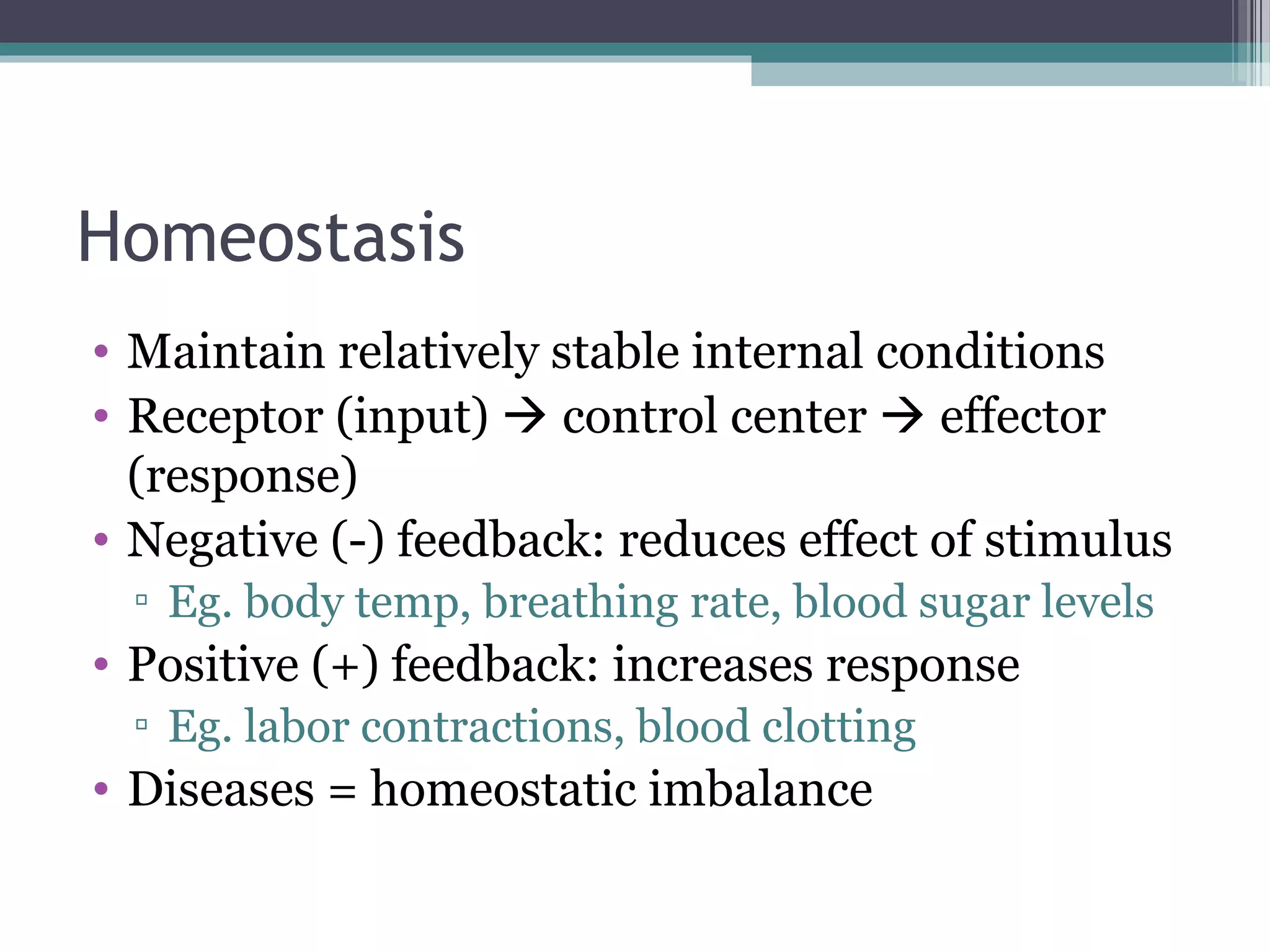
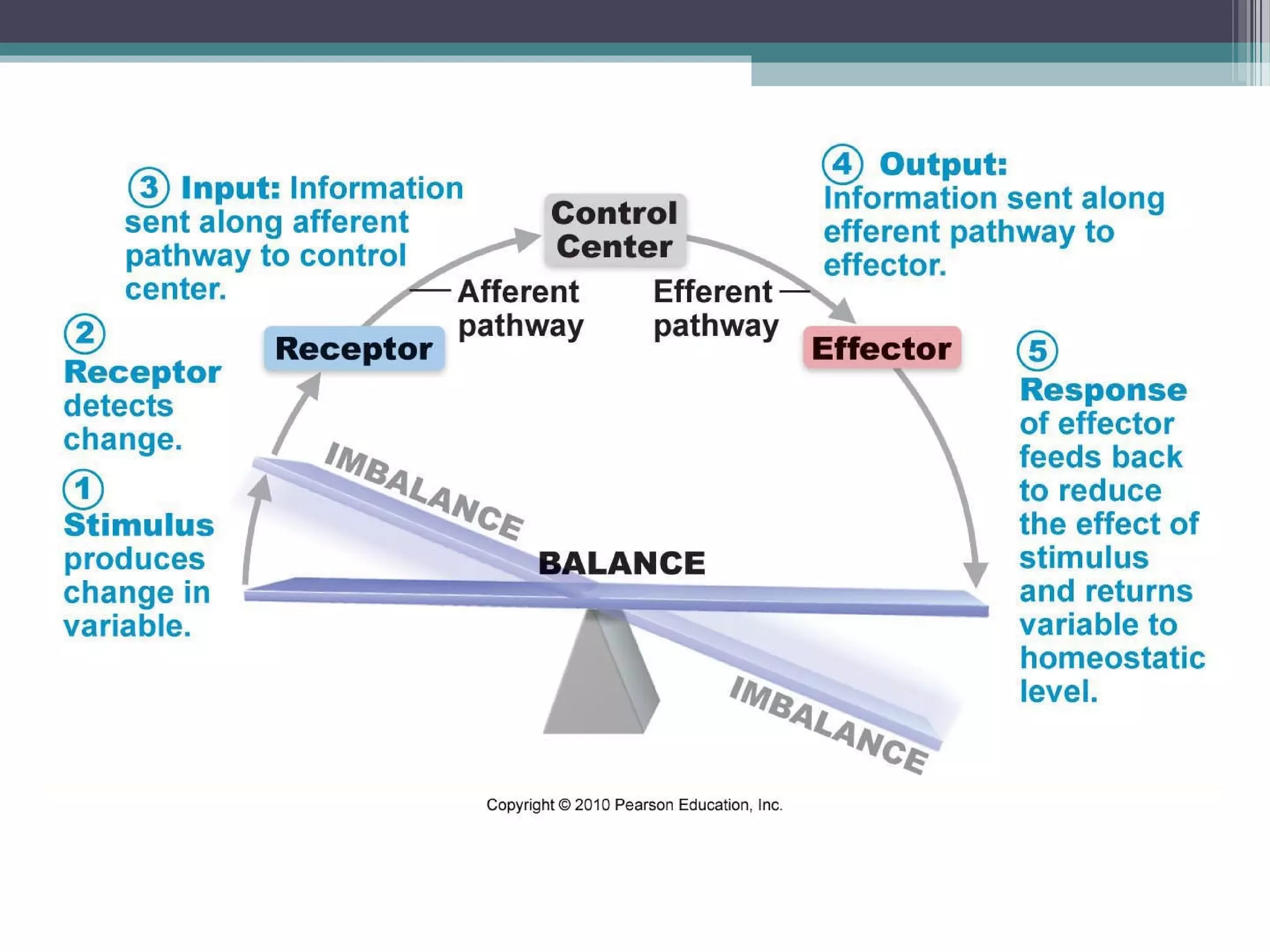
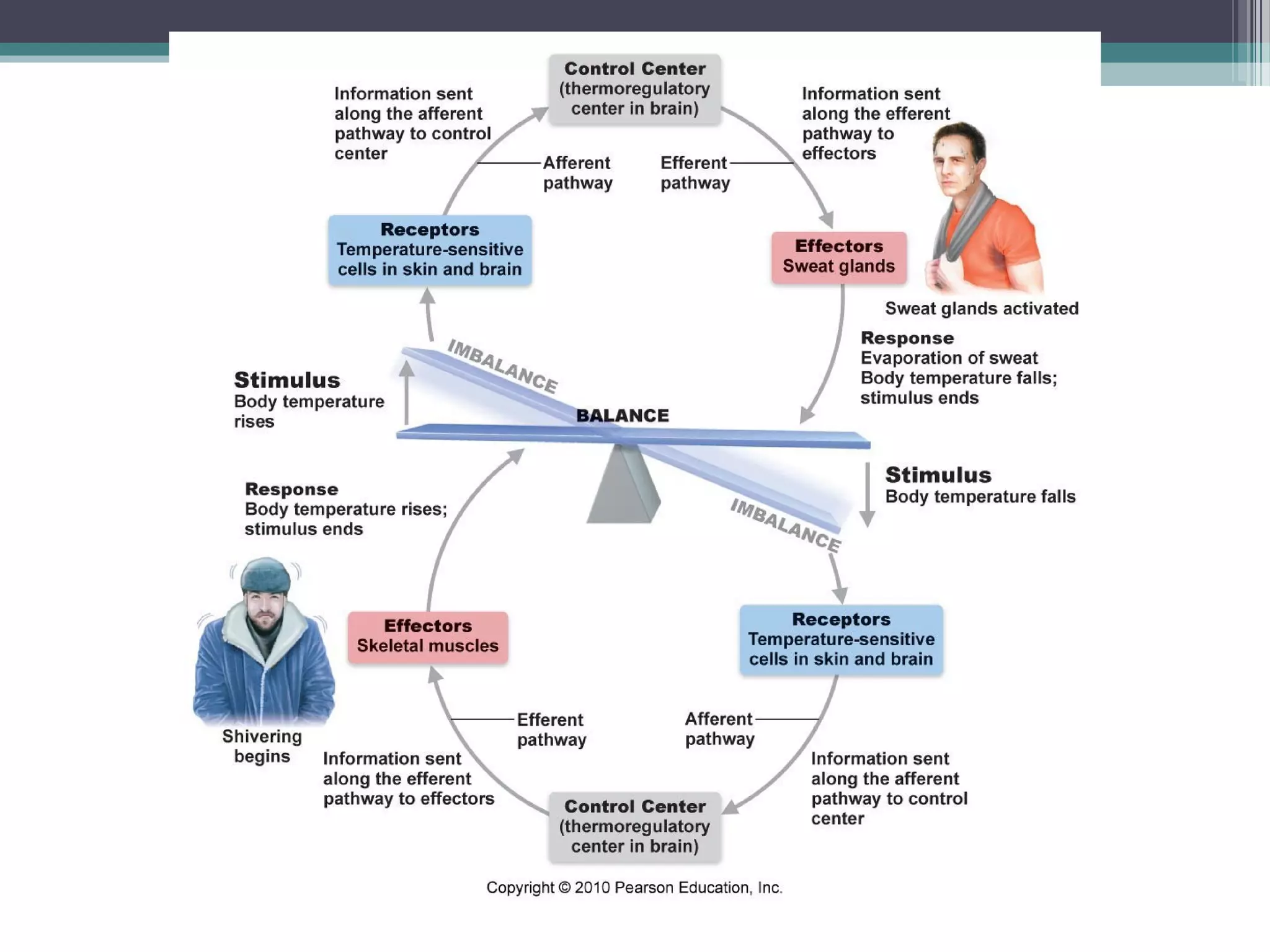
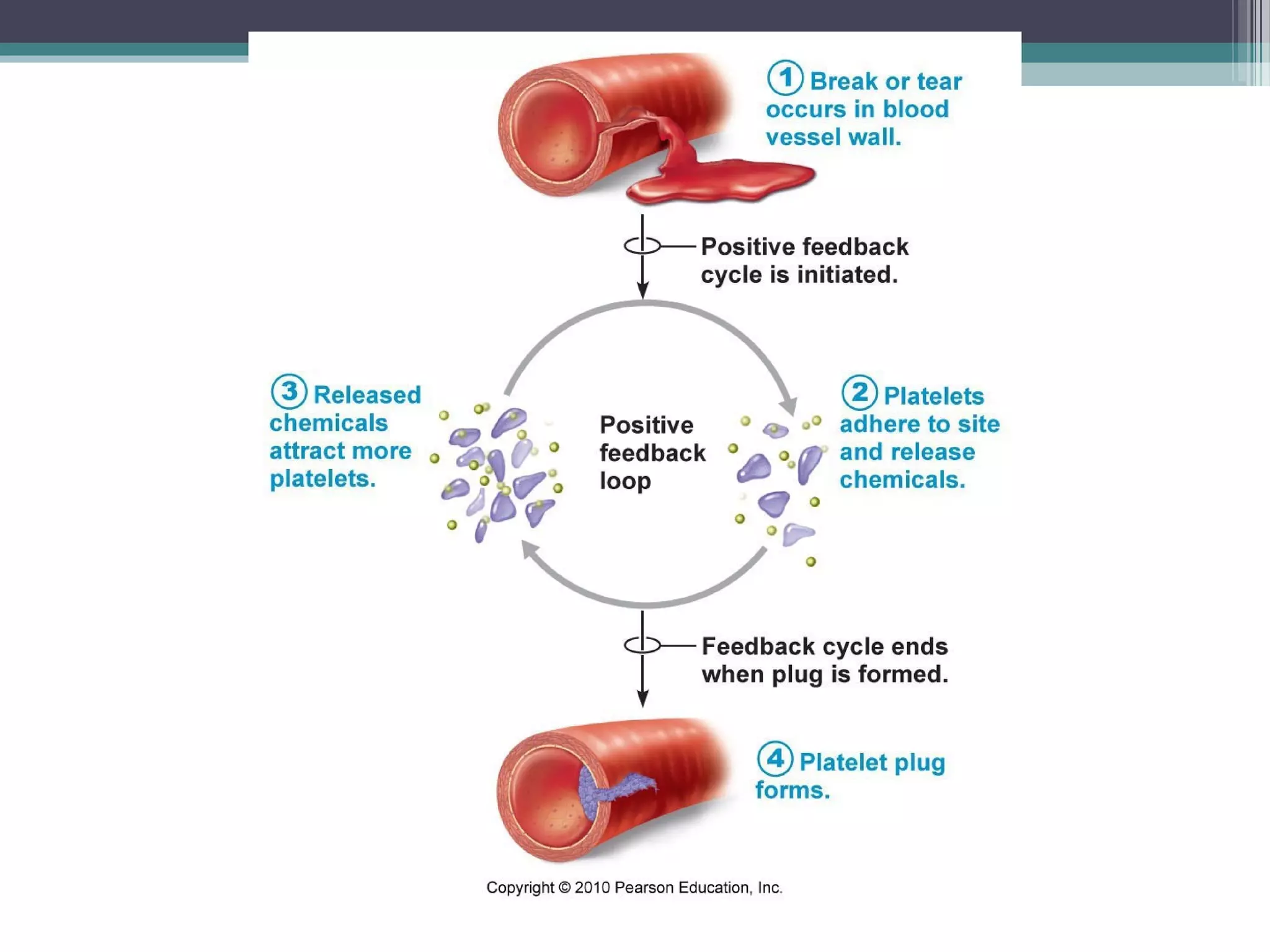
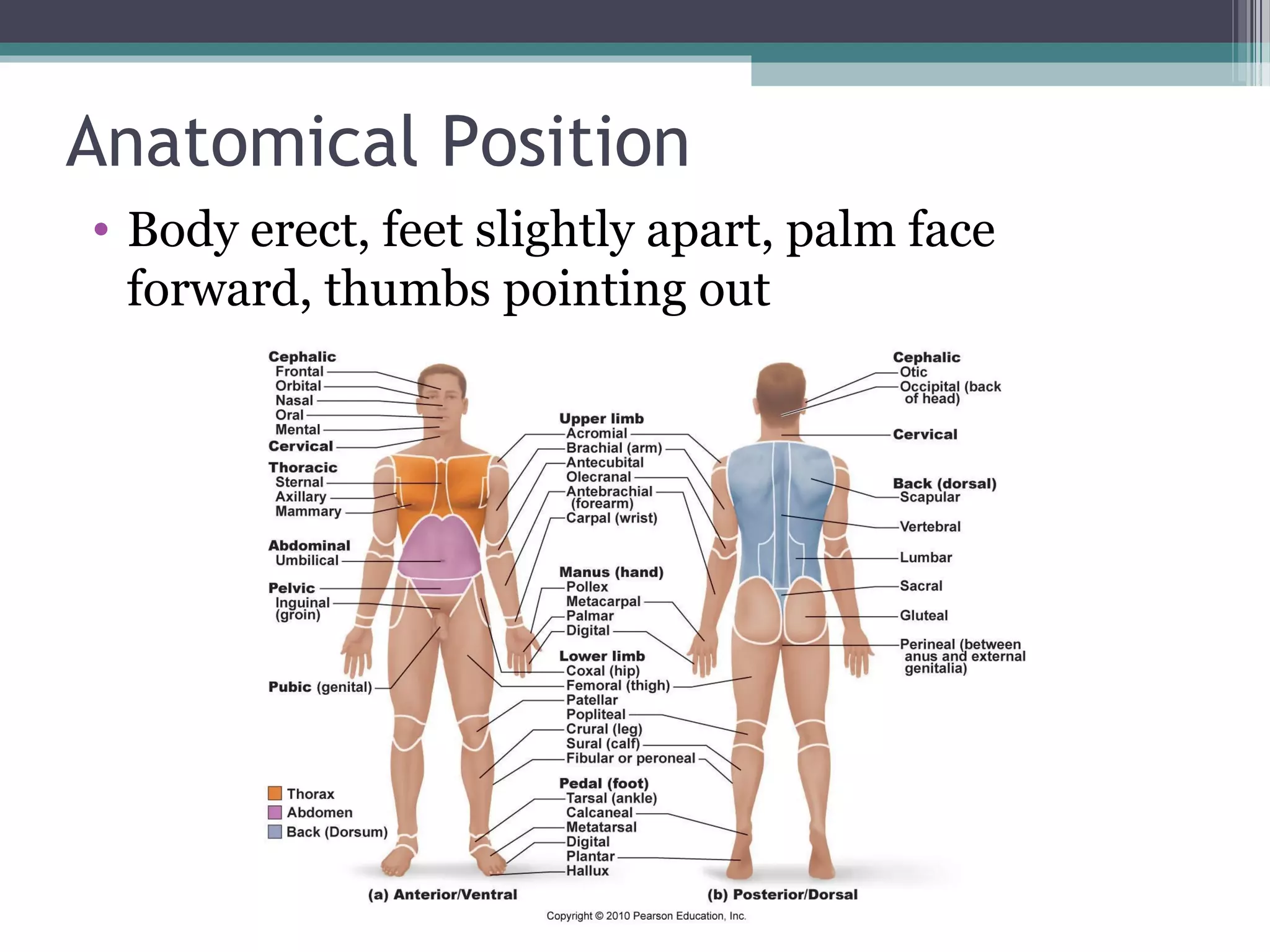
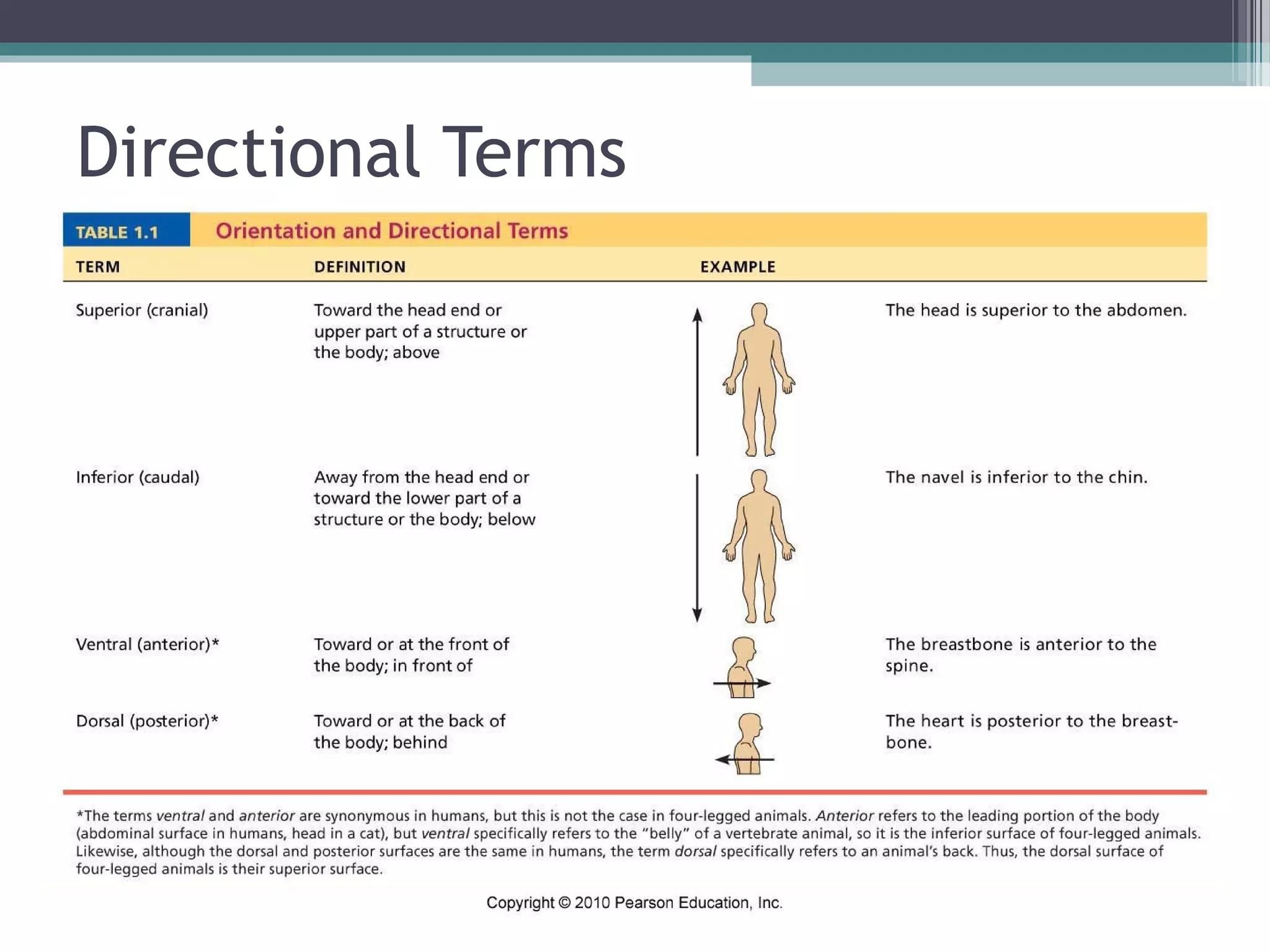
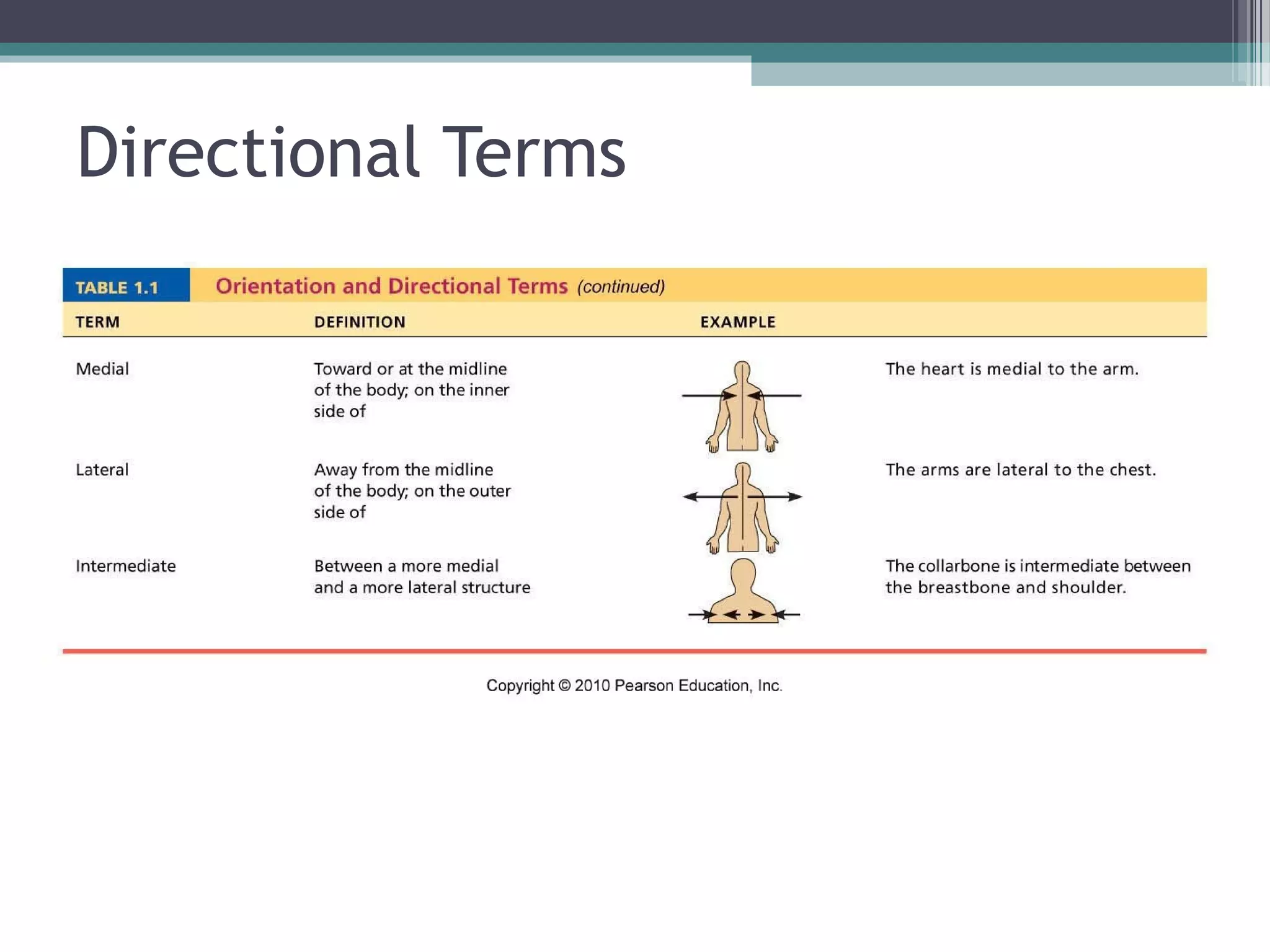
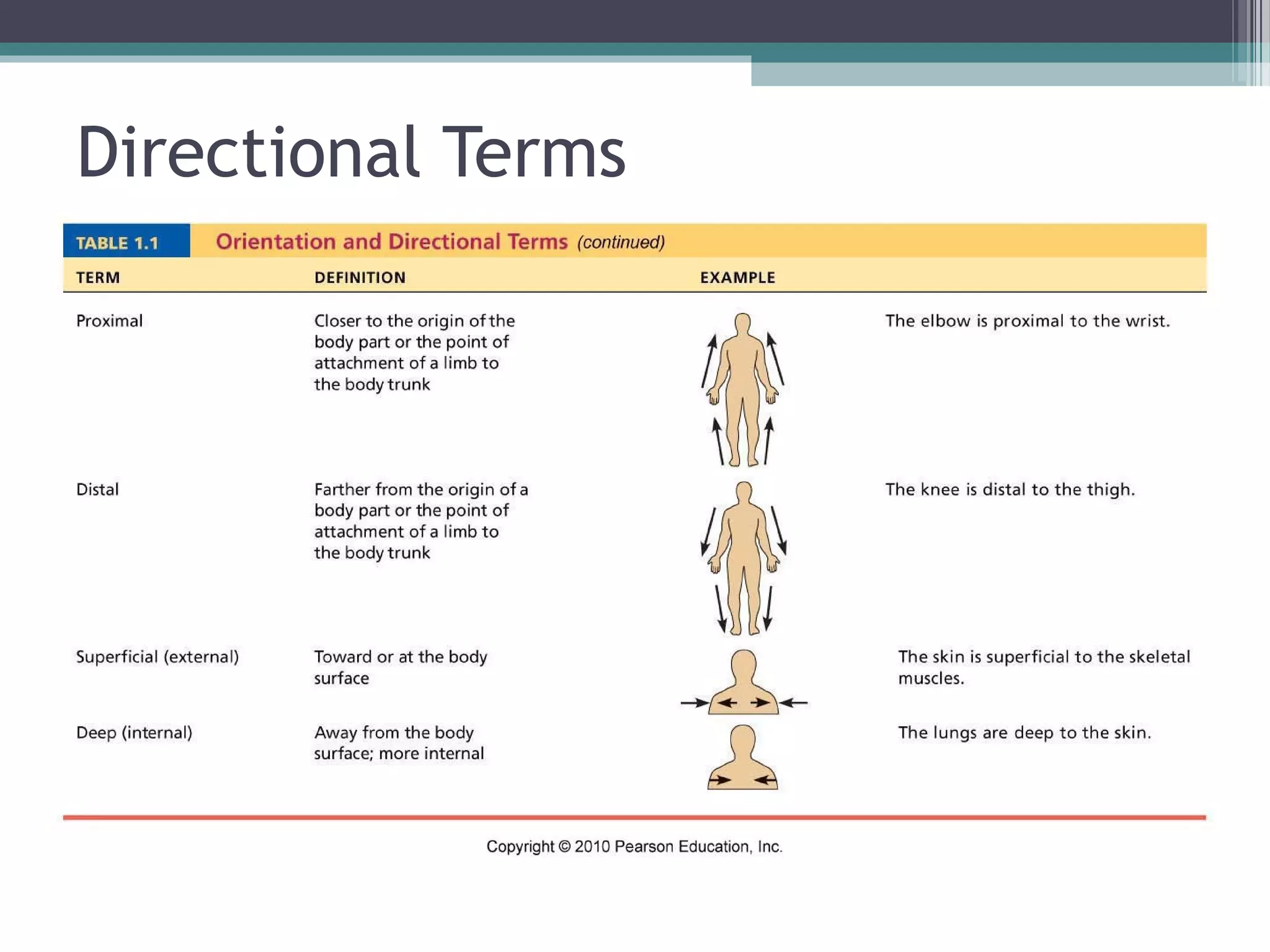
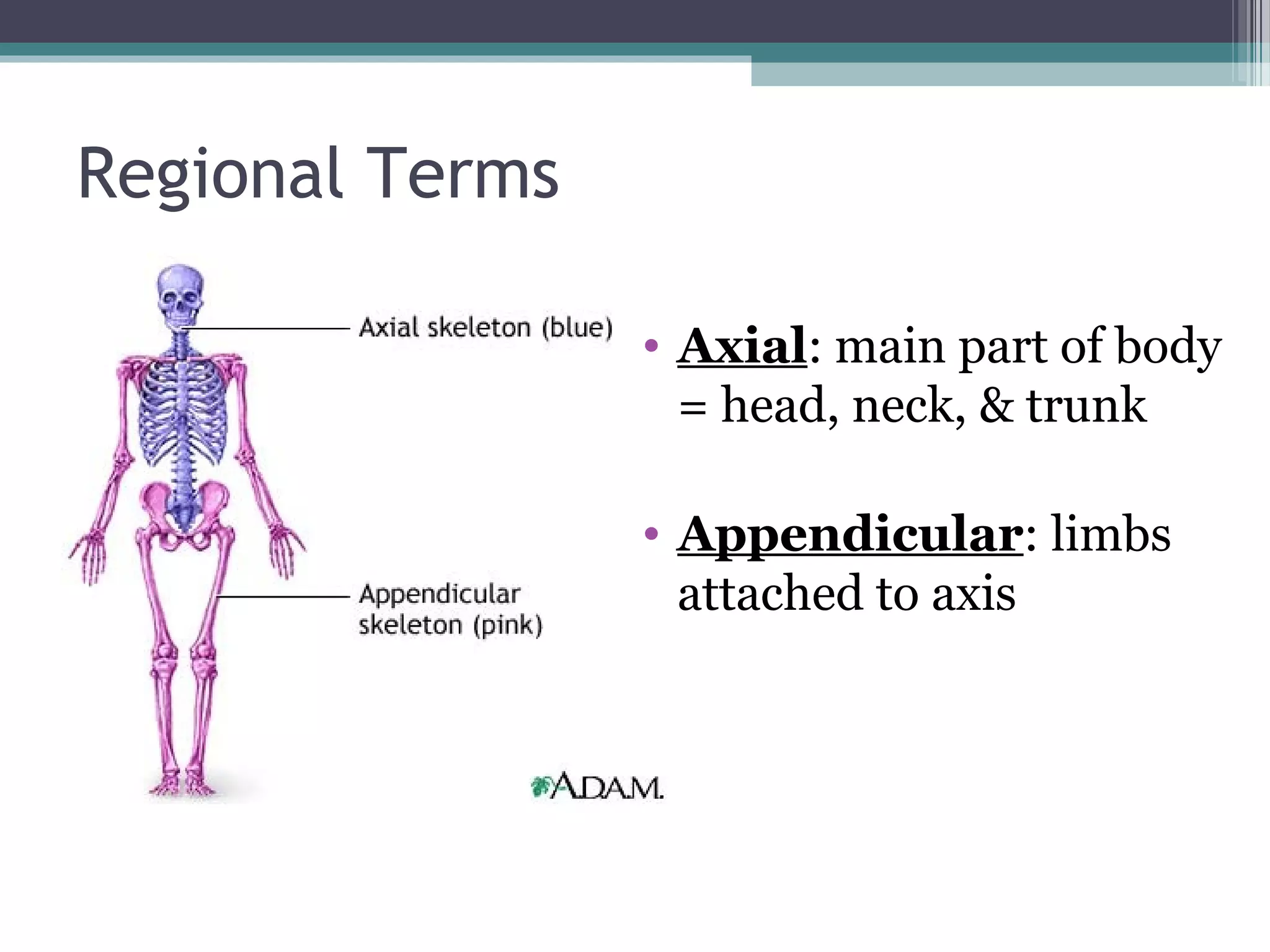
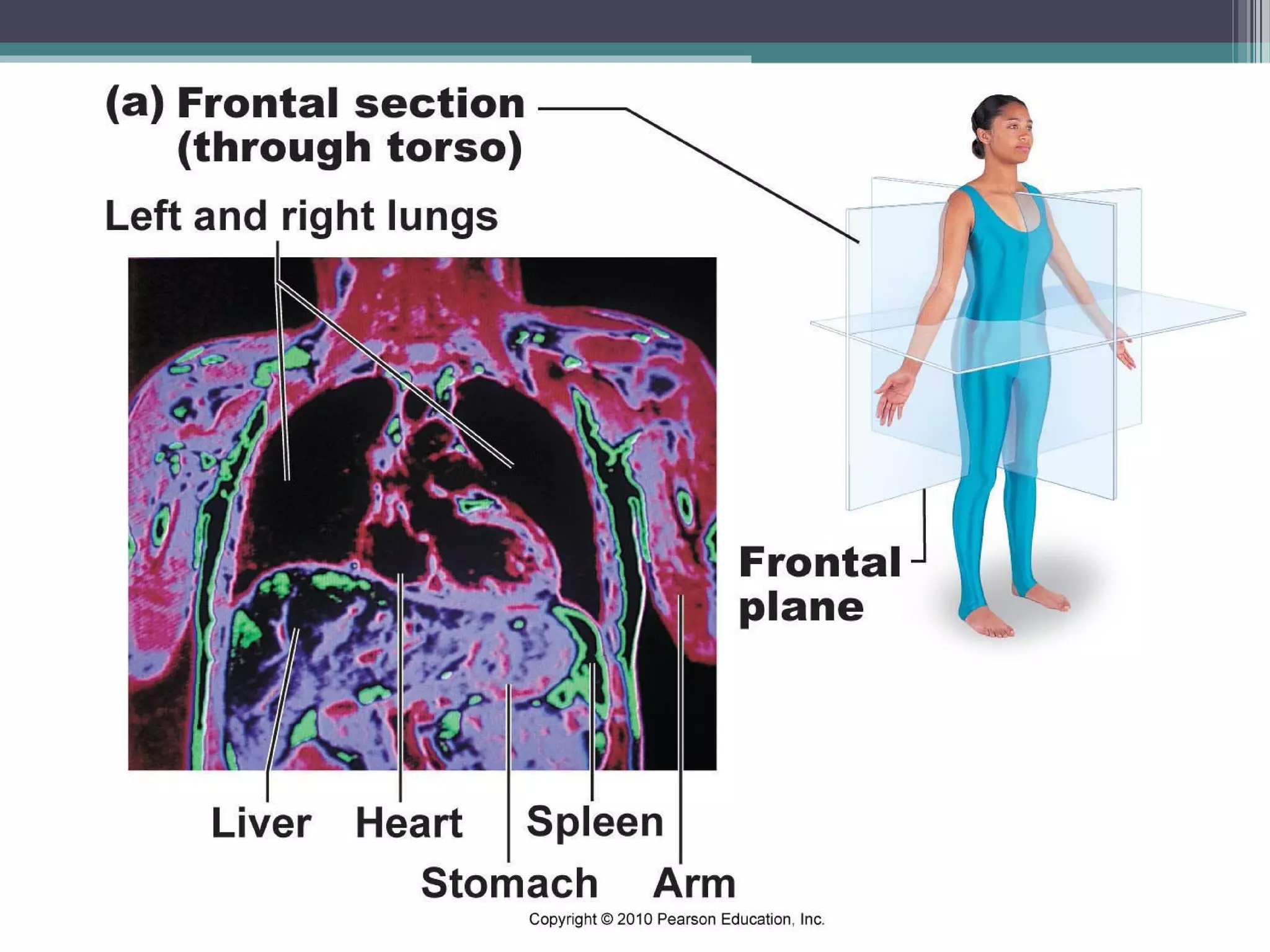
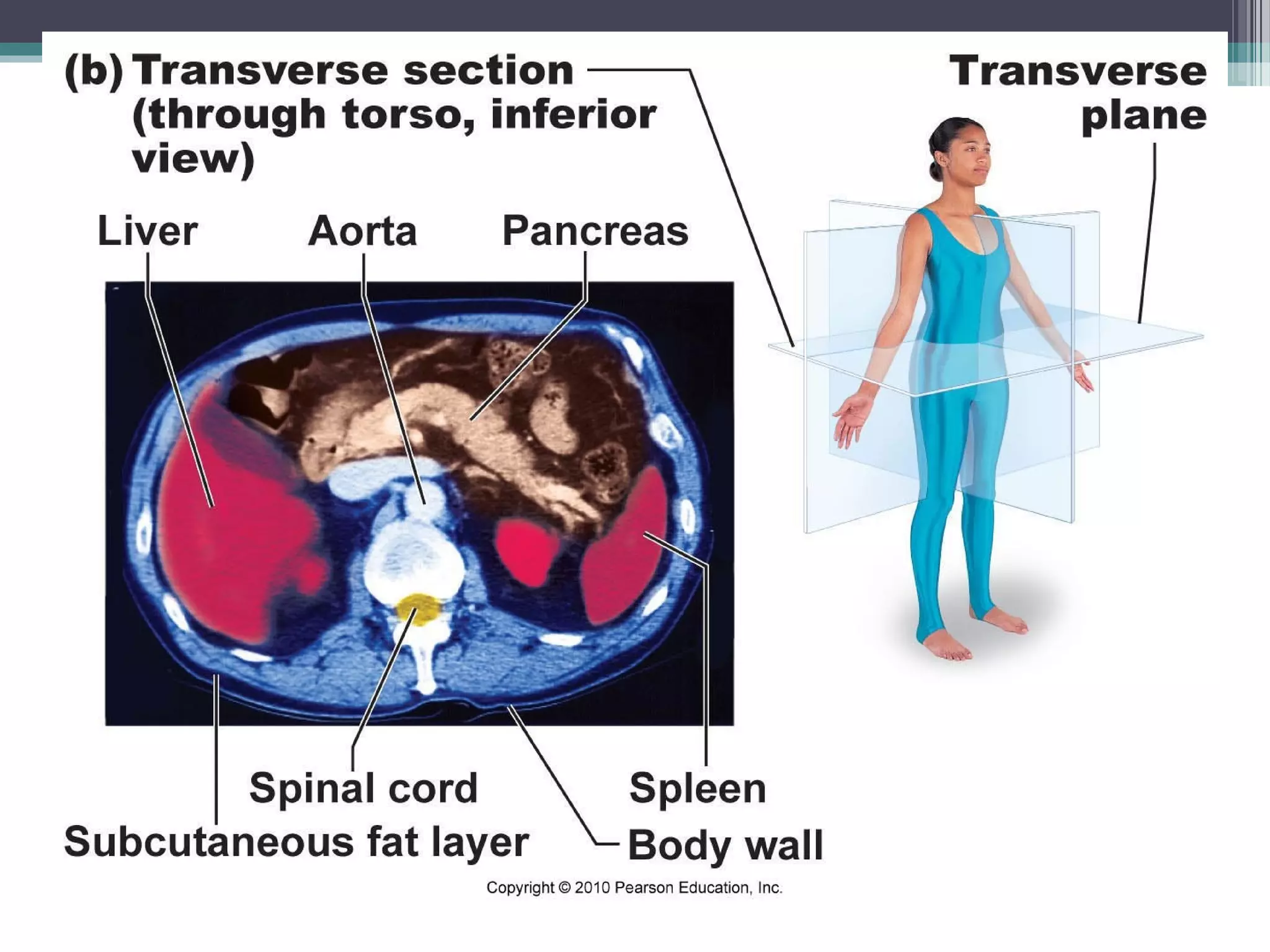
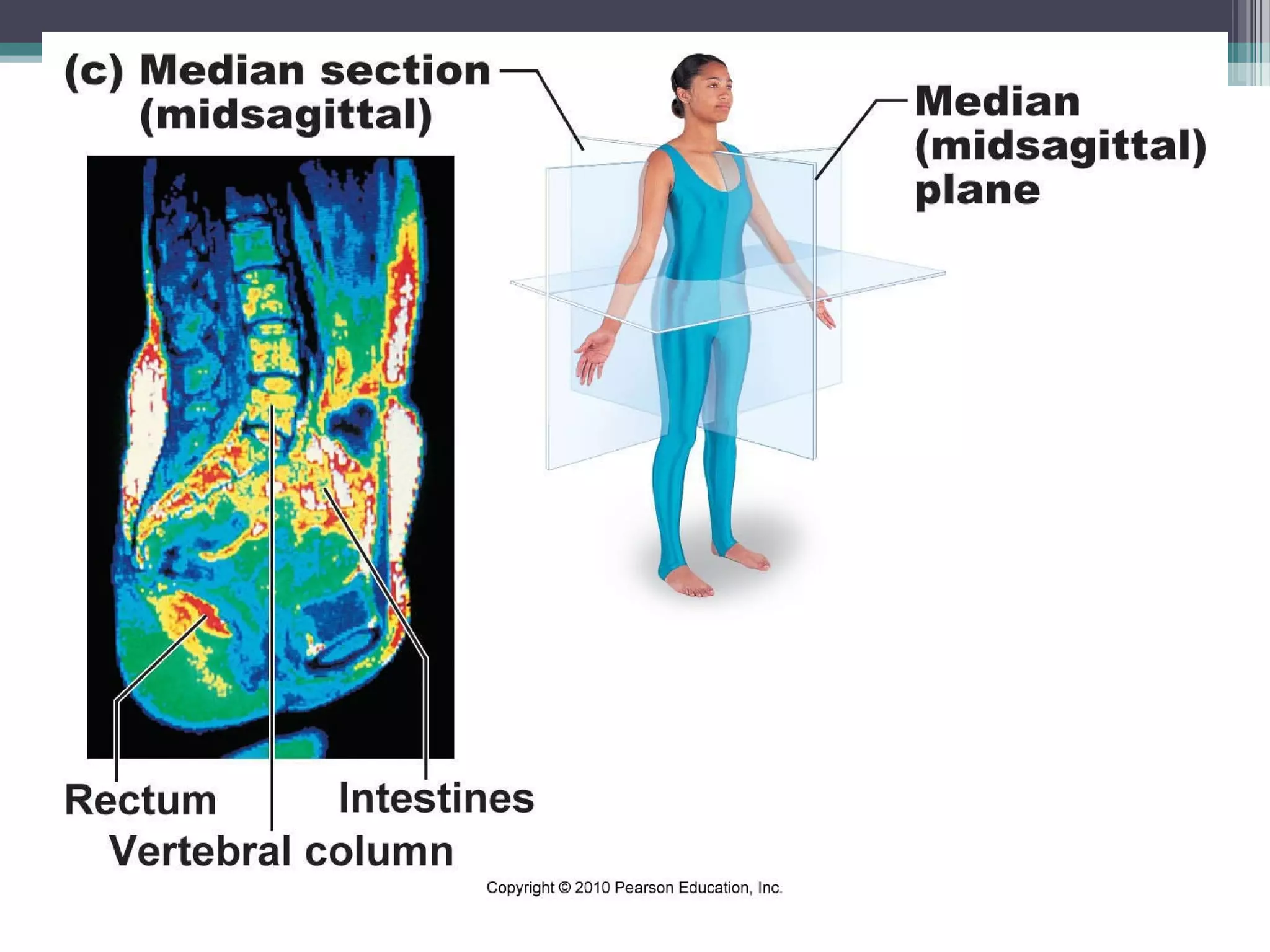
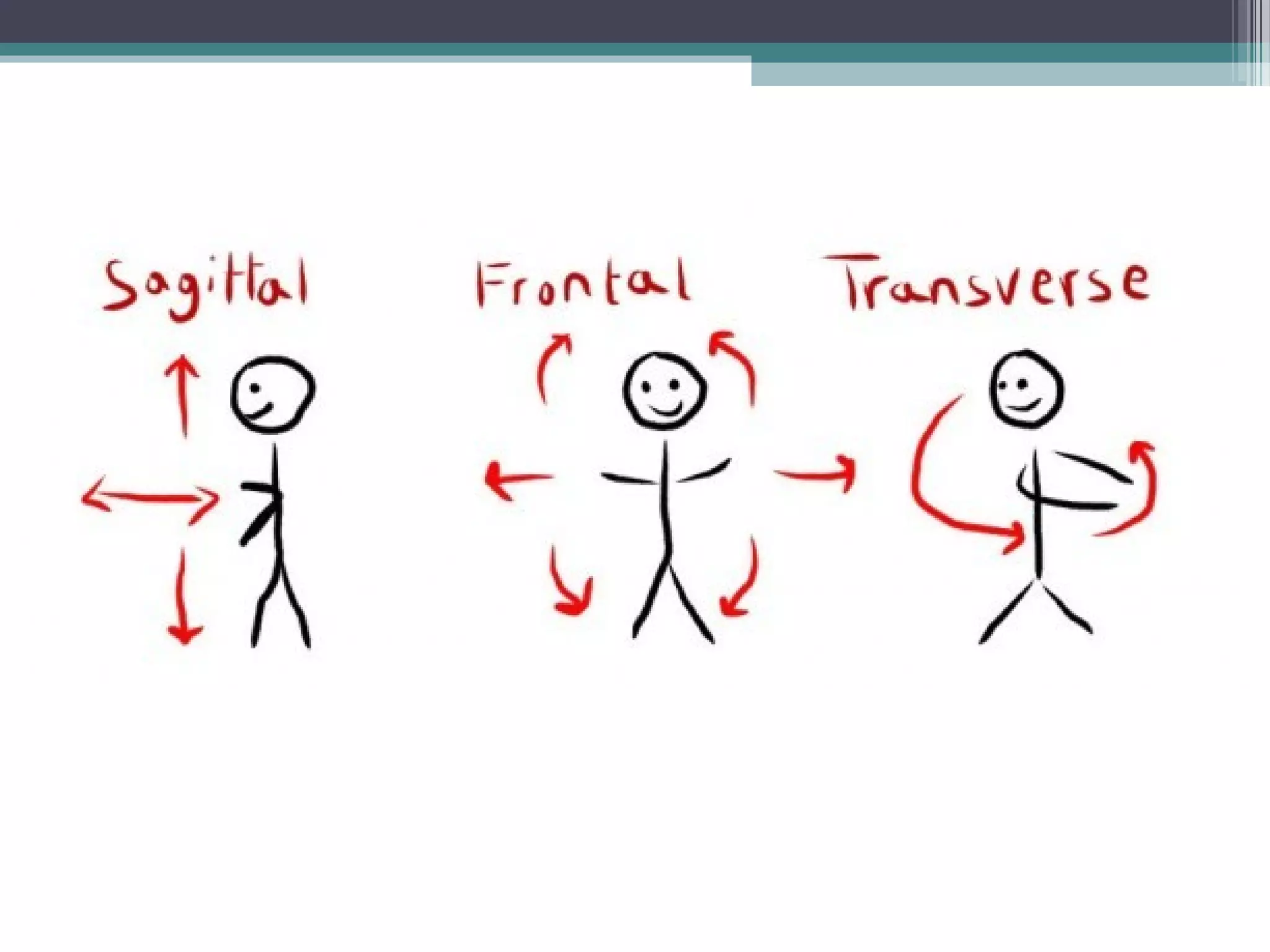
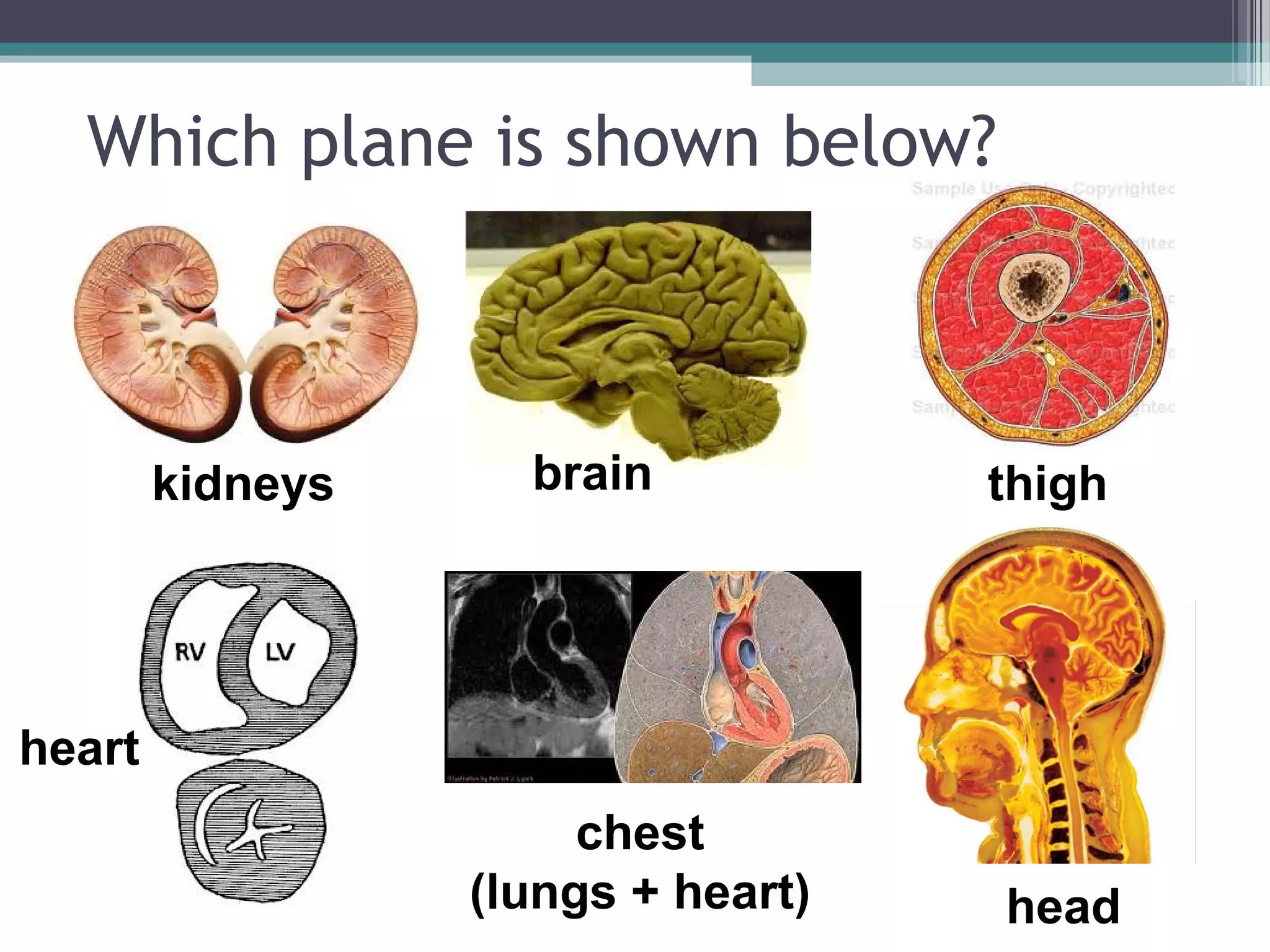
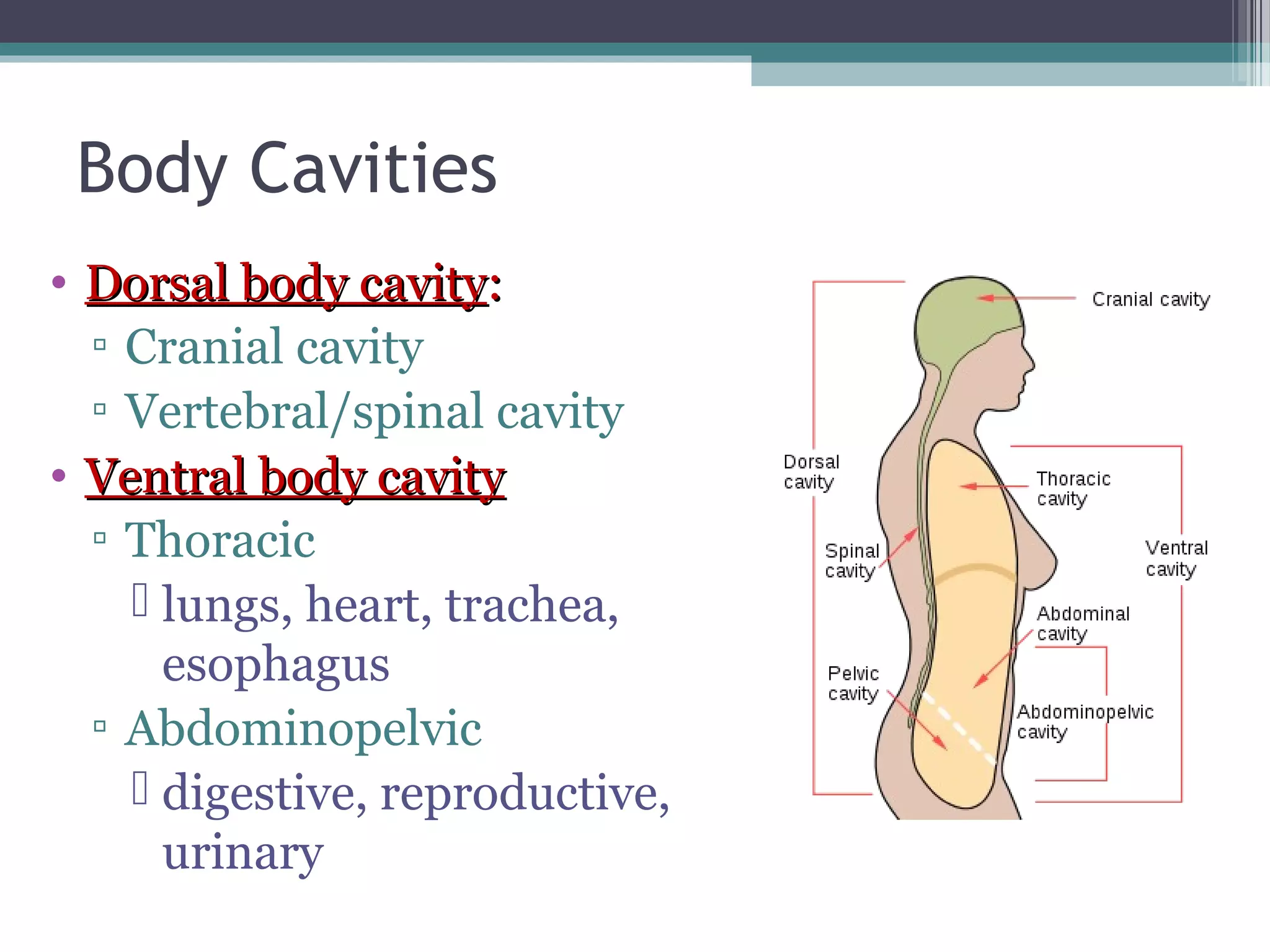
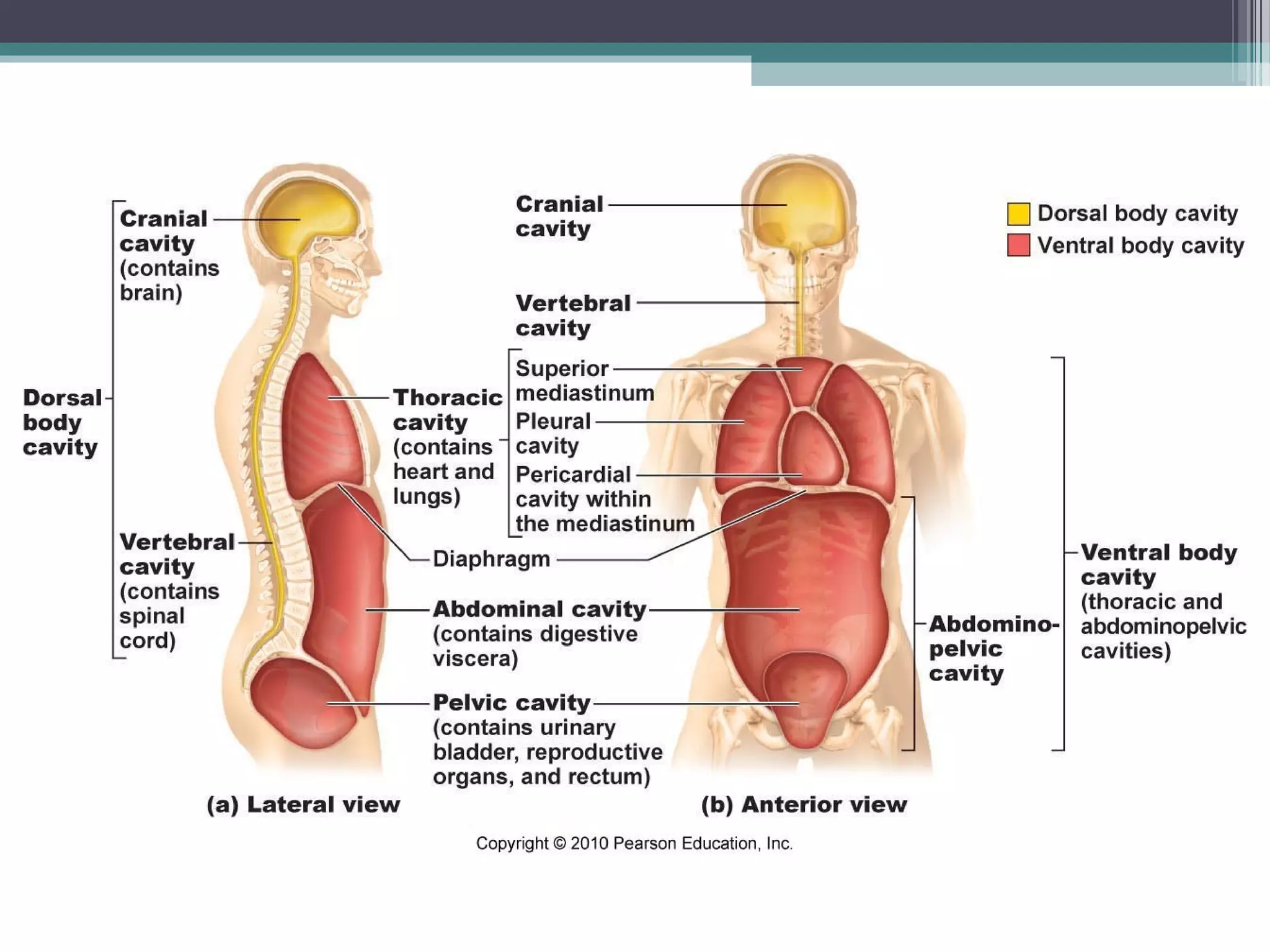
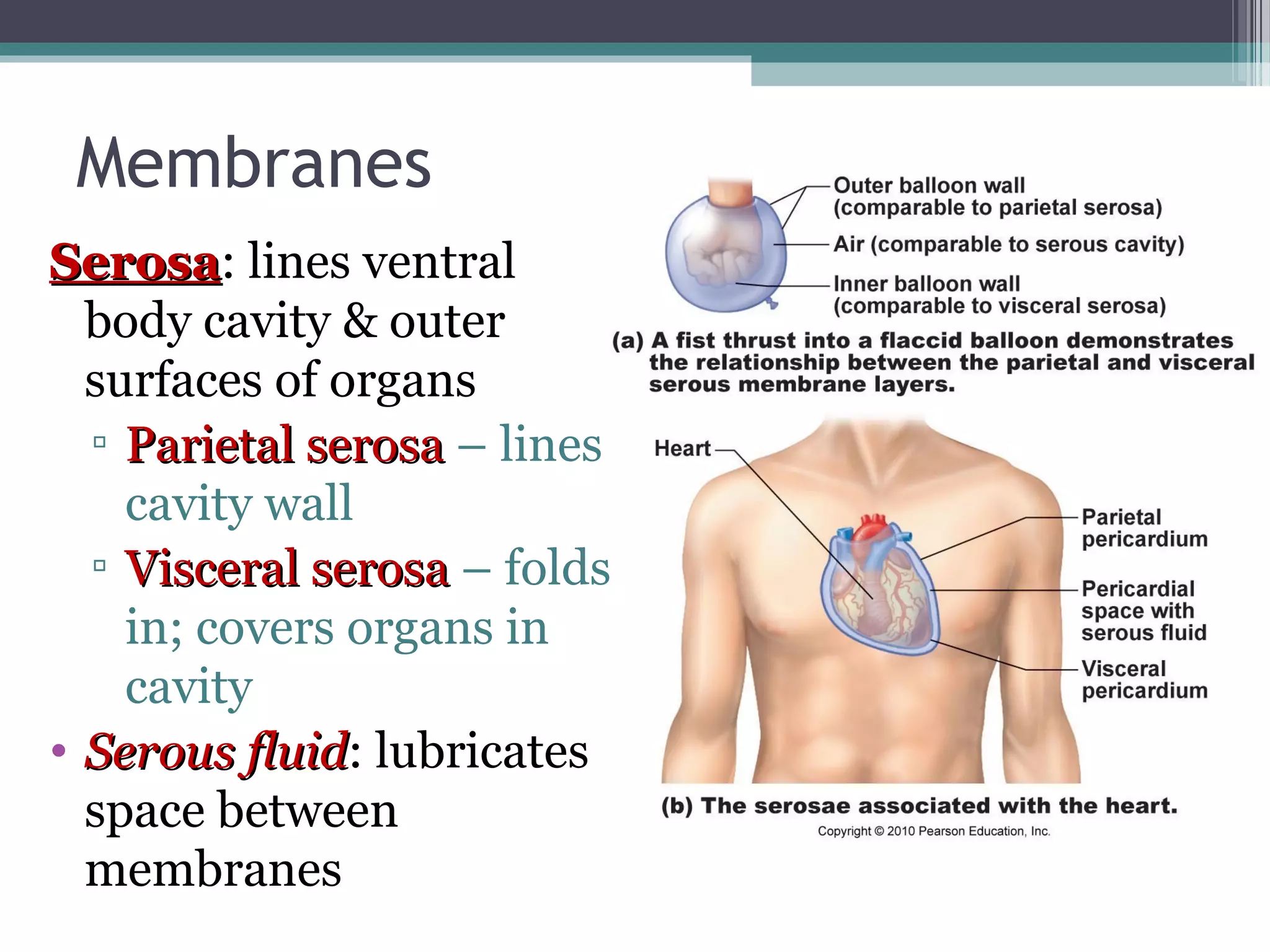
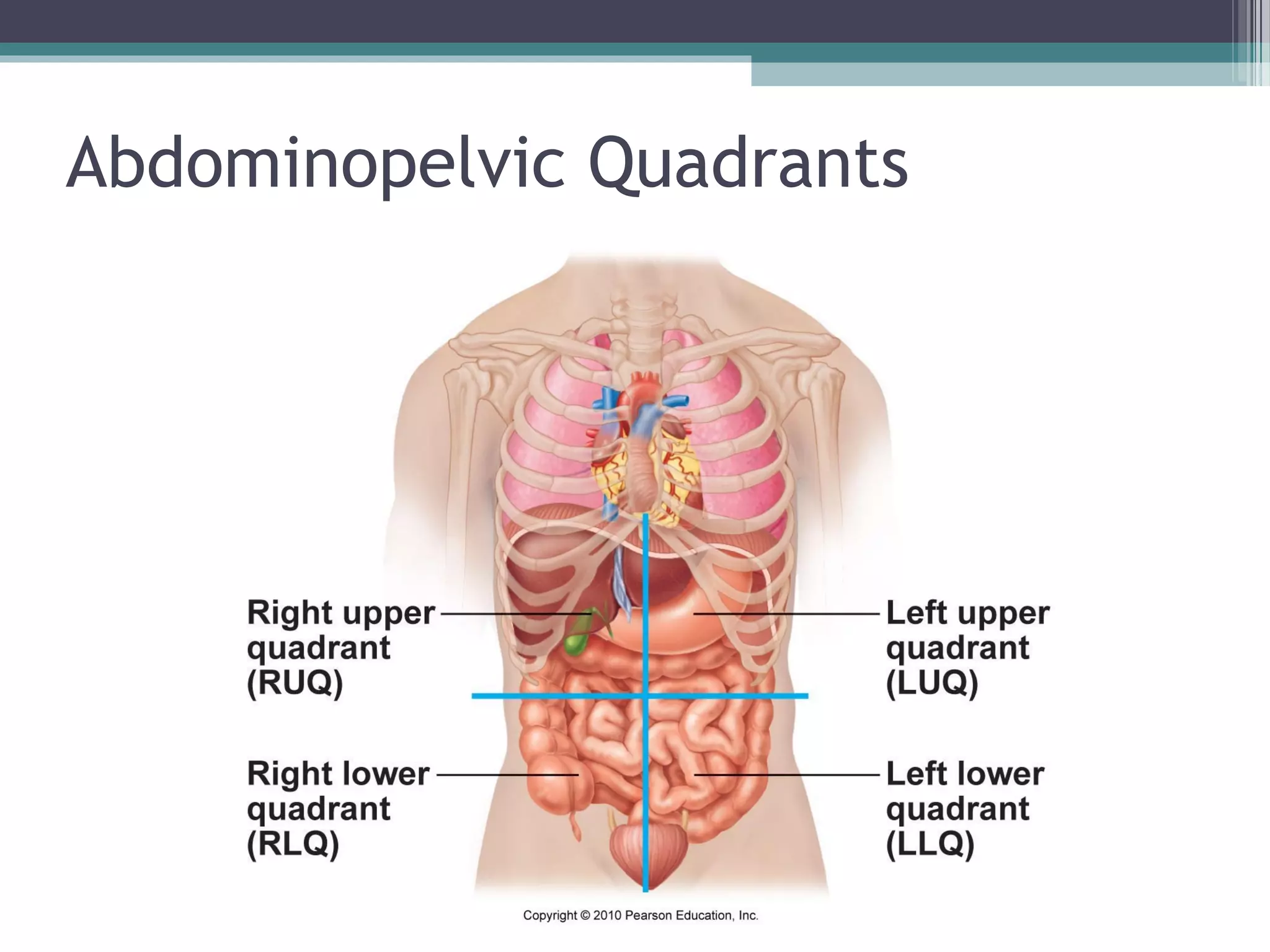
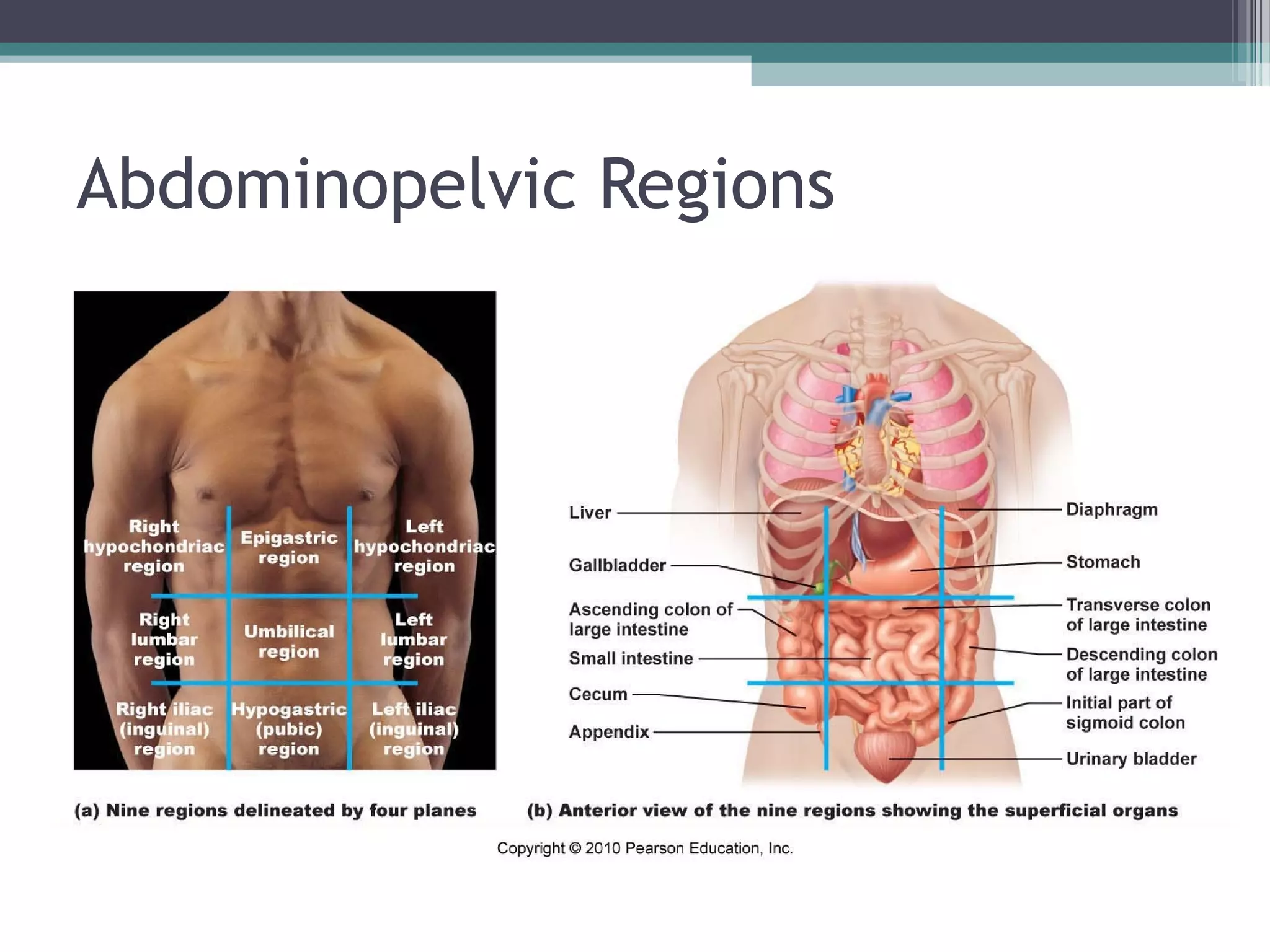
Chapter 1 covers the fundamentals of human anatomy and physiology, differentiating between the two and exploring levels of organization from chemical to organism. It outlines necessary life functions, survival needs, and the concept of homeostasis, along with anatomical terminology and body planes. Additionally, the chapter details body cavities and organ systems, emphasizing the significance of structure and function in human biology.